Human G-CSFR/CD114 PE-conjugated Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # FAB381P

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Glu25-Pro621
Accession # Q99062
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Human G-CSFR/CD114 PE-conjugated Antibody
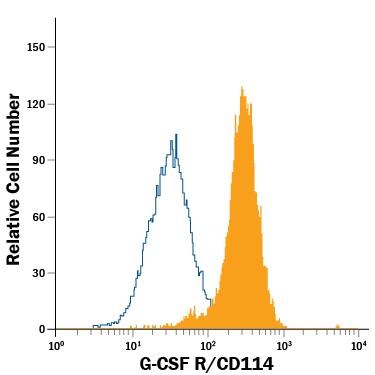
Detection of G‑CSF R/CD114 in Human Granulocytes by Flow Cytometry.
Human granulocytes were stained with Mouse Anti-Human G-CSF R/CD114 PE-conjugated Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # FAB381P, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (Catalog # IC002P, open histogram). View our protocol for Staining Membrane-associated Proteins.Applications for Human G-CSFR/CD114 PE-conjugated Antibody
Flow Cytometry
Sample: Human granulocytes
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
Background: G-CSFR/CD114
Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) is a pleiotropic cytokine best known for its specific effects on the proliferation, differentiation, and activation of hematopoietic cells of the neutrophilic granulocyte lineage. G-CSF plays an important role in defense against infection, in inflammation and repair, and in the maintenance of steady state hematopoiesis. Recombinant human G-CSF has been approved for the amelioration of chemotherapy induced neutropenia as well as for severe chronic neutropenia following marrow transplant.
Cell activation by G-CSF is mediated by a type I membrane protein belonging to the cytokine receptor superfamily. Human G-CSF R, also known as colony-stimulating factor 3 receptor (CSF3R) and designated CD114, is 863 amino acids (aa) in length, with a 604 aa extracellular domain, a 26 aa transmembrane domain, and a 183 aa cytoplasmic domain that include a 23 amino acid signal sequence. As a result of alternative splicing, at least four isoforms of G-CSF R that differ in their C-terminal region exist. Isoform 2 lacks the transmembrane region and may represent a soluble form of the receptor; however the existence of soluble G-CSF R in human serum has not been reported (1). Mutations have been found in the gene encoding G-CSF R in some patients with severe congenital neutropenia. These mutations typically led to a truncation in the cytoplasmic domain of the G-CSF R leading to maturation arrest of neutrophil precursors in the bone marrow and neutropenia in peripheral blood (2). Human and mouse G-CSF R have a homology of 62.5%.
G-CSF R is expressed in mature neutrophils, neutrophilic precursors, myeloid leukemia cells, and placenta. Binding of G-CSF to its receptor induces dimerization or oligomerization of the receptor activating cytoplasmic tyrosine kinases. Signal transduction from pathways that involve Janus tyrosine kinases/signal transducer and activator of transcription proteins (Jak1, Jak2, and Tyk2/STAT3, STAT3, and STATG), src-related protein tyrosine kinases (Lyn and Syk), Ras/MAP kinase, and phosphatidylinositol have been reported to be activated upon G-CSF stimulation (1).
References
- Nicola, N.A., in Cytokine Reference, (2001) Oppenhiem, J.J. and M. Feldmann, eds. Academic Press p. 1935
- Mitsui, T. et. al. (2003) Blood. 101:2990.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional G-CSFR/CD114 Products
Product Documents for Human G-CSFR/CD114 PE-conjugated Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human G-CSFR/CD114 PE-conjugated Antibody
For research use only