Detection of Mouse CD47 by Western Blot
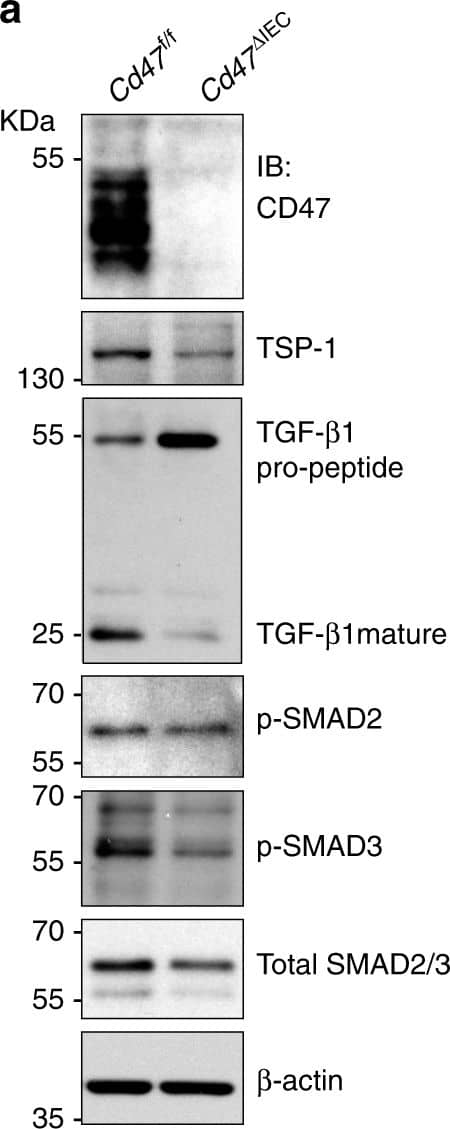
CD47 regulates thrombospondin-1, TGF-beta 1, and collagen deposition after injury. a Whole cell lysates from freshly isolated intestinal epithelial cells from Cd47f/f and Cd47 deltaIEC mice were subjected to SDS–PAGE and immunoblot for thrombospondin-1/TSP-1, TGF-beta 1, and phosphorylated SMAD2 and SMAD3. Results are representative of three independent experiments. b Representative Masson’s trichrome staining of wounds beds and chronic DSS-colitis colons from Cd47f/f and Cd47 deltaIEC mice. Scale bars = 50 μm. Results representative of three independent experiments with 5–7 mice per group. Source data are provided as a Source Data file Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31676794), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
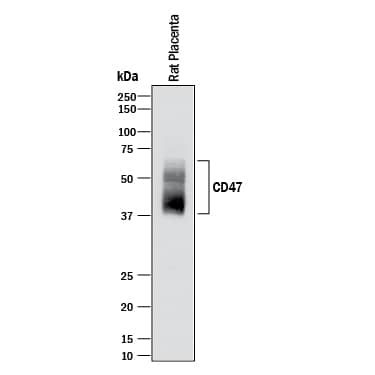
Detection of Mouse CD47 by Western Blot
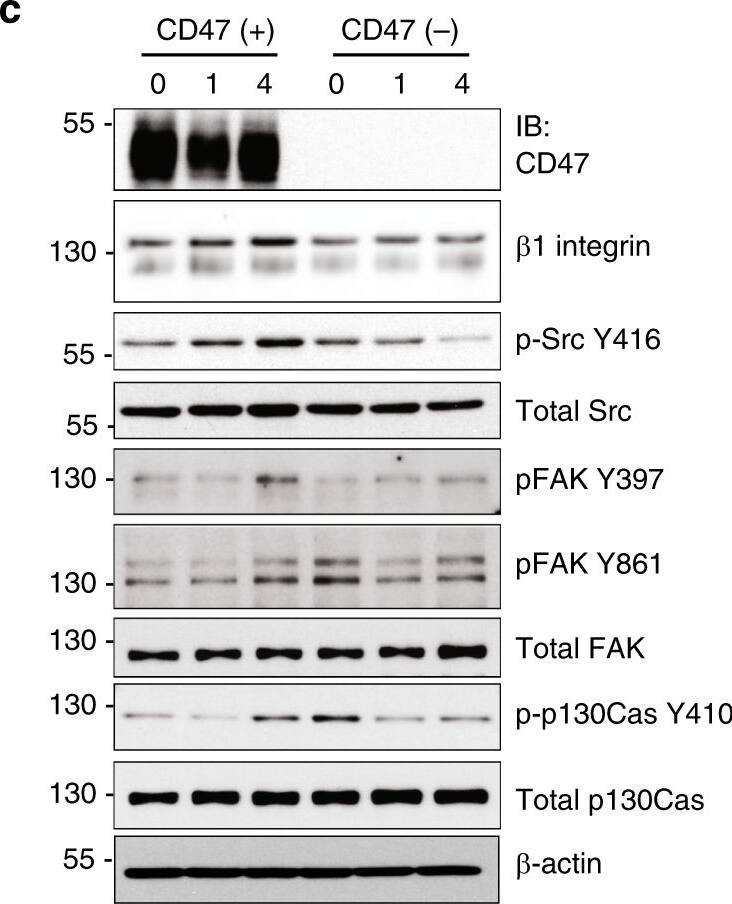
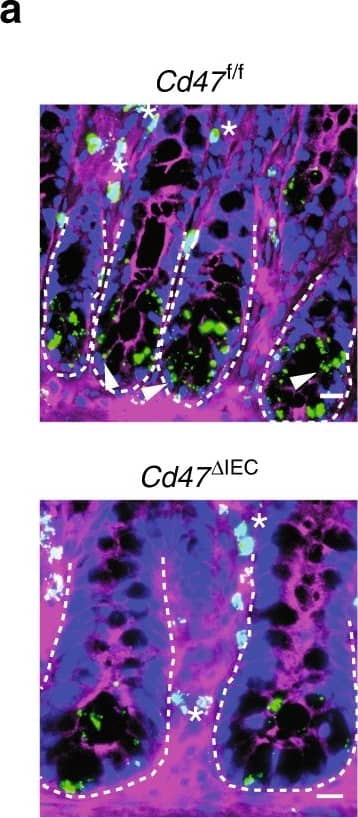
CD47 associates with beta1 integrin and promotes focal adhesion formation. a In situ proximity ligation assay utilizing antibodies against CD47 and beta1 integrin indicating close association between CD47 and beta1 integrin in the colonic epithelium. Positive PLA signals are shown in green, beta-catenin in magenta and DAPI/nuclei in blue. Crypts are indicated by dashed lines. Arrowheads and asterisks (*) indicate positive PLA signals on IECs and immune cells in the lamina propria, respectively. Strong PLA signals are detected in IECs that are mainly concentrated at the base of the crypts in Cd47f/f colon in contrast to very few PLA signals are observed in crypts IECs in Cd47 deltaIEC colons. Scale bars = 20 μm. The specificity of the PLA signals was evaluated in Supplementary figure 6 demonstrating no PLA signals in Cd47−/− colons. b Whole-cell lysates from freshly isolated intestinal epithelial cells from Cd47f/f and Cd47 deltaIEC mice were subjected to SDS–PAGE and immunoblot for signaling molecules downstream of beta1 integrin-dependent cell adhesion, revealing decreased beta1 integrin protein expression and reduced phosphorylation of SrcY416, FAKY397/Y861, and p130CASY410 in cells from Cd47 deltaIEC mice. Results are representative of three independent experiments. c Murine enteroid-derived primary epithelial cell monolayers were scratch-wounded and harvested at the indicated time points, then analyzed by SDS–PAGE and immunoblot. CD47-deficient epithelial cells show a reduction in phosphorylated SrcY416, FAKY397/Y861, and p130CASY410 upon wounding, whereas maintaining reduced beta1 integrin protein baseline expression. d Epithelial cells immediately adjacent to wounds from Cd47f/f and Cd47 deltaIEC mice were imaged by confocal microscopy, showing disrupted basal co-staining for phosphorylated FAKY861 and beta1 integrin (apical surface indicated by dashed line). Arrows indicate reduced colocalization of phospho-FAKY861 and beta1 integrin in the absence of CD47 