Mouse Fc gamma RI/CD64 Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # AF2074

Key Product Details
Validated by
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Glu25-Pro297
Accession # P26151
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Mouse Fc gamma RI/CD64 Antibody
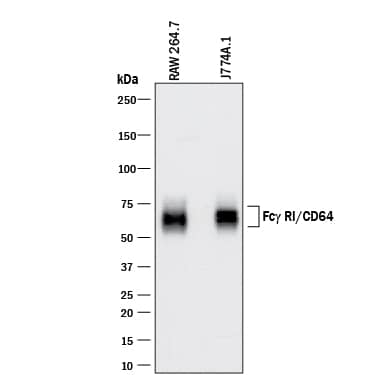
Detection of Mouse Fc gamma RI/CD64 by Western Blot.
Western blot shows lysates of RAW 264.7 mouse monocyte/macrophage cell line and J774A.1 mouse reticulum cell sarcoma macrophage cell line. PVDF membrane was probed with 0.5 µg/mL of Goat Anti-Mouse Fc gamma RI/CD64 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF2074) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF017). A specific band was detected for Fc gamma RI/CD64 at approximately 60-75 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 1.Detection of Mouse Fc gamma RI/CD64 by Western Blot
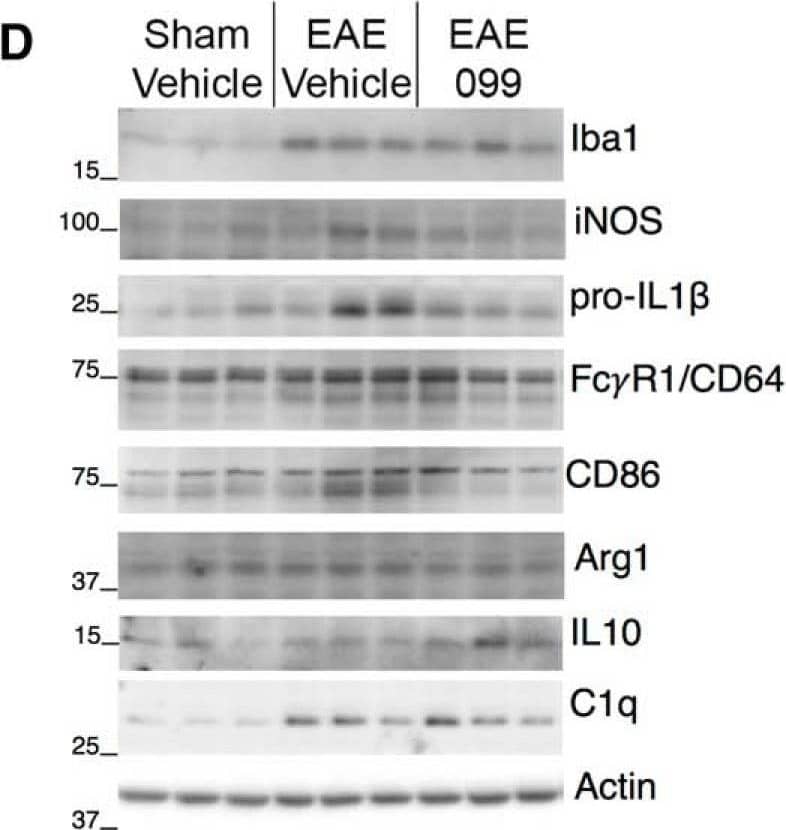
URMC-099 modulates the phenotype of activated microglia in EAE hippocampus. A, Staining for Iba1 in hippocampal area CA1 shows ramified microglia in sham-immunized mice, and microglia with shorter, thicker processes in EAE. B, Iba1-positive cells in the hippocampi of both sham and EAE mice coexpress microglia-specific marker Tmem119 along their processes and to a more variable extent in the cell body (upper panels). Iba1-positive, Tmem119-negative cells consistent with monocyte-derived macrophages could be found in the pia during EAE (inset), but not in or around the hippocampus. Staining for Ly-6B, expressed on neutrophils and some recently-generated macrophages, is sparse in sham and EAE hippocampi (lower panels, arrowheads), although clusters occurred sporadically in the pia and other area of some EAE brains (inset). Scale bars: 20 µm. s.o., CA1 stratum oriens; pyr, pyramidal layer; s.r., stratum radiatum. C, Quantification of microglial images shows increased Iba1 intensity and reduction in the ratio of surface area to volume in EAE microglia regardless of treatment with URMC-099 or CLFB1134. Microglial expression of lysosomal marker CD68 is increased in many hippocampi from vehicle-treated EAE mice but not in mice treated with URMC-099 or CLFB1134; n = 10 male mice (sham-vehicle), n = 6 male mice (EAE-vehicle and EAE-099), n = 7 male mice (EAE-1134). D, E, Western blottings and band densitometry for markers of inflammation and microglial phenotype in hippocampal protein extracts. Markers associated with proinflammatory microglial activation tended to increase in vehicle-treated EAE hippocampi and were decreased by URMC-099, with significant changes in iNOS (inducible nitric oxide synthase) and immunoglobulin receptor FC gammaR1/CD64 (lower single band), and a non-significant trend toward increased pro-IL1 beta. Proinflammatory marker CD86 does not significantly increase in vehicle-treated EAE but is decreased by URMC-099 treatment. Arg1 and IL-10, canonical markers of anti-inflammatory alternative activation, are not significantly changed in EAE or with URMC-099. Consistent with immunostaining results, Iba1 is up-regulated in vehicle-treated EAE hippocampi and is further increased with URMC-099 treatment. Complement component C1q follows a similar pattern; n = 10 male mice (sham-vehicle), n = 7 male mice (EAE-vehicle), n = 11 male mice (EAE-099); one representative blot with three lanes per condition is depicted; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, one-way ANOVA with Sidak (iNOS, FC gammaR1/CD64, CD86) or Tukey (Iba1, SA/Vol, C1q) post hoc test. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30627663), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Applications for Mouse Fc gamma RI/CD64 Antibody
Western Blot
Sample: RAW 264.7 mouse monocyte/macrophage cell line and J774A.1 mouse reticulum cell sarcoma macrophage cell line
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Fc gamma RI/CD64
Receptors for the Fc region of IgG (Fc gamma Rs) are members of the Ig superfamily that function in the activation or inhibition of immune responses such as degranulation, phagocytosis, ADCC (antibody-dependent cellular toxicity), cytokine release, and B cell proliferation (1‑3). The Fc gamma Rs have been divided into three classes based on close relationships in their extracellular domains; these groups are designated Fc gamma RI (also known as CD64), Fc gamma RII (CD32), and Fc gamma RIII (CD16). Each group may be encoded by multiple genes and exist in different isoforms depending on species and cell type. The CD64 proteins are high affinity receptors (~10‑8‑10‑9 M) capable of binding monomeric IgG, whereas the CD16 and CD32 proteins bind IgG with lower affinities (~10-6‑10-7 M) only recognizing IgG aggregates surrounding multivalent antigens (1, 4). Fc gamma Rs that deliver an activating signal either have an intrinsic immunoreceptor tyrosine‑based activation motif (ITAM) within their cytoplasmic domains or associate with one of the ITAM-bearing adapter subunits, Fc R gamma or zeta (3, 5). The only inhibitory member in human and mouse, Fc gamma RIIb, has an intrinsic cytoplasmic immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (ITIM). The coordinated functioning of activating and inhibitory receptors is necessary for successful initiation, amplification, and termination of immune responses (5).
Mouse Fc gamma RI is transmembrane protein with three extracellular Ig-like domains, and it delivers an activating signal via the associated Fc R gamma accessory chain (1, 2). The high affinity recognition of IgG by Fc gamma RI permits the triggering of effector responses at low IgG concentrations typical of early immune responses (2). Fc gamma RI is expressed constitutively on monocytes and macrophages and can be induced on neutrophils and eosinophils (1, 4). Its expression is up-regulated during bacterial infections and sepsis.
References
- Van de Winkel, J. and P. Capes (1993) Immunol. Today 14:215.
- Raghaven, M. and P. Bjorkman (1996) Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 12:181.
- Ravetch, J. and S. Bolland (2001) Annu. Rev. Immunol. 19:275.
- Takai, T. (2002) Nature Rev. Immunol. 2:580.
- Ravetch, J. and L. Lanier (2000) Science 290:84.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional Fc gamma RI/CD64 Products
Product Documents for Mouse Fc gamma RI/CD64 Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Mouse Fc gamma RI/CD64 Antibody
For research use only