Flow Cytometry: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239]
Flow Cytometry: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - HeLa cell.Black: Unlabelled sample was used as a control. Red: beta Catenin antibody [N1N2-2], N-term dilution: 1:50.Acquisition of 20,000 events were collected using a Dylight 488-conjugated secondary antibody for FACS analysis.
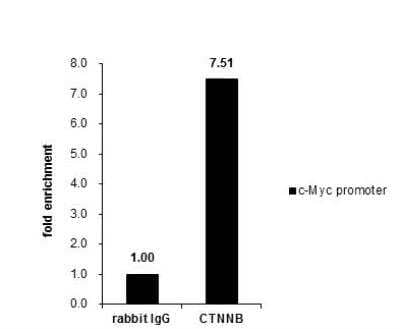
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP): beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - Cross-linked ChIP was performed with HCT116 chromatin extract and 5 ug of either control rabbit IgG or anti-beta Catenin antibody. The precipitated DNA was detected by PCR with primer set targeting to c-Myc promoter.
Western Blot: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239]
Western Blot: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - Western blot for beta-catenin in HEK 293 cells treated with LiCl (10mM) for 1 hr. Image from verified customer review.
Western Blot: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239]
Western Blot: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - Sample (50 ug of whole cell lysate) A: mouse brain 7.5% SDS PAGE diluted at 1:1000
Western Blot: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239]
Western Blot: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - A. 30 ug PC-12 whole cell lysate/extract 7.5 % SDS-PAGEbeta Catenin antibody [N1N2-2], N-term dilution: 1:1000
Western Blot: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239]
Western Blot: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - Non-transfected (-) and transfected (+) HeLa whole cell extracts (30 ug) were separated by 7.5% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with beta Catenin antibody [N1N2-2], N-term.
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239]
Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - HeLa cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: beta Catenin protein stained by beta Catenin antibody [N1N2-2], N-term diluted at 1:500. Blue: Hoechst 33342 staining.
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239]
Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - HCT 116 cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: beta Catenin protein stained by beta Catenin antibody [N1N2-2], N-term diluted at 1:500. Blue: Hoechst 33342 staining.
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239]
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - Paraffin-embedded mouse colon. Green: beta Catenin antibody [diluted at 1:500. Red: alpha Tubulin antibody diluted at 1:500. Blue: Hoechst 33342 staining.
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239]
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - Paraffin-embedded mouse urinary bladder diluted at 1:500.
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239]
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - Paraffin-embedded mouse skin dilution: 1:500.
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239]
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - Paraffin-embedded mouse colon dilution: 1:500.
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239]
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - Paraffin-embedded mouse duodenum. beta Catenin antibody [N1N2-2], N-term diluted at 1:500.
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239]
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - Paraffin-embedded human esophagus. beta Catenin antibody [N1N2-2], N-term diluted at 1:500.
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239]
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - Paraffin-embedded human cervix. beta Catenin antibody [N1N2-2], N-term diluted at 1:500.
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239]
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - Paraffin-embedded mouse duodenum. beta Catenin antibody [N1N2-2], N-term diluted at 1:500.
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239]
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - Paraffin-embedded rat colon. beta Catenin antibody [N1N2-2], N-term diluted at 1:500.
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239]
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - Paraffin-embedded rat duodenum. beta Catenin antibody [N1N2-2], N-term diluted at 1:500.
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239]
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - Paraffin-embedded mouse intestine. beta Catenin antibody [N1N2-2], N-term diluted at 1:500.