expression. Scale bars = 10 μm. Results are representative of three independent experiments with three mice per treatment group. e Lamellipodia of CD47(−) cells exhibited fewer phosphorylated FAKY861-positive focal adhesions in comparison with CD47-expressing cells (insets). Scale bars = 10 μm. Results are representative of three independent experiments with two independently derived enteroid culture lines. Source data are provided as a Source Data file Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31676794), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Detection of Mouse CD47 by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence
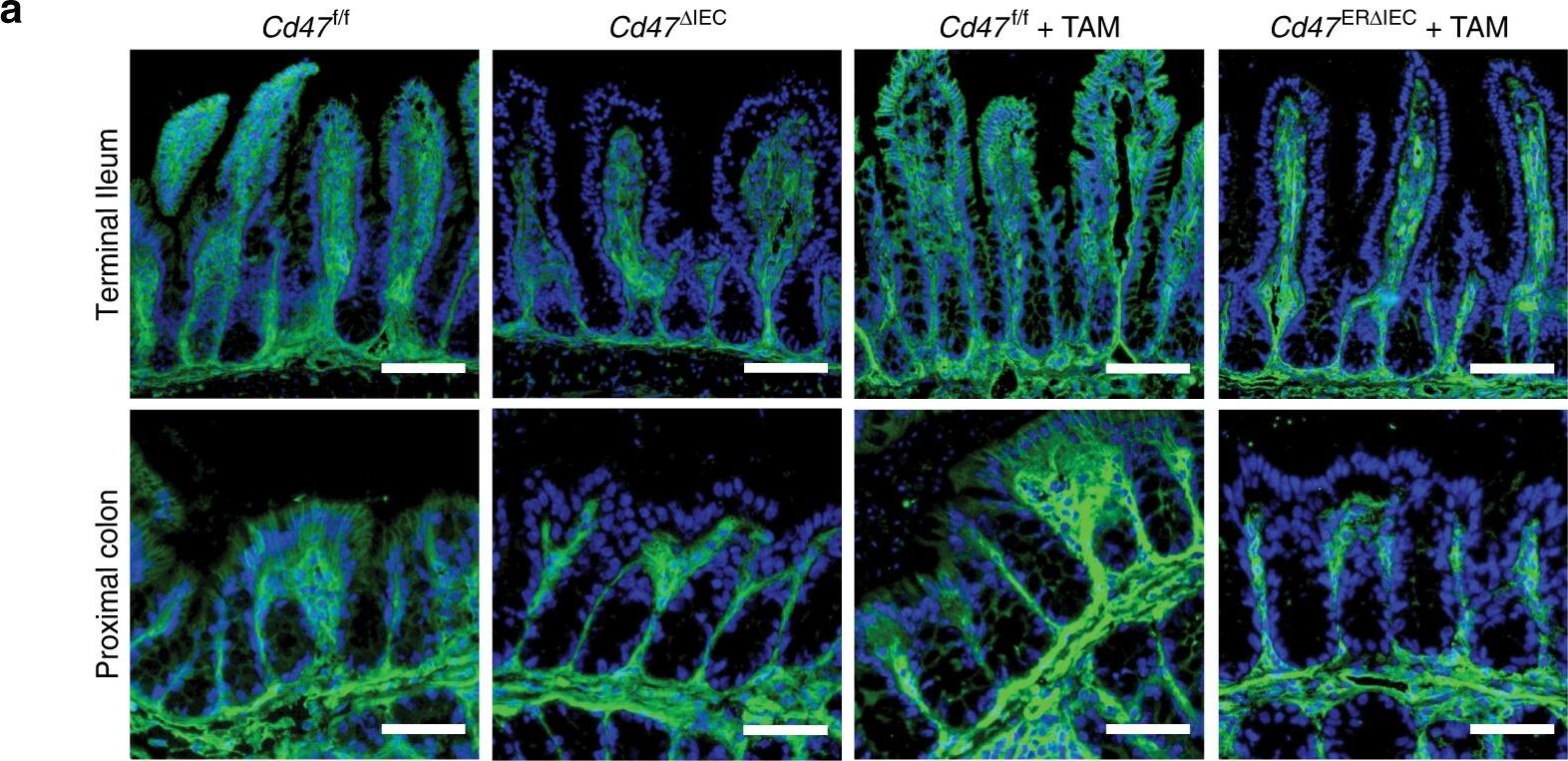
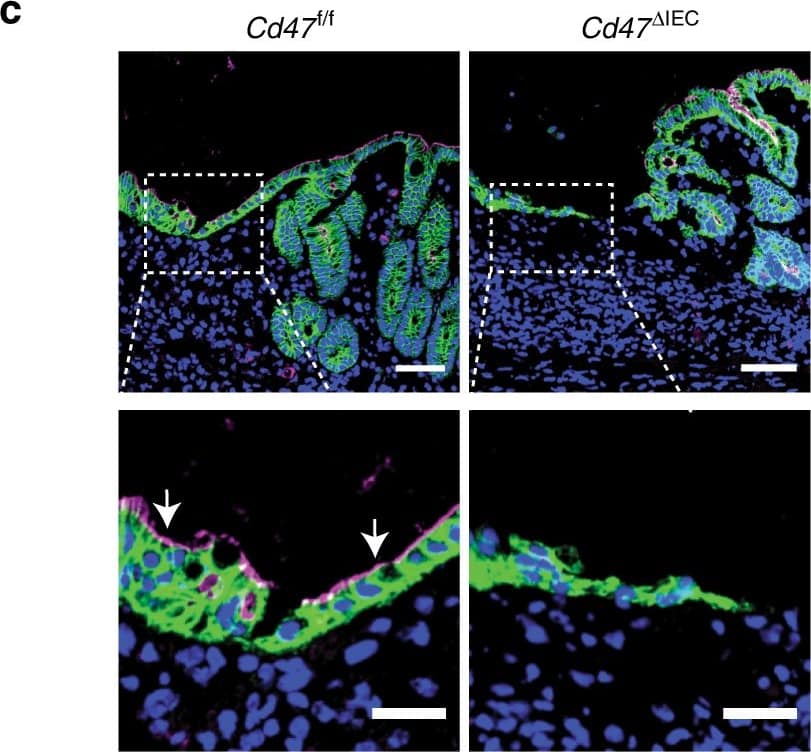
Loss of CD47 in IEC does not induce immune-mediated mucosal damage. a–c Naive Cd47 deltaIEC and tamoxifen-treated Cd47ER deltaIEC mice housed in pathogen-free conditions were analyzed for intestinal epithelial CD47 expression. Cd47ER deltaIEC mice were treated with tamoxifen to induce acute CD47 deletion in intestinal epithelial cells, and analyzed 2 weeks later. a Tissue sections from naive Cd47 deltaIEC and tamoxifen-treated Cd47ER deltaIEC mice were stained with anti-CD47 antibodies (green) with DAPI counterstain (blue). CD47 expression is absent in the epithelium but retained in the lamina propria and submucosa. Scale bars = 100 μm upper panels, 50 μm lower panels. b IECs were isolated from the terminal ileum of naive mice. Protein lysates were analyzed by SDS–PAGE and immunoblot for CD47. c IECs were isolated from Cd47ER deltaIEC mice treated with vehicle (corn oil) or tamoxifen, and analyzed as in b. Results are representative of three independent experiments with 3–5 mice per group. d Paraffin-embedded colon tissue sections from Cd47 deltaIEC mice were stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin counterstain for histological examination. Gross mucosal architecture is intact in the absence of epithelial CD47 expression. Scale bars = 50 μm upper panels, 100 μm lower panels. e Colon tissue digests from naive Cd47 deltaIEC mice were stained and analyzed by flow cytometry, showing no significant differences in major lamina propria immune cell populations. Points represent individual samples each containing two mice (n = 4 mice per group). Data are means ± SEM and are representative of three independent experiments. Source data are provided as a Source Data file Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31676794), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Detection of Mouse CD47 by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence
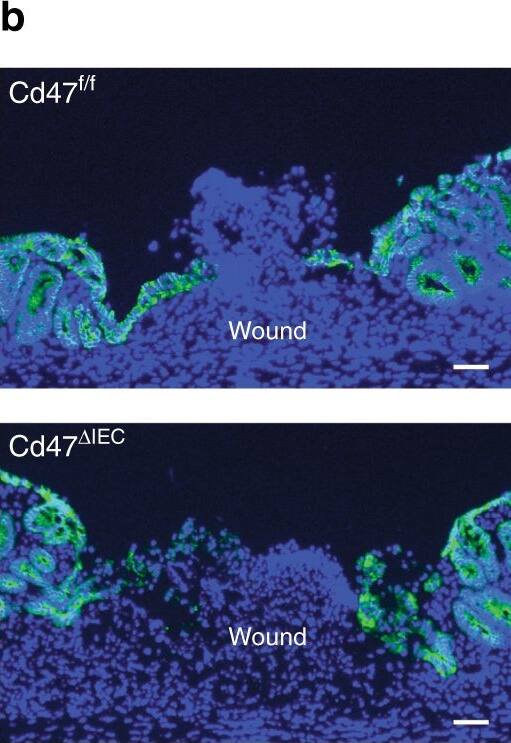
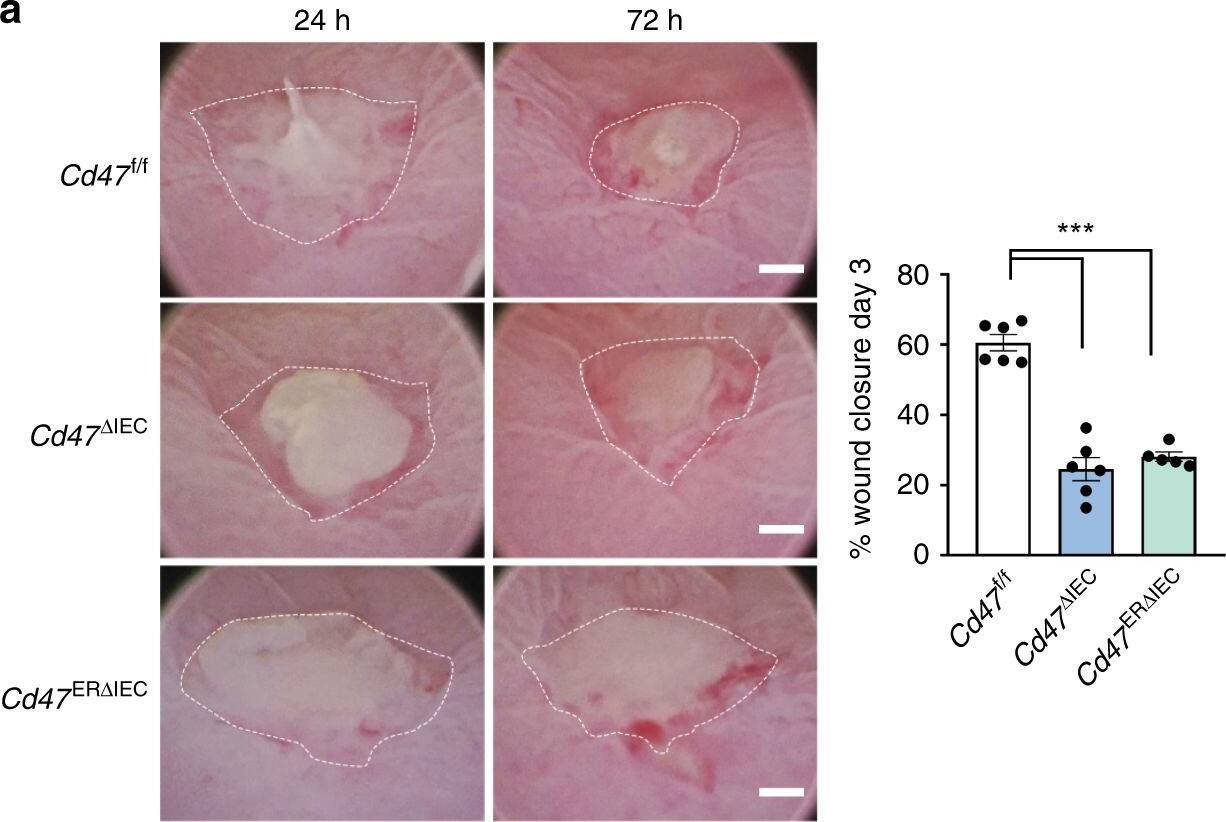
