Human M-CSF R/CD115 Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # MAB3291

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Ile20-Glu512 (Pro54Ala)
Accession # P07333.2
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Endotoxin Level
Scientific Data Images for Human M-CSF R/CD115 Antibody
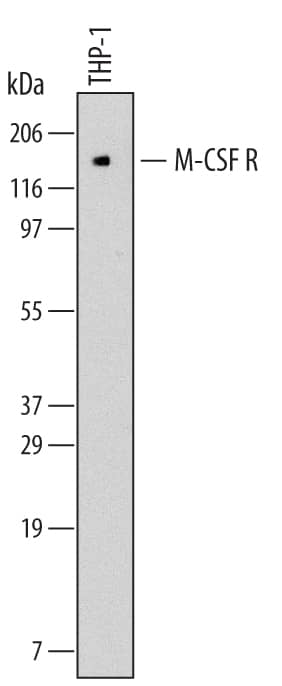
Detection of Human M-CSF R/CD115 by Western Blot.
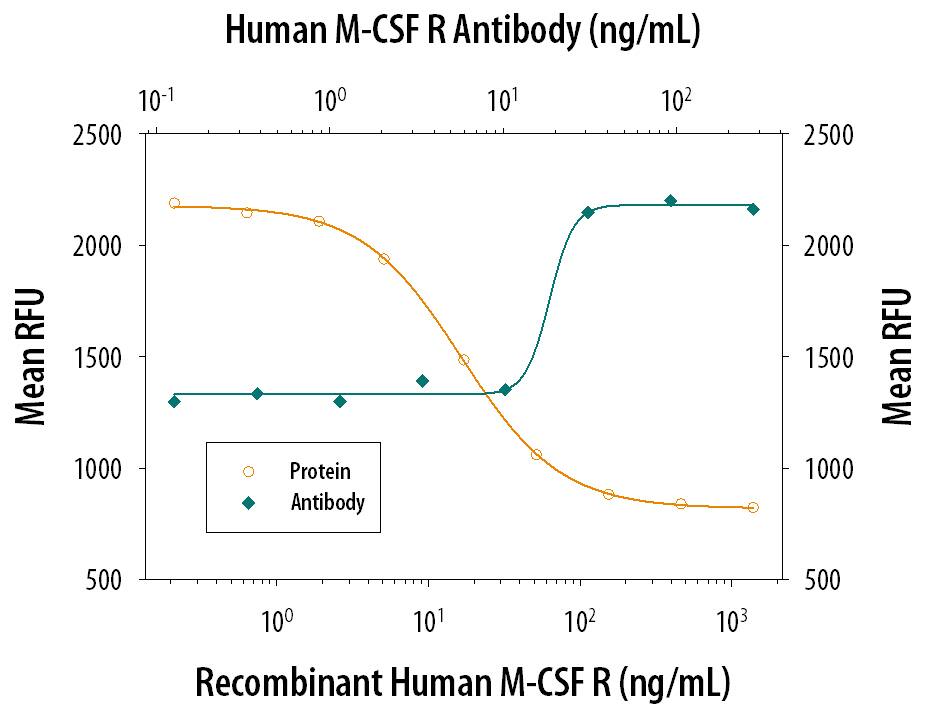
Western blot shows lysates of THP-1 human acute monocytic leukemia cell line. PVDF membrane was probed with 2 µg/mL of Mouse Anti-Human M-CSF R/CD115 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB3291) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (HAF007). A specific band was detected for M-CSF R/CD115 at approximately 130 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 1.M-CSF R/CD115 Inhibition of M-CSF-dependent Cell Proliferation and Neutralization by Human M-CSF R/CD115 Antibody.
Recombinant Human M-CSF R/CD115 Fc Chimera (329-MR) inhibits Recombinant Human M-CSF (Catalog # 216-MC) induced proliferation in the M-NFS-60 mouse myelogenous leukemia lymphoblast cell line in a dose-dependent manner (orange line). Inhibition of Recombinant Human M-CSF R/CD115 (1 ng/mL) activity elicited by Recombinant Human M-CSF R/CD115 Fc Chimera (30 ng/mL) is neutralized (green line) by increasing concentrations of Mouse Anti-Human M-CSF R/CD115 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB3291). The ND50 is typically 4-16 ng/mL.Detection of M-CSF R/CD115 in Human Spleen.
