Mouse HVEM/TNFRSF14 PE-conjugated Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # FAB2516P

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Applications
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Gln39-Val207
Accession # NP_849262
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Mouse HVEM/TNFRSF14 PE-conjugated Antibody
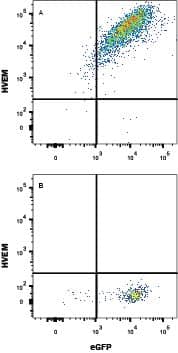
Detection of HVEM/TNFRSF14 in HEK293 human embryonic kidney cell line transfected with mouse HVEM/TNFRSF14 and eGFP by Flow Cytometry.
HEK293 human embryonic kidney cell line transfected with either (A) mouse HVEM/TNFRSF14 or (B) irrelevant transfectants and eGFP was stained with Rabbit Anti-Mouse HVEM/TNFRSF14 PE-conjugated Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # FAB2516P). Quadrant markers were set based on control antibody staining (Catalog # IC1051P). View our protocol for Staining Membrane-associated Proteins.Applications for Mouse HVEM/TNFRSF14 PE-conjugated Antibody
Flow Cytometry
Sample: HEK293 human embryonic kidney cell line transfected with mouse HVEM and eGFP
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, 2 to 8 °C as supplied.
Background: HVEM/TNFRSF14
HVEM (Herpesvirus Entry Mediator) is a type I membrane protein that is TNF receptor superfamily member 14 (TNFRSF14) (1). The mouse HVEM cDNA encodes a 275 amino acid (aa) protein. It contains a 36 aa signal peptide, a 170 aa extracellular domain with three cysteine rich domains (CRD), a 24 aa transmembrane region and a 45 aa cytoplasmic tail with a TRAF interaction domain (1). HVEM expression is highest on naïve, memory and regulatory T cells, but declines during T cell activation (2, 3). It is present at low levels on most resting leukocytes (4). HVEM is a receptor for the IGSF member BTLA (B and T Lymphocyte Attenuator), CD160, and the TNF family ligand LIGHT (2, 9). HVEM and BTLA are constitutively expressed on T cells, while LIGHT is generally considered to be inducible upon TCR activation. In the absence of activation, HVEM and BTLA interact monomerically, either in cis, or in trans. A same cell (or cis) interaction likely promotes general cell survival, while a between cell (or trans) interaction promotes a state of lymphocyte inactivity through the BTLA cytoplasmic domain. Following T cell activation, LIGHT appears and disrupts existing HVEM-BTLA bonds. A LIGHT-HVEM trimer now forms in trans, initiating HVEM-mediated NF kappaB signaling and a proinflammatory response (10). BTLA and LIGHT interactions are not mutually exclusive, but BTLA appears dominant (4, 6, 7). The herpesvirus envelope glycoprotein gD, which binds HVEM CRD1 to initiate membrane fusion, can antagonize both BTLA and LIGHT binding (1, 6, 7, 9). Human, but not mouse, HVEM can also bind lymphotoxin a within CRD2 3 (9, 11). Graft‑vs‑host disease and Th1 type intestinal inflammation can be ameliorated by interrupting T cell LIGHT/HVEM interactions, while disruption of BTLA/HVEM interaction promotes intestinal inflammation (12-14). Mouse HVEM ECD shares 89% and 53% aa identity with rat and human HVEM, respectively. Mouse HVEM can recognize human BTLA and LIGHT, but human HVEM does not recognize mouse ligands (2, 11).
References
- Hsu, H. et al. (1997) J. Biol. Chem. 272:13471.
- Sedy, J.R. et al. (2005) Nat. Immunol. 6:90.
- Tao, R. et al. (2008) J. Immunol. 180:6649.
- Wang, Y. et al. (2005) J. Clin. Invest. 115:711.
- Nelson, C.A. et al. (2008) J. Immunol. 180:940.
- Gonzales, L.C. et al. (2005) Proc. Natl. Acad Sci. USA 102:1116.
- Compaan, D.M. et al. (2005) J. Biol. Chem. 280:39553.
- Cai, G. et al. (2008) Nat. Immunol. 9:176.
- Mauri, D.N. et al. (1998) Immunity 8:21.
- Ware, C.F. (2008) Immunol. Rev. 223:186.
- Bossen, C. et al. (2006) J. Biol. Chem. 281:13964.
- Xu, Y. et al. (2007) Blood 109:4097.
- Wang, J. et al. (2005) J. Immunol. 174:8173.
- Steinberg, M.W. et al. (2008) J. Exp. Med. 205:1463.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional HVEM/TNFRSF14 Products
Product Documents for Mouse HVEM/TNFRSF14 PE-conjugated Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Mouse HVEM/TNFRSF14 PE-conjugated Antibody
For research use only