IEC-specific deletion of CD47 results in impaired mucosal healing. Utilizing a miniature video endoscope and biopsy scissors, 5–7 wounds were created in the dorsal aspect of the descending colon mucosa of anesthetized mice. Cd47ER deltaIEC mice were wounded 2 weeks after tamoxifen treatment. a Digital measurement of wound surface area at 24 and 72 h post wounding revealed a striking impairment in wound closure in Cd47 deltaIEC and tamoxifen-treated Cd47ER deltaIEC mice. Points represent mean value within all wounds from an individual mouse. Data are representative of two independent experiments with 5–6 mice per group. Data are means ± SEM. ***p < 0.001; one-way ANOVA. b Tissue sections taken from day 3 wounds were stained with the epithelial-specific marker E-Cadherin (green), plus DAPI counterstain (blue). Re-epithelialization of the wound is disorganized in the absence of CD47 (Cd47 deltaIEC) compared with control Cd47f/f. c Tissue sections taken from day 3 wounds were stained with the epithelial-specific marker E-Cadherin (green), brush border protein Villin (magenta), and DAPI (blue). Insets of epithelial cells on top of the wound bed show polarized wound-associated epithelial cells (WAE) expressing Villin (arrows) in Cd47f/f wounds while cells are not polarized in Cd47 deltaIEC wounds. Scale bars = 100 μm. d Ki67 staining of frozen sections of wounded colon mucosa 3 days post-wounding (red) revealed similar proliferation rates in crypt epithelial cells immediately adjacent to wounds in the absence of epithelial CD47. Sections were counterstained with E-Cadherin (green) and DAPI (blue). Scale bars = 50 μm. Points represent the average number of Ki67-positive cells for four crypts adjacent to wounds for each individual mouse. Data are means ± SEM and are representative of two independent experiments with 4–6 mice per group. Source data are provided as a Source Data file Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31676794), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Detection of Mouse CD47 by Western Blot
CD47 associates with beta1 integrin and promotes focal adhesion formation. a In situ proximity ligation assay utilizing antibodies against CD47 and beta1 integrin indicating close association between CD47 and beta1 integrin in the colonic epithelium. Positive PLA signals are shown in green, beta-catenin in magenta and DAPI/nuclei in blue. Crypts are indicated by dashed lines. Arrowheads and asterisks (*) indicate positive PLA signals on IECs and immune cells in the lamina propria, respectively. Strong PLA signals are detected in IECs that are mainly concentrated at the base of the crypts in Cd47f/f colon in contrast to very few PLA signals are observed in crypts IECs in Cd47 deltaIEC colons. Scale bars = 20 μm. The specificity of the PLA signals was evaluated in Supplementary figure 6 demonstrating no PLA signals in Cd47−/− colons. b Whole-cell lysates from freshly isolated intestinal epithelial cells from Cd47f/f and Cd47 deltaIEC mice were subjected to SDS–PAGE and immunoblot for signaling molecules downstream of beta1 integrin-dependent cell adhesion, revealing decreased beta1 integrin protein expression and reduced phosphorylation of SrcY416, FAKY397/Y861, and p130CASY410 in cells from Cd47 