SLC6A3/DAT1 Products
The dopamine transporter (DAT) is a 70 - 80 kDa member of the Na+-neurotransmitter symporter family of transmembrane (TM) proteins. DAT plays a crucial role in the synaptic clearance of dopamine (DA). It mediates the uptake of dopamine by the presynaptic terminal, thus limiting the strength of the dopamingeric response. One molecule of DA is accompanied by two Na+ and one Cl- ion. Molecules such as amphetamine both competitively inhibit DA uptake, and induce DA release through the DAT, increasing the rewarding property of DA.
The human dopamine transporter is a 620 amino acid (aa), 12 TM phosphoglycoprotein with an N- and C-terminal cytoplasmic domain. Human DAT exists as a disulfide-linked oligomer on the cell surface. Phosphorylation of the N-terminus (S7/12) promotes DA release. The C-terminus binds CaMKII, as well as Hic5, Pick1, and synuclein which regulate receptor trafficking and expression. There is an extended 71 aa extracellular (EC) loop between TM segments 3 and 4. Glycosylation at this site is necessary for oligomer expression on the cell membrane. The human 42 aa DAT C-terminus is 93% aa identical to the mouse DAT C-terminus. The human EC loop is also 93% aa identical to the rhesus monkey EC loop.
70 results for "SLC6A3/DAT1" in Products
70 results for "SLC6A3/DAT1" in Products
SLC6A3/DAT1 Products
The dopamine transporter (DAT) is a 70 - 80 kDa member of the Na+-neurotransmitter symporter family of transmembrane (TM) proteins. DAT plays a crucial role in the synaptic clearance of dopamine (DA). It mediates the uptake of dopamine by the presynaptic terminal, thus limiting the strength of the dopamingeric response. One molecule of DA is accompanied by two Na+ and one Cl- ion. Molecules such as amphetamine both competitively inhibit DA uptake, and induce DA release through the DAT, increasing the rewarding property of DA.
The human dopamine transporter is a 620 amino acid (aa), 12 TM phosphoglycoprotein with an N- and C-terminal cytoplasmic domain. Human DAT exists as a disulfide-linked oligomer on the cell surface. Phosphorylation of the N-terminus (S7/12) promotes DA release. The C-terminus binds CaMKII, as well as Hic5, Pick1, and synuclein which regulate receptor trafficking and expression. There is an extended 71 aa extracellular (EC) loop between TM segments 3 and 4. Glycosylation at this site is necessary for oligomer expression on the cell membrane. The human 42 aa DAT C-terminus is 93% aa identical to the mouse DAT C-terminus. The human EC loop is also 93% aa identical to the rhesus monkey EC loop.
| Reactivity: | Mouse, Rat, Human (Negative) |
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 Monoclonal Clone #mAb16 |
| Applications: | IHC, WB, ELISA, ICC/IF, IP |
| Reactivity: | Human, Primate |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB, IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat, Primate, Hamster, +1 More |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | IHC, WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Primate |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | IHC, WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Primate |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB, IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 Monoclonal Clone #CL3123 |
| Applications: | IHC |
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Monoclonal Clone #SR1877 |
| Applications: | WB, Flow, IP |
| Applications: | WB, ELISA, MA, AP |
| Reactivity: | Rat |
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 kappa Monoclonal Clone #C3 |
| Applications: | ELISA |
| Applications: | ELISA |
| Reactivity: | Mouse, Rat |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | IHC, WB |
