Human CD83 Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # MAB1774


Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Human CD83 Antibody
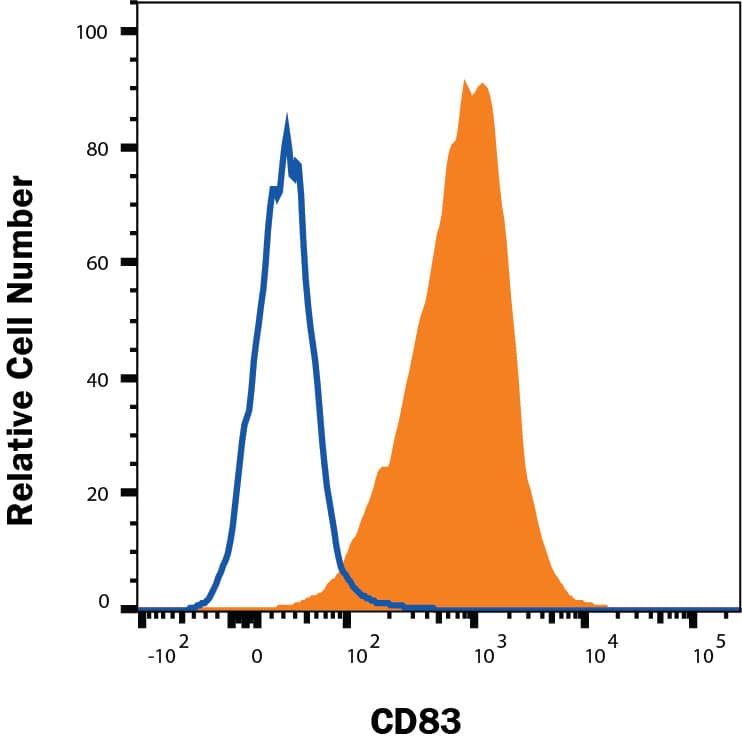
Detection of CD83 in Human Mature Dendritic Cells by Flow Cytometry.
Human mature dendritic cells were stained with Mouse Anti-Human CD83 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB1774, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (MAB002, open histogram), followed by Phycoerythrin-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # F0102B).CD83 in Human Dendritic Cells.
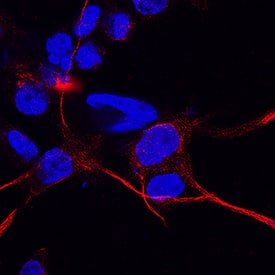
CD83 was detected in immersion fixed human dendritic cells using 10 µg/mL Mouse Anti-Human CD83 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB1774) for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained with the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (red; NL007) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). View our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Non-adherent Cells.CD83 in THP‑1 Human Cell Line.
CD83 was detected in immersion fixed THP-1 human acute monocytic leukemia cell line using Mouse Anti-Human CD83 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB1774) at 8 µg/mL for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained using the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (red; NL007) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Specific staining was localized to cell surfaces. View our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Cells on Coverslips.Applications for Human CD83 Antibody
CyTOF-ready
Flow Cytometry
Sample: Human mature dendritic cells, Daudi human Burkitt's lymphoma cell line
Immunocytochemistry
Sample: Immersion fixed human dendritic cells and THP-1 human acute monocytic leukemia cell line
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: CD83
Human CD83 is a 40‑50 kDa member of the Siglec (or sialic-acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin) family of transmembrane proteins (1, 2, 3). CD83 is synthesized as a type I transmembrane glycoprotein that contains a 125 amino acid (aa) extracellular region, a 22 aa transmembrane segment, and 39 aa cytoplasmic domain. It contains one V type Ig-like domain in the extracellular region with no inhibitory cytoplasmic motif(s). Although in vitro studies suggest CD83 may form membrane-bound covalent homodimers, in vivo this does not appear to be the case (1, 4). In the extracellular region, mouse and human CD83 are 66% aa identical (1, 2, 4, 5). Relative to human, mouse CD83 is 11 aa shorter in its extracellular domain and is expressed as a 30‑35 kDa protein (1, 4, 5). Human CD83 is active in the mouse system (4). One alternate splice form has been reported. This leads to a small monomeric soluble form of 74 aa that includes aa 20‑52 and aa 164‑205 (6, 7). In human, proteolytic cleavage and solubilization of CD83 has also been suggested, and this could lead to dimeric circulating CD83 (4, 6). CD83 is a primary marker for dendritic cells (3, 6, 8). It is also found on B cells (6, 9), neutrophils (10), monocytes and macrophages (11). Except for dendritic cells, CD83 expression is often transient. CD83 binds to sialic acids on target cells (12). Membrane CD83 appears to promote T cell proliferation, particularly of CD8+ cytotoxic T cells (13, 14). Soluble CD83, however, appears to be immunosuppressive and blocks T cell activation (15, 16). On monocytes, CD83 is suggested to drive monocytes into a fibrocyte phenotype (13). A lack of membrane-expressed CD83 leads to an unusual IL-4/IL-10 producing CD4+ T cell phenotype (17).
References
- Zhou, L-J. et al. (1992) J. Immunol. 149:735.
- Kozlow, E.J. et al. (1993) Blood 81:454.
- Fujimoto, Y and T.F. Tedder (2006) J. Med. Dent. Sci. 53:85.
- Lechmann, M. et al. (2005) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 329:132.
- Berchtold, S. et. al. (1999) FEBS Lett. 461:211.
- Hock, B.D. et al. (2001) Int. Immunol. 13:959.
- Dudziak, D. et al. (2005) J. Immunol. 174:6672.
- Velten, F.W. et al. (2007) Mol. Immunol. 44:1544.
- Cramer, S.O. et al. (2000) Int. Immunol. 12:1347.
- Yamashiro, S. et al. (2000) Blood 96:3958.
- Cao, W. et al. (2005) Biochem. J. 385:85.
- Scholler, N. et al. (2001) J. Immunol. 166:3865.
- Scholler, N. et al. (2002) J. Immunol. 168:2599.
- Hirano, N. et al. (2006) Blood 107:1528.
- Kotzor, N. et al. (2004) Immunobiology 209:129.
- Zinser, E. et al. (2006) Immunobiology 211:449.
- Garcia-Martinez, L.F. et al. (2004) J. Immunol. 173:2995.
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
Additional CD83 Products
Product Documents for Human CD83 Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human CD83 Antibody
For research use only