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] -
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - P-cadherin is co-localized with other junctional proteins at the RPE cell border in mice.Immunofluorescence of mouse RPE flat-mounts. Double staining: P-cadherin (red; A, E, I) & either ZO-1 (green; B), beta-catenin (green; F), or F-actin (green; J), with nuclear stain by DAPI (blue; C, G, K). Merged images (D, H, L) show the co-localization of P-cadherin with ZO-1 (tight junction), beta-catenin (adherens junction), & F-actin (adherens junction) at the cell-cell border. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29338041), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] -
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - WNT10A/ beta-catenin signalling is required for region-specific differentiation.(a–d) Filiform papillae are present in Wnt10a−/− & inducible beta-catenin mutant dorsal tongue (yellow arrows), but horny structures & expression of hard keratins (in situ hybridization, purple signals) are decreased (red arrows). (e–l) Epithelial deletion of Wnt10a (e–f″,i,j) or beta-catenin (g–h″,k,l) induced from P25, P110 or P15 as indicated causes decreased expression of nuclear beta-catenin, LEF1 & HOXC13 (white arrows, LEF1+ proliferating cells; yellow arrows, HOXC13+ differentiating cells). (m) qPCR shows significantly decreased Hoxc13 levels in Wnt10a & beta-catenin mutant tongue epithelium. (n–r) IF & qPCR reveal reduced levels of KRT9 protein (n–q) & mRNA (r) in Wnt10a−/− & inducible beta-catenin mutant footpad epidermis. (s–v″) Co-IF for KRT9 & KRT10 in plantar epidermis from patients homozygous for WNT10A c.756+1G>A (s–t″) or WNT10A c.391G>A (u–v″) compared with similarly aged sex-matched controls. For qPCR, RNA levels were quantified in six control & six mutant (P40) or four control & four mutant (P20-100) samples with three technical replicates for each, & normalized to beta-actin mRNA. Significance was calculated with two-tailed Student's t-test. Error bars indicate s.e.m. Scale bar, 25 μm (e–l) or 50 μm (a–d,n–q,s–v″). Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://www.nature.com/articles/ncomms15397), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] -
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - WNT10A/ beta-catenin signalling is required for region-specific differentiation.(a–d) Filiform papillae are present in Wnt10a−/− & inducible beta-catenin mutant dorsal tongue (yellow arrows), but horny structures & expression of hard keratins (in situ hybridization, purple signals) are decreased (red arrows). (e–l) Epithelial deletion of Wnt10a (e–f″,i,j) or beta-catenin (g–h″,k,l) induced from P25, P110 or P15 as indicated causes decreased expression of nuclear beta-catenin, LEF1 & HOXC13 (white arrows, LEF1+ proliferating cells; yellow arrows, HOXC13+ differentiating cells). (m) qPCR shows significantly decreased Hoxc13 levels in Wnt10a & beta-catenin mutant tongue epithelium. (n–r) IF & qPCR reveal reduced levels of KRT9 protein (n–q) & mRNA (r) in Wnt10a−/− & inducible beta-catenin mutant footpad epidermis. (s–v″) Co-IF for KRT9 & KRT10 in plantar epidermis from patients homozygous for WNT10A c.756+1G>A (s–t″) or WNT10A c.391G>A (u–v″) compared with similarly aged sex-matched controls. For qPCR, RNA levels were quantified in six control & six mutant (P40) or four control & four mutant (P20-100) samples with three technical replicates for each, & normalized to beta-actin mRNA. Significance was calculated with two-tailed Student's t-test. Error bars indicate s.e.m. Scale bar, 25 μm (e–l) or 50 μm (a–d,n–q,s–v″). Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://www.nature.com/articles/ncomms15397), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] -
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - WNT10A/ beta-catenin signalling is required for region-specific differentiation.(a–d) Filiform papillae are present in Wnt10a−/− & inducible beta-catenin mutant dorsal tongue (yellow arrows), but horny structures & expression of hard keratins (in situ hybridization, purple signals) are decreased (red arrows). (e–l) Epithelial deletion of Wnt10a (e–f″,i,j) or beta-catenin (g–h″,k,l) induced from P25, P110 or P15 as indicated causes decreased expression of nuclear beta-catenin, LEF1 & HOXC13 (white arrows, LEF1+ proliferating cells; yellow arrows, HOXC13+ differentiating cells). (m) qPCR shows significantly decreased Hoxc13 levels in Wnt10a & beta-catenin mutant tongue epithelium. (n–r) IF & qPCR reveal reduced levels of KRT9 protein (n–q) & mRNA (r) in Wnt10a−/− & inducible beta-catenin mutant footpad epidermis. (s–v″) Co-IF for KRT9 & KRT10 in plantar epidermis from patients homozygous for WNT10A c.756+1G>A (s–t″) or WNT10A c.391G>A (u–v″) compared with similarly aged sex-matched controls. For qPCR, RNA levels were quantified in six control & six mutant (P40) or four control & four mutant (P20-100) samples with three technical replicates for each, & normalized to beta-actin mRNA. Significance was calculated with two-tailed Student's t-test. Error bars indicate s.e.m. Scale bar, 25 μm (e–l) or 50 μm (a–d,n–q,s–v″). Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://www.nature.com/articles/ncomms15397), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] -
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - WNT10A/ beta-catenin signalling is required for region-specific differentiation.(a–d) Filiform papillae are present in Wnt10a−/− & inducible beta-catenin mutant dorsal tongue (yellow arrows), but horny structures & expression of hard keratins (in situ hybridization, purple signals) are decreased (red arrows). (e–l) Epithelial deletion of Wnt10a (e–f″,i,j) or beta-catenin (g–h″,k,l) induced from P25, P110 or P15 as indicated causes decreased expression of nuclear beta-catenin, LEF1 & HOXC13 (white arrows, LEF1+ proliferating cells; yellow arrows, HOXC13+ differentiating cells). (m) qPCR shows significantly decreased Hoxc13 levels in Wnt10a & beta-catenin mutant tongue epithelium. (n–r) IF & qPCR reveal reduced levels of KRT9 protein (n–q) & mRNA (r) in Wnt10a−/− & inducible beta-catenin mutant footpad epidermis. (s–v″) Co-IF for KRT9 & KRT10 in plantar epidermis from patients homozygous for WNT10A c.756+1G>A (s–t″) or WNT10A c.391G>A (u–v″) compared with similarly aged sex-matched controls. For qPCR, RNA levels were quantified in six control & six mutant (P40) or four control & four mutant (P20-100) samples with three technical replicates for each, & normalized to beta-actin mRNA. Significance was calculated with two-tailed Student's t-test. Error bars indicate s.e.m. Scale bar, 25 μm (e–l) or 50 μm (a–d,n–q,s–v″). Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://www.nature.com/articles/ncomms15397), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] -
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - Oxidative stress-induced dissociation of adherens junctions results in nuclear translocation of beta-catenin & an increase of EMT-related factors in mouse RPE.(A) Immunofluorescence of mouse RPE flat-mounts. Mice were injected with NaIO3 (15 mg/kg body weight) on Day 0, & the localization of beta-catenin (green) & P-cadherin (red) was analyzed along with nuclear stain by DAPI (blue) on Days 0 (a-c), 1 (d-f), 3 (g-i) & 7 (j-l). Double staining: beta-catenin (a, d, g, j), P-cadherin (b, e, h, k), & merged images with DAPI (c, f, i, l). The localization of beta-catenin & P-cadherin at the cell-cell border was significantly disrupted, & instead prominently detected on/in the nucleus on Day 3. (B) Immunofluorescence of mouse retinal sections with a focus on the RPE nuclei. Mice were injected with NaIO3 (15 mg/kg body weight) on Day 0, & the localization of beta-catenin (green) & P-cadherin (red) was analyzed along with nuclear stain by DAPI (blue) on Days 0 (m-o) & 3 (two representative nuclei; p-r & s-u). Double staining: beta-catenin (m, p, s), P-cadherin (n, q, t), & merged images with DAPI (o, r, u). On Day 3, beta-catenin was detected in the nuclei of mouse RPE. (C) Western blot analyses of mouse RPE proteins. Mice were injected with NaIO3 (15 mg/kg body weight) on Day 0, & RPE protein lysates were prepared on Days 0, 1, 3, & 7. The protein levels were analyzed using Western blotting with antibodies against P-cadherin, beta-catenin, SNAI1 (Snail), vimentin, & control beta-actin. The protein levels of beta-catenin & SNAI1 increased similarly on Day 1 following oxidative stress. Image collected & cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29338041), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by Novus Biologicals.
Western Blot: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] -
Western Blot: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - Whole cell extract (30 ug) was separated by 7.5% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with beta-Catenin antibody (NBP1-32239) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody was used to detect the primary antibody, and the signal was developed with Trident ECL plus-Enhanced.