deltaIEC mice. Results are representative of three independent experiments. c Murine enteroid-derived primary epithelial cell monolayers were scratch-wounded and harvested at the indicated time points, then analyzed by SDS–PAGE and immunoblot. CD47-deficient epithelial cells show a reduction in phosphorylated SrcY416, FAKY397/Y861, and p130CASY410 upon wounding, whereas maintaining reduced beta1 integrin protein baseline expression. d Epithelial cells immediately adjacent to wounds from Cd47f/f and Cd47 deltaIEC mice were imaged by confocal microscopy, showing disrupted basal co-staining for phosphorylated FAKY861 and beta1 integrin (apical surface indicated by dashed line). Arrows indicate reduced colocalization of phospho-FAKY861 and beta1 integrin in the absence of CD47 expression. Scale bars = 10 μm. Results are representative of three independent experiments with three mice per treatment group. e Lamellipodia of CD47(−) cells exhibited fewer phosphorylated FAKY861-positive focal adhesions in comparison with CD47-expressing cells (insets). Scale bars = 10 μm. Results are representative of three independent experiments with two independently derived enteroid culture lines. Source data are provided as a Source Data file Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31676794), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Detection of Mouse CD47 by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence
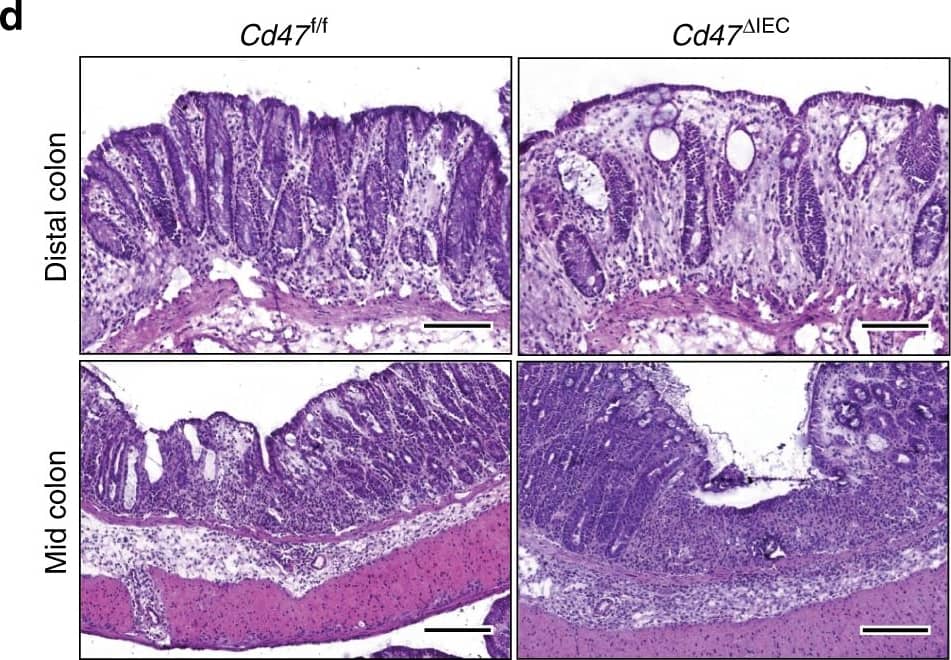
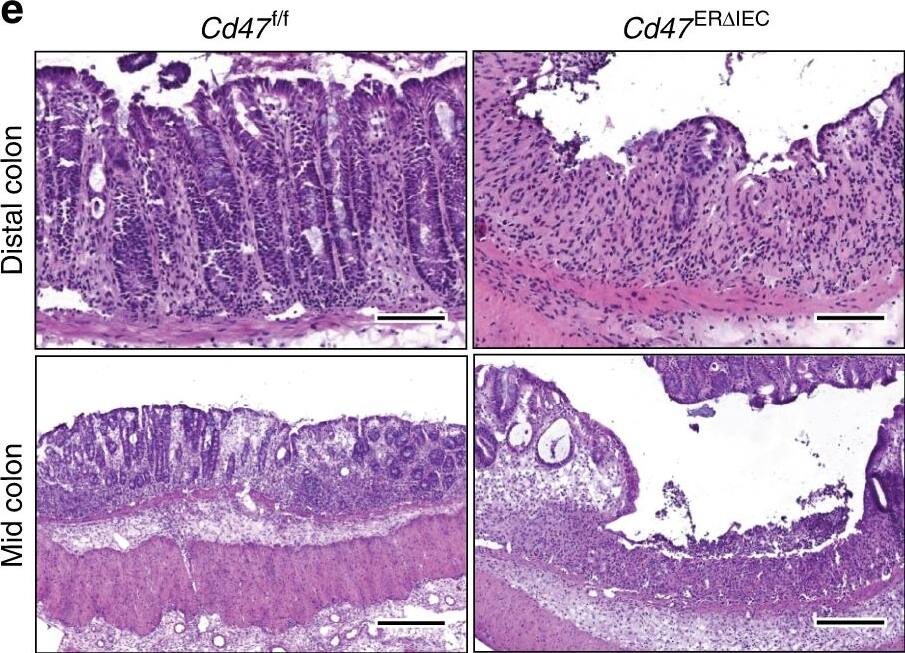
Loss of CD47 in IEC results in impaired recovery from DSS-induced colitis. Age- and sex-matched Cd47 deltaIEC and tamoxifen-treated Cd47ER deltaIEC mice were treated with three consecutive cycles of 2.5% DSS in drinking water for either 4 days (Cd47 deltaIEC) or 3 days (Cd47ER deltaIEC), followed by 5 days of water recovery. Cd47ER deltaIEC mice were treated with DSS 2 weeks after tamoxifen treatment. a–b Disease activity index scores are represented as an average of scores 0–4 for percent weight loss, stool consistency, and presence of blood in stools. Cyclical treatment of aCd47 deltaIEC and b tamoxifen-treated Cd47ER deltaIEC mice with 2.5% DSS in drinking water, followed by a plain water recovery period, induced greater DAI scores in the absence of epithelial CD47. Data are representative of two independent experiments with 5–6 mice per group and are expressed as means ± SEM. a *p = 0.02, b *p = 0.036 by two-way ANOVA. c Histological scoring of hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)-stained tissue sections of colonic mucosa: percentage of injury/ulceration represents a ratio of the length of injured/ulcerated areas (≥ 50% crypt loss) relative to the entire colon length, as assessed in Swiss roll mounts of the entire colon. Results indicate greater damage in the absence of epithelial CD47. Points represent individual mice. Data are representative of two independent experiments with 5–6 mice per group and are expressed as means ± SEM. Significance determined by two-tailed Student’s t test. *p = 0.016, ***p = 0.001. d, e Representative H&E staining of colon tissue sections after three cycles of DSS/water revealed extensive crypt destruction in distal colon of Cd47 deltaIEC and Cd47ER deltaIEC mice. Large areas of ulcerated mucosa with granulocytic infiltrates were present in the mid colon in Cd47 deltaIEC and Cd47ER deltaIEC mice, in comparison with littermate controls. Scale bars = 100 μm upper panels, 300 μm lower panels. Results are representative of at least two independent experiments with 5–6 mice per group. Source data are provided as a Source Data file Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31676794), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Detection of Mouse CD47 by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence
IEC-specific deletion of CD47 results in impaired mucosal healing. Utilizing a miniature video endoscope and biopsy scissors, 5–7 wounds were created in the dorsal aspect of the descending colon mucosa of anesthetized mice. Cd47ER deltaIEC mice were wounded 2 weeks after tamoxifen treatment. a Digital measurement of wound surface area at 24 and 72 h post wounding revealed a striking impairment in wound closure in Cd47 deltaIEC and tamoxifen-treated Cd47ER deltaIEC mice. Points represent mean value within all wounds from an individual mouse. Data are representative of two independent experiments with 5–6 mice per group. Data are means ± SEM. ***p < 0.001; one-way ANOVA. b Tissue sections taken from day 3 wounds were stained with the epithelial-specific marker E-Cadherin (green), plus DAPI counterstain (blue). Re-epithelialization of the wound is disorganized in the absence of CD47 (Cd47 deltaIEC) compared with control Cd47f/f. c Tissue sections taken from day 3 wounds were stained with the epithelial-specific marker E-Cadherin (green), brush border protein Villin (magenta), and DAPI (blue). Insets of epithelial cells on top of the wound bed show polarized wound-associated epithelial cells (WAE) expressing Villin (arrows) in Cd47f/f wounds while cells are not polarized in Cd47 deltaIEC wounds. Scale bars = 100 μm. d Ki67 staining of frozen sections of wounded colon mucosa 3 days post-wounding (red) revealed similar proliferation rates in crypt epithelial cells immediately adjacent to wounds in the absence of epithelial CD47. Sections were counterstained with E-Cadherin (green) and DAPI (blue). Scale bars = 50 μm. Points represent the average number of Ki67-positive cells for four crypts adjacent to wounds for each individual mouse. Data are means ± SEM and are representative of two independent experiments with 4–6 mice per group. Source data are provided as a Source Data file Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31676794), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Detection of Mouse CD47 by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence
CD47 associates with beta1 integrin and promotes focal adhesion formation. a In situ proximity ligation assay utilizing antibodies against CD47 and beta1 integrin indicating close association between CD47 and beta1 integrin in the colonic epithelium. Positive PLA signals are shown in green, beta-catenin in magenta and DAPI/nuclei in blue. Crypts are indicated by dashed lines. Arrowheads and asterisks (*) indicate positive PLA signals on IECs and immune cells in the lamina propria, respectively. Strong PLA signals are detected in IECs that are mainly concentrated at the base of the crypts in Cd47f/f colon in contrast to very few PLA signals are observed in crypts IECs in Cd47 deltaIEC colons. Scale bars = 20 μm. The specificity of the PLA signals was evaluated in Supplementary figure 6 demonstrating no PLA signals in Cd47−/− colons. b Whole-cell lysates from freshly isolated intestinal epithelial cells from Cd47f/f and Cd47 deltaIEC mice were subjected to SDS–PAGE and immunoblot for signaling molecules downstream of beta1 integrin-dependent cell adhesion, revealing decreased beta1 integrin protein expression and reduced phosphorylation of SrcY416, FAKY397/Y861, and p130CASY410 in cells from Cd47 deltaIEC mice. Results are representative of three independent experiments. c Murine enteroid-derived primary epithelial cell monolayers were scratch-wounded and harvested at the indicated time points, then analyzed by SDS–PAGE and immunoblot. CD47-deficient epithelial cells show a reduction in phosphorylated SrcY416, FAKY397/Y861, and p130CASY410 upon wounding, whereas maintaining reduced beta1 integrin protein baseline expression. d Epithelial cells immediately adjacent to wounds from Cd47f/f and Cd47 deltaIEC mice were imaged by confocal microscopy, showing disrupted basal co-staining for phosphorylated FAKY861 and beta1 integrin (apical surface indicated by dashed line). Arrows indicate reduced colocalization of phospho-FAKY861 and beta1 integrin in the absence of CD47 expression. Scale bars = 10 μm. Results are representative of three independent experiments with three mice per treatment group. e Lamellipodia of CD47(−) cells exhibited fewer phosphorylated FAKY861-positive focal adhesions in comparison with CD47-expressing cells (insets). Scale bars = 10 μm. Results are representative of three independent experiments with two independently derived enteroid culture lines. Source data are provided as a Source Data file Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31676794), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Detection of Mouse CD47 by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence
Loss of CD47 in IEC results in impaired recovery from DSS-induced colitis. Age- and sex-matched Cd47 deltaIEC and tamoxifen-treated Cd47ER deltaIEC mice were treated with three consecutive cycles of 2.5% DSS in drinking water for either 4 days (Cd47 deltaIEC) or 3 days (Cd47ER deltaIEC), followed by 5 days of water recovery. Cd47ER deltaIEC mice were treated with DSS 2 weeks after tamoxifen treatment. a–b Disease activity index scores are represented as an average of scores 0–4 for percent weight loss, stool consistency, and presence of blood in stools. Cyclical treatment of aCd47 deltaIEC and b tamoxifen-treated Cd47ER deltaIEC mice with 2.5% DSS in drinking water, followed by a plain water recovery period, induced greater DAI scores in the absence of epithelial CD47. Data are representative of two independent experiments with 5–6 mice per group and are expressed as means ± SEM. a *p = 0.02, b *p = 0.036 by two-way ANOVA. c Histological scoring of hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)-stained tissue sections of colonic mucosa: percentage of injury/ulceration represents a ratio of the length of injured/ulcerated areas (≥ 50% crypt loss) relative to the entire colon length, as assessed in Swiss roll mounts of the entire colon. Results indicate greater damage in the absence of epithelial CD47. Points represent individual mice. Data are representative of two independent experiments with 5–6 mice per group and are expressed as means ± SEM. Significance determined by two-tailed Student’s t test. *p = 0.016, ***p = 0.001. d, e Representative H&E staining of colon tissue sections after three cycles of DSS/water revealed extensive crypt destruction in distal colon of Cd47 deltaIEC and Cd47ER deltaIEC mice. Large areas of ulcerated mucosa with granulocytic infiltrates were present in the mid colon in Cd47 deltaIEC and Cd47ER deltaIEC mice, in comparison with littermate controls. Scale bars = 100 μm upper panels, 300 μm lower panels. Results are representative of at least two independent experiments with 5–6 mice per group. Source data are provided as a Source Data file Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31676794), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Detection of Mouse CD47 by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence
IEC-specific deletion of CD47 results in impaired mucosal healing. Utilizing a miniature video endoscope and biopsy scissors, 5–7 wounds were created in the dorsal aspect of the descending colon mucosa of anesthetized mice. Cd47ER deltaIEC mice were wounded 2 weeks after tamoxifen treatment. a Digital measurement of wound surface area at 24 and 72 h post wounding revealed a striking impairment in wound closure in Cd47 deltaIEC and tamoxifen-treated Cd47ER deltaIEC mice. Points represent mean value within all wounds from an individual mouse. Data are representative of two independent experiments with 5–6 mice per group. Data are means ± SEM. ***p < 0.001; one-way ANOVA. b Tissue sections taken from day 3 wounds were stained with the epithelial-specific marker E-Cadherin (green), plus DAPI counterstain (blue). Re-epithelialization of the wound is disorganized in the absence of CD47 (Cd47 deltaIEC) compared with control Cd47f/f. c Tissue sections taken from day 3 wounds were stained with the epithelial-specific marker E-Cadherin (green), brush border protein Villin (magenta), and