| Applications: | WB, ELISA, MA, AP, PAGE |
| Applications: | ELISA |
| Applications: | ELISA |
| Reactivity: | Mouse, Rat, Human (Negative) |
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 Monoclonal Clone #mAb16 |
| Applications: | IHC, WB, ELISA, ICC/IF, IP |
| Applications: | AC |
| Reactivity: | Mouse, Rat, Human (Negative) |
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 Monoclonal Clone #mAb16 |
| Applications: | IHC, WB, ELISA, ICC/IF, IP |
| Reactivity: | Mouse, Rat, Human (Negative) |
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 Monoclonal Clone #mAb16 |
| Applications: | IHC, WB, ELISA, ICC/IF, IP |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 Monoclonal Clone #CL3123 |
| Applications: | IHC |
Non-selective inhibitor of dopamine and noradrenalin transporters
| Chemical Name: | 1-(3-Chlorophenyl)-2-[(1,1-dimethylethyl)amino]-1-propanone hydrochloride |
| Purity: | ≥99% (HPLC) |
Selective DA uptake inhibitor; also σ ligand
| Chemical Name: | 1-[2-[Bis-(4-fluorophenyl)methoxy]ethyl]-4-(3-phenylpropyl)piperazine dihydrochloride |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
Potent noradrenalin and dopamine uptake inhibitor. Antidepressant
| Chemical Name: | 1,2,3,4-Tetrahydro-2-methyl-4-phenyl-8-isoquinolinamine maleate |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |

![Western Blot: SLC6A3/DAT1 Antibody (mAb16) [NBP2-22164] Western Blot: SLC6A3/DAT1 Antibody (mAb16) [NBP2-22164]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/SLC6A3-DAT1-Antibody-mAb16-Western-Blot-NBP2-22164-img0005.jpg)

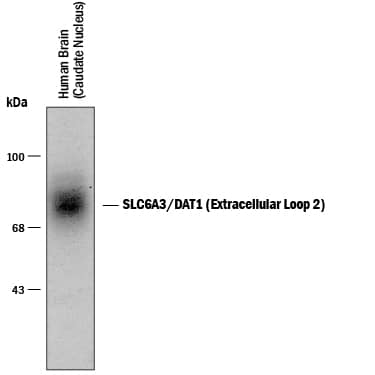
![Western Blot: SLC6A3/DAT1 Antibody [NB300-254] Western Blot: SLC6A3/DAT1 Antibody [NB300-254]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/SLC6A3-DAT1-Antibody-Western-Blot-NB300-254-img0005.jpg)
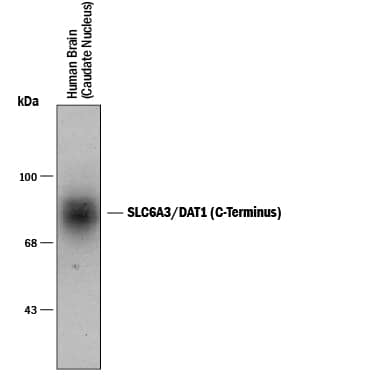
![Western Blot: SLC6A3/DAT1 Antibody [NB300-255] Western Blot: SLC6A3/DAT1 Antibody [NB300-255]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/DAT1-Antibody-Western-Blot-NB300-255-img0001.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: SLC6A3/DAT1 Antibody (CL3123) [NBP2-46649] Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: SLC6A3/DAT1 Antibody (CL3123) [NBP2-46649]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/SLC6A3-DAT1-Antibody-3123-Immunohistochemistry-NBP2-46649-img0007.jpg)
![Western Blot: SLC6A3/DAT1 Antibody (SR1877) [NBP3-21721] -](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nbp3-21721_rabbit-slc6a3-dat1-mab-sr1877-5720231754825.jpg)
![ELISA: Human SLC6A3/DAT1 ELISA Kit (Colorimetric) [NBP2-67271] - Human SLC6A3/DAT1 ELISA Kit (Colorimetric)](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nbp2-67271_human-slc6a3-dat1-elisa-kit-colorimetric-132202416225253.jpg)
![Western Blot: SLC6A3/DAT1 [p Thr53] Antibody [NBP2-29533] Western Blot: SLC6A3/DAT1 [p Thr53] Antibody [NBP2-29533]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/DAT1-[p-Thr53]-Antibody-Western-Blot-NBP2-29533-img0001.jpg)
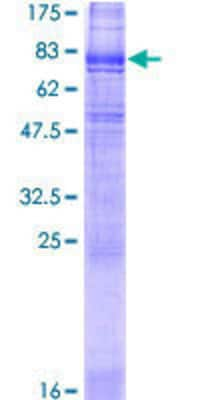
![SDS-PAGE: Recombinant Human SLC6A3/DAT1 GST (N-Term) Protein [H00006531-Q01] SDS-PAGE: Recombinant Human SLC6A3/DAT1 GST (N-Term) Protein [H00006531-Q01]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/qc_test-H00006531-Q01-1.jpg)
![ELISA: Rat SLC6A3/DAT1 ELISA Kit (Colorimetric) [NBP2-67273] - Rat SLC6A3/DAT1 ELISA Kit (Colorimetric)](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nbp2-67273_rat-slc6a3-dat1-elisa-kit-colorimetric-132202416184888.jpg)
![ELISA: Mouse SLC6A3/DAT1 ELISA Kit (Colorimetric) [NBP2-67272] - Mouse SLC6A3/DAT1 ELISA Kit (Colorimetric)](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nbp2-67272_mouse-slc6a3-dat1-elisa-kit-colorimetric-13220241626119.jpg)