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] -
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - beta-Catenin antibody detects beta-Catenin protein at cell membrane by immunohistochemical analysis.Sample: Paraffin-embedded cat liver.beta-Catenin stained by beta-Catenin antibody (NBP1-32239) diluted at 1:500.Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] -
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - beta-Catenin antibody detects beta-Catenin protein at cell membrane by immunohistochemical analysis.Sample: Paraffin-embedded cat colon.beta-Catenin stained by beta-Catenin antibody (NBP1-32239) diluted at 1:500.Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min
Immunohistochemistry: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] -
Immunohistochemistry: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - beta-Catenin antibody [N1N2-2], N-term detects Ctnnb1 protein on zebrafish by whole mount immunohistochemical analysis.
Sample: 2 days-post-fertilization zebrafish embryo.
beta-Catenin antibody [N1N2-2], N-term (NBP1-32239) dilution: 1:100.
Western Blot: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] -
Western Blot: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - Various tissue extracts (30 ug) were separated by 7.5% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with beta-Catenin antibody (NBP1-32239) diluted at 1:500. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody was used to detect the primary antibody.
Immunohistochemistry: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] -
Immunohistochemistry: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - Immunohistochemical analysis of agarose-embedded zebrafish embryo, using beta-Catenin antibody [N1N2-2], N-term NBP1-32239) at 1:100. dilution. (This image was provided courtesy of the Schilling Lab at UC, Irvine.)
Immunohistochemistry: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] -
Immunohistochemistry: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - beta-Catenin antibody [N1N2-2], N-term detects Ctnnb1 protein on zebrafish by whole mount immunohistochemical analysis.
Sample: 1 day-post-fertilization zebrafish embryo.
beta-Catenin antibody [N1N2-2], N-term (NBP1-32239) dilution: 1:100.
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] -
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - beta-Catenin antibody [N1N2-2], N-term detects beta-Catenin protein by immunohistochemical analysis.Sample: Paraffin-embedded rat tissues.beta-Catenin stained by beta-Catenin antibody [N1N2-2], N-term (NBP1-32239) diluted at 1:500.Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] -
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - beta-Catenin antibody [N1N2-2] detects beta-Catenin protein at cell membrane in mouse colon by immunohistochemical analysis.
Sample: Paraffin-embedded mouse colon.
Green: beta-Catenin antibody [N1N2-2] (NBP1-32239) diluted at 1:500.
Red: alpha Tubulin antibody [GT114] diluted at 1:500.
Blue: Hoechst 33342 staining.
Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min
Immunohistochemistry: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] -
Immunohistochemistry: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - beta-Catenin antibody [N1N2-2], N-term detects Ctnnb1 protein on zebrafish by whole mount immunohistochemical analysis.
Sample: 2 days-post-fertilization zebrafish embryo.
beta-Catenin antibody [N1N2-2], N-term (NBP1-32239) dilution: 1:100.
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] -
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - beta-Catenin antibody detects beta-Catenin protein at cell membrane by immunofluorescent analysis.Sample: MDCK cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min.Green: beta-Catenin stained by beta-Catenin antibody (NBP1-32239) diluted at 1:1000.
Immunohistochemistry: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] -
Immunohistochemistry: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded zebrafish tissue, using beta-Catenin antibody [N1N2-2], N-term (NBP1-32239) at 1:300 dilution.
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] -
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - beta-Catenin antibody [N1N2-2], N-term detects beta-Catenin protein by immunohistochemical analysis.Sample: Paraffin-embedded mouse tissues.beta-Catenin stained by beta-Catenin antibody [N1N2-2], N-term (NBP1-32239) diluted at 1:500.Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min
Western Blot: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] -
Western Blot: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - Whole cell extract (30 ug) was separated by 7.5% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with beta-Catenin antibody (NBP1-32239) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody was used to detect the primary antibody.
Western Blot: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] -
Western Blot: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - Wild-type (WT) and beta Catenin knockout (KO) 293T cell extracts (9 ug) were separated by 7.5% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with beta Catenin antibody [N1N2-2], N-term diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody was used to detect the primary antibody.

