Mouse Thrombomodulin/BDCA-3 APC-conjugated Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # FAB3894A

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Applications
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Leu17-Ser517
Accession # P15306
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Mouse Thrombomodulin/BDCA-3 APC-conjugated Antibody
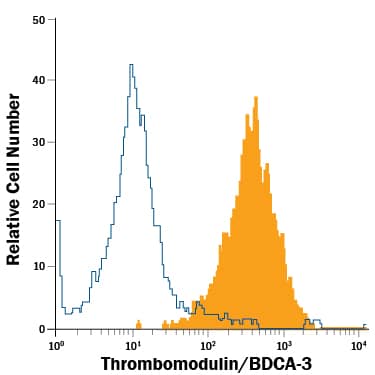
Detection of Thrombomodulin/BDCA‑3 in bEnd.3 Mouse Cell Line by Flow Cytometry.
bEnd.3 mouse endothelioma cell line was stained with Rat Anti-Mouse Thrombomodulin/BDCA-3 APC-conjugated Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # FAB3894A, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (Catalog # IC013A, open histogram). View our protocol for Staining Membrane-associated Proteins.Applications for Mouse Thrombomodulin/BDCA-3 APC-conjugated Antibody
Flow Cytometry
Sample: bEnd.3 mouse endothelioma cell line
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
Background: Thrombomodulin/BDCA-3
Encoded by the THBD gene, Thrombomodulin is also known as CD141 antigen. The deduced amino acid (aa) sequence of mouse THBD predicts a signal peptide (aa 1 to 16) and a mature chain (aa 17 to 577) that consists of the following domains: C-type lectin (aa 31 to 167), EGF-like (aa 240 to 280, aa 283 to 323, aa 324 to 362, aa 364 to 404, aa 405 to 439, and aa 440 to 480), transmembrane (aa 518 to 541) and cytoplasmic (aa 542 to 577) (1). Predominantly synthesized by vascular endothelial cells, THBD inhibits coagulation and fibrinolysis (2‑4). It functions as a cell surface receptor and an essential cofactor for active thrombin, which in turn activates protein C and thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor (TAFI), also known as carboxypeptidase B2 (CPB2). Activated protein C (APC), facilitated by protein S, degrades coagulation factors Va and VIIIa, which are required for thrombin activation. Activated CPB2 cleaves basic C-terminal amino acid residues from its substrates, including fibrin, preventing the conversion of plasminogen to plasmin. In addition, THBD gene polymorphisms are associated with human disease and THBD plays a role in thrombosis, stroke, arteriosclerosis, and cancer (5). For example, increased serum levels of THBD, due to protease cleavage, have been associated with smoking, atherosclerosis, liver cirrhosis, diabetes mellitus, cerebral and myocardial infarction, and multiple sclerosis (6). Over aa 17-517, mouse Thrombomodulin shares 84% and 66% aa sequence identity with rat and human thrombomoduli, respectively.
References
- Dittman, W.A. and P.W. Majerus (1989) Nucleic Acids Res. 17:802.
- Van de Wouwer, M. et al. (2004) Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 24:1374.
- Wu, K.K. et al. (2000) Ann Med. 32:73.
- Li, Y.H. et al. (2006) Cardiovasc. Hematol. Agents Med. Chem. 4:183.
- Weiler, H. and B.H. Isermann (2003) J. Thromb. Haemost. 1:1515.
- Califano, F. et al. (2000) Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 4:59.
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional Thrombomodulin/BDCA-3 Products
Product Documents for Mouse Thrombomodulin/BDCA-3 APC-conjugated Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Mouse Thrombomodulin/BDCA-3 APC-conjugated Antibody
For research use only