Human/Mouse Angiopoietin-2 Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # MAB098

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Asp68-Phe496
Accession # O15123
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Human/Mouse Angiopoietin-2 Antibody
Angiopoietin‑2 in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Tissue.
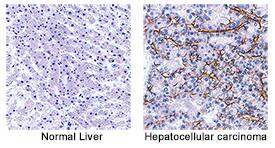
Angiopoietin-2 was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human hepatocellular carcinoma tissue (right panel; positive stain) using Mouse Anti-Human/Mouse Angiopoietin-2 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB098) at 5 µg/mL for 1 hour at room temperature followed by incubation with the Anti-Mouse IgG VisUCyte™ HRP Polymer Antibody (Catalog # VC001). Before incubation with the primary antibody, tissue was subjected to heat-induced epitope retrieval using Antigen Retrieval Reagent-Basic (Catalog # CTS013). Tissue was stained using DAB (brown) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to secreted and plasma membrane. View our protocol for IHC Staining with VisUCyte HRP Polymer Detection Reagents.Angiopoietin-2 in Mouse Lymph Node Tissue.
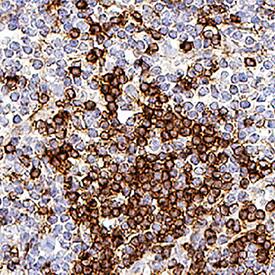
Angiopoietin-2 was detected in perfusion fixed frozen sections of mouse lymph node tissue using Mouse Anti-Human/Mouse Angiopoietin-2 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB098) at 1 µg/mL overnight at 4 °C. Before incubation with the primary antibody, tissue was subjected to heat-induced epitope retrieval using Antigen Retrieval Reagent-Basic (Catalog # CTS013). Tissue was stained using the Anti-Mouse IgG VisUCyte™ HRP Polymer Antibody (brown; Catalog # VC001) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to cell membrane. View our protocol for IHC Staining with VisUCyte HRP Polymer Detection Reagents.Angiopoietin-2 in Mouse Colon Tissue.
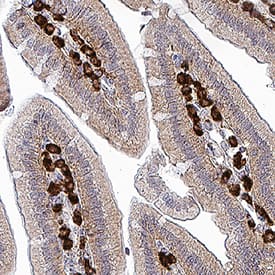
Angiopoietin-2 was detected in perfusion fixed frozen sections of mouse colon tissue using Mouse Anti-Human/Mouse Angiopoietin-2 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB098) at 1 µg/mL overnight at 4 °C. Before incubation with the primary antibody, tissue was subjected to heat-induced epitope retrieval using Antigen Retrieval Reagent-Basic (Catalog # CTS013). Tissue was stained using the Anti-Mouse IgG VisUCyte™ HRP Polymer Antibody (brown; Catalog # VC001) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to lymphocytes in colon mucosa. View our protocol for IHC Staining with VisUCyte HRP Polymer Detection Reagents.Applications for Human/Mouse Angiopoietin-2 Antibody
Immunohistochemistry
Sample: Immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human hepatocellular carcinoma tissue, perfusion fixed frozen sections of mouse lymph node tissue, and perfusion fixed frozen sections of mouse colon tissue
Human Angiopoietin-2 Sandwich Immunoassay
Reviewed Applications
Read 6 reviews rated 4.3 using MAB098 in the following applications:
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Angiopoietin-2
Angiopoietin-2 (Ang-2; also ANGPT2) is a secreted glycoprotein that plays a complex role in angiogenesis and inflammation (1, 2). Mature Ang-2 is 478 amino acids (aa) in length. It contains one coiled-coil domain (aa 166 - 248) that mediates multimerization, and a C-terminal fibrinogen-like domain (aa 275 - 495) that mediates receptor binding. Under reducing conditions, secreted monomeric Ang-2 is 65 - 66 kDa in size. Under nonreducing conditions, both natural and recombinant Ang-2 form 140 kDa dimers, 200 kDa trimers, and 250 - 300 kDa tetramers and pentamers (3 - 6). Alternate splicing generates a short isoform that lacks 52 amino acids (aa) preceding the coiled-coil domain (4). Mature human Ang-2 shares 86% aa sequence identity with mouse and rat Ang-2. Ang-2 is widely expressed during development, but it is restricted postnatally to highly angiogenic tissues such as the placenta, ovaries, and uterus (3). It is particularly abundant in vascular endothelial cells (EC) where it is stored in intracellular Weibel-Palade bodies (1, 3, 7). Both Ang-2 and the related Angiopoietin-1 (Ang-1) are ligands for the receptor tyrosine kinase Tie-2 (2). While Ang-1 is a potent Tie-2 agonist, Ang-2 may act as either a Tie-2 antagonist or agonist, depending upon its state of multimerization. The higher the order of oligomer, the more effective Ang-2 becomes as a Tie-2 agonist (3, 8 - 11). The short isoform appears to block the binding of either Ang-1 or full-length Ang-2 to Tie-2 (4). Ang-2 functions as a pro-angiogenic factor, although it can also induce EC death and vessel regression (12, 13). Upon its release from quiescent EC, it regulates vascular remodeling by promoting EC survival, proliferation, and migration and destabilizing the interaction between EC and perivascular cells (8, 13, 14). Ang-2 is required for postnatal vascular remodeling, and it cooperates with Ang-1 during lymphatic vessel development (7, 15). It mediates the upregulation of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 on EC, which facilitates the adhesion of leukocytes during inflammation (16). Ang-2 is upregulated in both the endothelium and tumor cells of several cancers as well as in ischemic tissue (17 - 20). Its direct interaction with Integrins promotes tumor cell invasion (21, 22). Ang-2 also promotes the neuronal differentiation and migration of subventricular zone progenitor cells (20).
References
- Augustin, H.G. et al. (2009) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 10:165.
- Murdoch, C. et al. (2007) J. Immunol. 178:7405.
- Maisonpierre, P.C. et al. (1997) Science 27:55.
- Kim, I. et al. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275:18550.
- Procopio, W.N. et al. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274:30196.
- Kim, K-T. et al. (2005) J. Biol. Chem. 280:20126.
- Gale, N.W. et al. (2002) Dev. Cell 3:411.
- Yuan, H.T. et al. (2009) Mol. Cell. Biol. 29:2011.
- Falcon, B.L. et al. (2009) Am. J. Pathol. 175:2159.
- Kim, H-Z. et al. (2009) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1793:772.
- Kim, I. et al. (2001) Cardiovasc. Res. 49:872.
- Lobov, I.B. et al. (2002) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 99:11205.
- Cao, Y. et al. (2007) Cancer Res. 67:3835.
- Nasarre, P. et al. (2009) Cancer Res. 69:1324.
- Dellinger, M. et al. (2008) Dev. Biol. 319:309.
- Fiedler, U. et al. (2006) Nat. Med. 12:235.
- Koga, K. et al. (2001) Cancer Res. 61:6248.
- Etoh, T. et al. (2001) Cancer Res. 61:2145.
- Tressel, S.L. et al. (2008) Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 28:1989.
- Liu, X.S. et al. (2009) J. Biol. Chem. 284:22680.
- Hu, B. et al. (2006) Cancer Res. 66:775.
- Imanishi, Y. et al. (2007) Cancer Res. 67:4254.
Alternate Names
Entrez Gene IDs
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional Angiopoietin-2 Products
Product Documents for Human/Mouse Angiopoietin-2 Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human/Mouse Angiopoietin-2 Antibody
For research use only