DAPI (blue). Insets of epithelial cells on top of the wound bed show polarized wound-associated epithelial cells (WAE) expressing Villin (arrows) in Cd47f/f wounds while cells are not polarized in Cd47 deltaIEC wounds. Scale bars = 100 μm. d Ki67 staining of frozen sections of wounded colon mucosa 3 days post-wounding (red) revealed similar proliferation rates in crypt epithelial cells immediately adjacent to wounds in the absence of epithelial CD47. Sections were counterstained with E-Cadherin (green) and DAPI (blue). Scale bars = 50 μm. Points represent the average number of Ki67-positive cells for four crypts adjacent to wounds for each individual mouse. Data are means ± SEM and are representative of two independent experiments with 4–6 mice per group. Source data are provided as a Source Data file Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31676794), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Detection of Mouse CD47 by Immunohistochemistry
IEC-specific deletion of CD47 results in impaired mucosal healing. Utilizing a miniature video endoscope and biopsy scissors, 5–7 wounds were created in the dorsal aspect of the descending colon mucosa of anesthetized mice. Cd47ER deltaIEC mice were wounded 2 weeks after tamoxifen treatment. a Digital measurement of wound surface area at 24 and 72 h post wounding revealed a striking impairment in wound closure in Cd47 deltaIEC and tamoxifen-treated Cd47ER deltaIEC mice. Points represent mean value within all wounds from an individual mouse. Data are representative of two independent experiments with 5–6 mice per group. Data are means ± SEM. ***p < 0.001; one-way ANOVA. b Tissue sections taken from day 3 wounds were stained with the epithelial-specific marker E-Cadherin (green), plus DAPI counterstain (blue). Re-epithelialization of the wound is disorganized in the absence of CD47 (Cd47 deltaIEC) compared with control Cd47f/f. c Tissue sections taken from day 3 wounds were stained with the epithelial-specific marker E-Cadherin (green), brush border protein Villin (magenta), and DAPI (blue). Insets of epithelial cells on top of the wound bed show polarized wound-associated epithelial cells (WAE) expressing Villin (arrows) in Cd47f/f wounds while cells are not polarized in Cd47 deltaIEC wounds. Scale bars = 100 μm. d Ki67 staining of frozen sections of wounded colon mucosa 3 days post-wounding (red) revealed similar proliferation rates in crypt epithelial cells immediately adjacent to wounds in the absence of epithelial CD47. Sections were counterstained with E-Cadherin (green) and DAPI (blue). Scale bars = 50 μm. Points represent the average number of Ki67-positive cells for four crypts adjacent to wounds for each individual mouse. Data are means ± SEM and are representative of two independent experiments with 4–6 mice per group. Source data are provided as a Source Data file Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31676794), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.