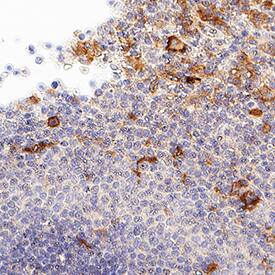
M-CSF R/CD115 was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of Human Spleen using Mouse Anti-Human M-CSF R/CD115 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB3291) at 15 µg/mL for 1 hour at room temperature followed by incubation with the Anti-Mouse IgG VisUCyte™ HRP Polymer Antibody (Catalog # VC001). Before incubation with the primary antibody, tissue was subjected to heat-induced epitope retrieval using VisUCyte Antigen Retrieval Reagent-Basic (Catalog # VCTS021). Tissue was stained using DAB (brown) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to cell surface and cytoplasm in lymphocytes. View our protocol for IHC Staining with VisUCyte HRP Polymer Detection Reagents.Applications for Human M-CSF R/CD115 Antibody
Immunohistochemistry
Sample: Immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of Human Spleen
Western Blot
Sample: THP‑1 human acute monocytic leukemia cell line under reducing conditions only
Neutralization
M-CSF.
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: M-CSF R/CD115
M-CSF receptor, the product of the c-fms proto-oncogene, is a member of the type III subfamily of receptor tyrosine kinases that also includes receptors for SCF and PDGF. These receptors each contain five immunoglobulin-like domains in their extracellular domain (ECD) and a split kinase domain in their intracellular region (1-4). M-CSF receptor is expressed primarily on cells of the monocyte/macrophage lineage, dendritic cells, stem cells and in the developing placenta (1). Human M-CSF receptor cDNA encodes a 972 amino acid (aa) type I membrane protein with a 19 aa signal peptide, a 493 aa extracellular region containing the ligand-binding domain, a 25 aa transmembrane domain, and a 435 aa cytoplasmic domain. The human M-CSF R ECD shares 60%, 64%, 72%, 75%, 75%, and 76% aa identity with mouse, rat, bovine, canine, feline, and equine M-CSF R, respectively. Activators of protein kinase C induce TACE/ADAM17 cleavage of the M-CSF receptor, releasing the functional ligand-binding extracellular domain (5). M-CSF binding induces receptor homodimerization, resulting in transphosphorylation of specific cytoplasmic tyrosine residues and signal transduction (6). The intracellular domain of activated M-CSF R binds more than 150 proteins that affect cell proliferation, survival, differentiation and cytoskeletal reorganization. Among these, PI3Kinase, P42/44 ERK, and c-Cbl are key transducers of M-CSF R signals (3, 4). M-CSF R engagement is continuously required for macrophage survival and regulates lineage decisions and maturation of monocytes, macrophages, osteoclasts, and DC (3, 4). M-CSF R and integrin alphav beta3 share signaling pathways during osteoclastogenesis and deletion of either causes osteopetrosis (7, 8). In the brain, microglia expressing increased M-CSF R are concentrated with Alzheimers a beta peptide, but their role in pathogenesis is unclear (9, 10).
References
- deParseval, N. et al. (1993) Nucleic Acids Res. 21:750.
- Rothwell, V.M. and L.R. Rohrschneider (1987) Oncogene Res. 1:311.
- Chitu, V. and E.R. Stanley (2006) Curr. Opin. Immunol. 18:39.
- Ross, F.P. and S.L. Teitelbaum (2005) Immunol. Rev. 208:88.
- Rovida, E. et al. (2001) J. Immunol. 166:1583.
- Yeung, Y. et al. (1998) J. Biol. Chem. 273:17128.
- Dai, X. et al. (2002) Blood 99:111.
- Faccio, R. et al. (2003) J. Clin. Invest. 111:749.
- Li, M. et al. (2004) J. Neurochem. 91:623.
- Mitrasinovic, O.M. et al. (2005) J. Neurosci. 25:4442.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional M-CSF R/CD115 Products
Product Documents for Human M-CSF R/CD115 Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human M-CSF R/CD115 Antibody
For research use only