Mouse DCC Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # AF844

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Phe32-Asn1097
Accession # P70211
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Endotoxin Level
Scientific Data Images for Mouse DCC Antibody
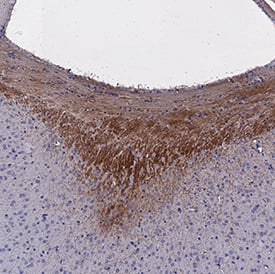
Detection of DCC in Mouse Embryo Developing Brain.
DCC was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of Mouse Embryo Developing Brain using Goat Anti-Mouse DCC Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF844) at 15 µg/mL for 1 hour at room temperature followed by incubation with the Anti-Goat IgG VisUCyte™ HRP Polymer Antibody (Catalog # VC004). Before incubation with the primary antibody, tissue was subjected to heat-induced epitope retrieval using VisUCyte Antigen Retrieval Reagent-Basic (Catalog # VCTS021). Tissue was stained using DAB (brown) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to cytoplasm in neuronal processes. View our protocol for IHC Staining with VisUCyte HRP Polymer Detection Reagents.Applications for Mouse DCC Antibody
Blockade of Receptor-ligand Interaction
Immunohistochemistry
Sample: Immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of Mouse Embryo Developing Brain.
Western Blot
Sample: Recombinant Mouse DCC Fc Chimera (Catalog # 844-DC)
Reviewed Applications
Read 1 review rated 4 using AF844 in the following applications:
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: DCC
Deleted in colorectal cancer (DCC) was originally identified as a putative tumor suppressor gene that is lost in more than 70% of colorectal cancers. This gene has also been found to be deleted in several different kinds of cancers. DCC encodes a type I transmembrane glycoprotein that belongs to the immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily. The extracellular domain is composed of four Ig-like domains and six fibronectin type III repeats. Two forms of the protein (the long and the short isoforms) are produced from the same gene by the use of alternative initiation sites. A third isoform that is produced by alternative splicing is expressed only in the embryo. The extracellular domain of mouse DCC shares 97% and 99% amino acid sequence identity with the human and rat DCC extracellular domains, respectively. In adults, DCC is highly expressed in the brain but is also expressed at very low levels in multiple tissues. In the embryo, high levels of expression are detected in the brain and neural tube. DCC has been shown to be a receptor for the netrins that are important for axon guidance. DCC has also been shown to induce apoptosis in the absence of ligand binding and to block apoptosis when engaged by netrin-1. DCC has been shown to be a caspase substrate. The pro-apoptotic effects of DCC were found to be dependent on the proteolytic cleavage of the unoccupied receptor by caspase. It is likely that DCC functions as a tumor-suppressor gene by inducing apoptosis in cells that are not exposed to netrins.
References
- Fearon, E.R. et al. (1990) Science 247:49.
- Keino-Masu, K. et al. (1996) Cell 87:175.
- Mehlen, P. et al. (1998) Nature 395:801.
- Culotti, J.G. and D.C. Merz (1998) Current Opinion in Cell Biology 10:609.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional DCC Products
Product Documents for Mouse DCC Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Mouse DCC Antibody
This product or the use of this product is covered by U.S. Patents owned by The Regents of the University of California. This product is for research use only and is not to be used for commercial purposes. Use of this product to produce products for sale or for diagnostic, therapeutic or drug discovery purposes is prohibited. In order to obtain a license to use this product for such purposes, contact The Regents of the University of California.
U.S. Patent # 5,939,271, 6,277,585, and other U.S. and international patents pending.
For research use only