![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/beta-Catenin-Antibody-Immunocytochemistry-Immunofluorescence-NBP1-32239-img0017.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/beta-Catenin-Antibody-Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin-NBP1-32239-img0043.jpg)
![Flow Cytometry: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] Flow Cytometry: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/beta-Catenin-Antibody-Flow-Cytometry-NBP1-32239-img0031.jpg)
![Western Blot: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] Western Blot: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/beta-Catenin-Antibody-Western-Blot-NBP1-32239-img0033.jpg)
![Western Blot: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] Western Blot: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/beta-Catenin-Antibody-Western-Blot-NBP1-32239-img0008.jpg)
![Western Blot: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] Western Blot: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/beta-Catenin-Antibody-Western-Blot-NBP1-32239-img0013.jpg)
![Western Blot: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] Western Blot: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/beta-Catenin-Antibody-Western-Blot-NBP1-32239-img0014.jpg)
![Western Blot: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] Western Blot: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/beta-Catenin-Antibody-Western-Blot-NBP1-32239-img0026.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/beta-Catenin-Antibody-Immunocytochemistry-Immunofluorescence-NBP1-32239-img0032.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/beta-Catenin-Antibody-Immunocytochemistry-Immunofluorescence-NBP1-32239-img0035.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/beta-Catenin-Antibody-Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin-NBP1-32239-img0018.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/beta-Catenin-Antibody-Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin-NBP1-32239-img0019.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/beta-Catenin-Antibody-Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin-NBP1-32239-img0020.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/beta-Catenin-Antibody-Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin-NBP1-32239-img0021.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/beta-Catenin-Antibody-Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin-NBP1-32239-img0036.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/beta-Catenin-Antibody-Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin-NBP1-32239-img0037.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/beta-Catenin-Antibody-Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin-NBP1-32239-img0038.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/beta-Catenin-Antibody-Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin-NBP1-32239-img0039.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/beta-Catenin-Antibody-Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin-NBP1-32239-img0040.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/beta-Catenin-Antibody-Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin-NBP1-32239-img0041.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/beta-Catenin-Antibody-Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin-NBP1-32239-img0042.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - beta-Catenin Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nbp1-32239_rabbit-polyclonal-beta-catenin-antibody-310202415171344.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - beta-Catenin Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nbp1-32239_rabbit-polyclonal-beta-catenin-antibody-31020241617146.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - beta-Catenin Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nbp1-32239_rabbit-polyclonal-beta-catenin-antibody-310202416171420.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - beta-Catenin Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nbp1-32239_rabbit-polyclonal-beta-catenin-antibody-31020241618265.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - beta-Catenin Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nbp1-32239_rabbit-polyclonal-beta-catenin-antibody-31020241618934.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - beta-Catenin Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nbp1-32239_rabbit-polyclonal-beta-catenin-antibody-310202416165641.jpg)
![Western Blot: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - beta-Catenin Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nbp1-32239_rabbit-polyclonal-beta-catenin-antibody-91020242011415.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - beta-Catenin Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nbp1-32239_rabbit-polyclonal-beta-catenin-antibody-91020242075974.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - beta-Catenin Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nbp1-32239_rabbit-polyclonal-beta-catenin-antibody-910202420122025.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - beta-Catenin Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nbp1-32239_rabbit-polyclonal-beta-catenin-antibody-910202420134025.jpg)
![Western Blot: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - beta-Catenin Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nbp1-32239_rabbit-polyclonal-beta-catenin-antibody-910202420104461.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - beta-Catenin Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nbp1-32239_rabbit-polyclonal-beta-catenin-antibody-910202420115056.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - beta-Catenin Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nbp1-32239_rabbit-polyclonal-beta-catenin-antibody-910202420564.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - beta-Catenin Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nbp1-32239_rabbit-polyclonal-beta-catenin-antibody-9102024202461.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - beta-Catenin Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nbp1-32239_rabbit-polyclonal-beta-catenin-antibody-91020242001070.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - beta-Catenin Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nbp1-32239_rabbit-polyclonal-beta-catenin-antibody-9102024202198.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - beta-Catenin Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nbp1-32239_rabbit-polyclonal-beta-catenin-antibody-91020242010443.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - beta-Catenin Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nbp1-32239_rabbit-polyclonal-beta-catenin-antibody-91020242075983.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - beta-Catenin Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nbp1-32239_rabbit-polyclonal-beta-catenin-antibody-91020242075987.jpg)
![Western Blot: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - beta-Catenin Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nbp1-32239_rabbit-polyclonal-beta-catenin-antibody-910202420131247.jpg)
![Western Blot: beta-Catenin Antibody [NBP1-32239] - beta-Catenin Antibody](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nbp1-32239_rabbit-polyclonal-beta-catenin-antibody-1610202419405728.jpg)