Human LDLR Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # AF2148

Key Product Details
Validated by
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Asp193-Arg788
Accession # P01130
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Human LDLR Antibody
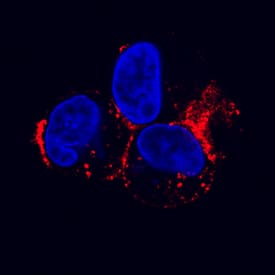
LDL R in HepG2 Human Cell Line.
LDL R was detected in immersion fixed HepG2 human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line using Goat Anti-Human LDL R Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF2148) at 1.7 µg/mL for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained using the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (red; Catalog # NL001) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Specific staining was localized to cytoplasm. View our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Cells on Coverslips.LDL R in Human Liver.
LDL R was detected in formalin fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human liver using Goat Anti-Human LDL R Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF2148) at 15 µg/mL overnight at 4 °C. Tissue was stained using the Anti-Goat HRP-DAB Cell & Tissue Staining Kit (brown; Catalog # CTS008) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). View our protocol for Chromogenic IHC Staining of Paraffin-embedded Tissue Sections.Detection of Human LDLR by Knockdown Validated
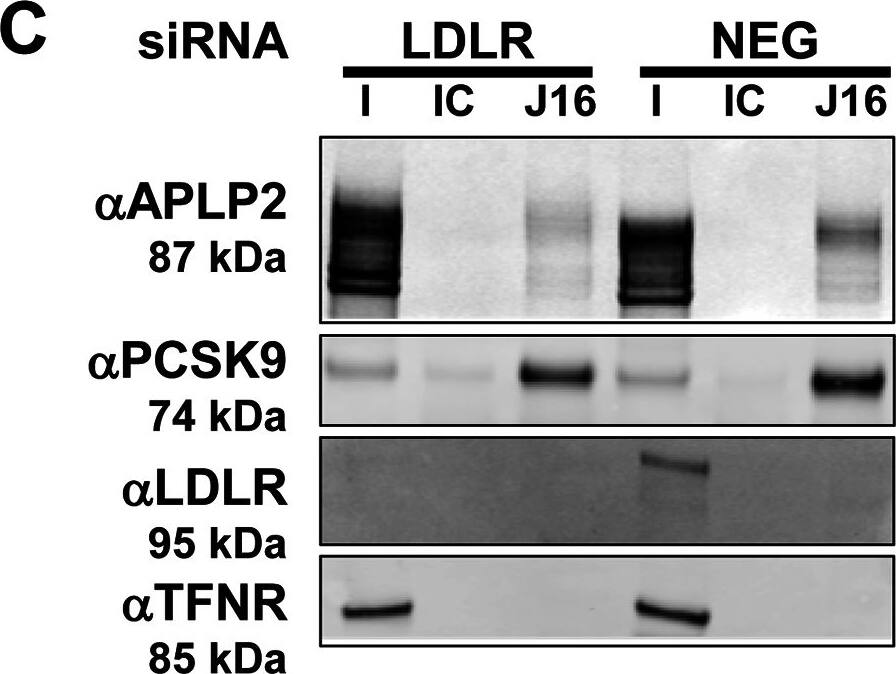
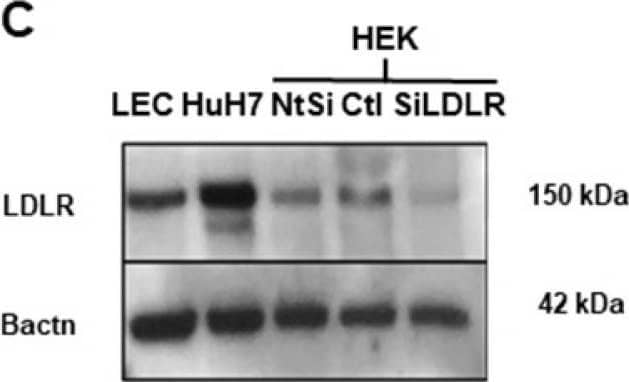
APLP2 and LDLR interactions with PCSK9 and their regulation of PCSK9 function.(A and B) Western blot showing APLP2, PCSK9, or Transferrin receptor (TFNR) levels in input fraction (I), IC or J16 immunoprecipitated samples (IP Ab.) in the absence or presence of 5F6 Fab or 12E3 Fab, as indicated. (B) Quantification of (A); shown as average APLP2 normalized to PCSK9 of 3 independent experiments with SEM. (C and D) J16 coIPs of PCSK9 from Neg or LDLR siRNA treated HepG2 cells with IC control, as indicated. (D) Quantification of (C); shown as average APLP2 normalized to PCSK9 from 3 independent experiments with SEM. (E, F, and G) Western blot of LDLR, APOER2, or TFNR in siRNA treated cells following treatment with PCSK9 at 0, 20, 50, or 100 μg/ml. (F) LDLR levels from (E) quantified as percent LDLR degradation of untreated cells and normalized to Neg siRNA samples. Shown as average with SEM from 4 independent experiments. (G) Same as F, but measuring APOER2 levels. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25905719), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Applications for Human LDLR Antibody
Blockade of Receptor-ligand Interaction
Immunocytochemistry
Sample: Immersion fixed HepG2 human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line
Immunohistochemistry
Sample: Immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human liver
Western Blot
Sample: Recombinant Human LDL R (Catalog # 2148-LD)
Reviewed Applications
Read 3 reviews rated 5 using AF2148 in the following applications:
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
*Small pack size (-SP) is supplied either lyophilized or as a 0.2 µm filtered solution in PBS.
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: LDLR
The low density lipoprotein receptor (LDL R) is the founding member of the LDL R family of scavenger receptors. This family contains transmembrane molecules that are characterized by the presence of EGF repeats, complement-like repeats, and YWTD motifs that form beta-propellers. Although members of the family were originally thought to be endocytic receptors, it is now clear that some members interact with adjacent cell‑surface molecules, expanding their range of activities. Human LDL R is synthesized as an 860 amino acid (aa) precursor that contains a 21 aa signal sequence, a 767 aa extracellular region, a 22 aa transmembrane segment and a 50 aa cytoplasmic tail. The extracellular region is complex. It consists of seven N-terminal complement-like cysteine-rich repeats that bind ligand. Cysteine residues in this region participate in intrachain disulfide bonds. This region is followed by three EGF-like repeats with a beta-propeller YWTD containing motif. The EGF-like repeats are responsible for ligand bonding and dissociation. Finally, there is a 50 aa membrane proximal Ser/Thr‑rich region that serves as a carbohydrate attachment point. There is extensive O‑linked and modest N-linked glycosylation. Thus the receptor’s predicted molecular weight of 93 kDa is increased to a native molecular weight of 120 ‑ 160 kDa. Within the 50 aa cytoplasmic tail, there is an NPXY motif that links the receptor to clathrin pits. The extracellular region of human LDL R is 51% aa identical to the extracellular region of human VLDL R, and 79% aa identical to the extracellular region of mouse LDL R. LDL R is constitutively expressed and binds apoB of LDL and apoE of VLDL. It is responsible for clearing 70% of plasma LDL in liver. Mutations in the LDL R gene cause the autosomal dominant disorder, familial hypercholesterolemia.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Entrez Gene IDs
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional LDLR Products
Product Documents for Human LDLR Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human LDLR Antibody
For research use only