Mouse IL-1 beta/IL-1F2 DuoSet ELISA Best Seller
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # DY401

Key Product Details
Assay Type
Assay Range
Sample Type
Note: Diluents for complex matrices, such as serum and plasma, should be evaluated prior to use in this DuoSet
Reactivity
Mouse IL-1 beta/IL-1F2 DuoSet ELISA Features
- Optimized capture and detection antibody pairings with recommended concentrations save lengthy development time
- Development protocols are provided to guide further assay optimization
- Assay can be customized to your specific needs
- Economical alternative to complete kits
Product Summary for Mouse IL-1 beta/IL-1F2 DuoSet ELISA
This DuoSet ELISA Development kit contains the basic components required for the development of sandwich ELISAs to measure natural and recombinant mouse IL-1 beta/IL-1F2. The suggested diluent is suitable for the analysis of most cell culture supernate samples. Diluents for complex matrices, such as serum and plasma, should be evaluated prior to use in this DuoSet.
Product Specifications
Assay Format
Sample Volume Required
Detection Method
Conjugate
Specificity
Label
Scientific Data Images for Mouse IL-1 beta/IL-1F2 DuoSet ELISA
Mouse IL-1 beta / IL-1F2 ELISA Standard Curve
Detection of Mouse IL-1 beta/IL-1F2 by ELISA
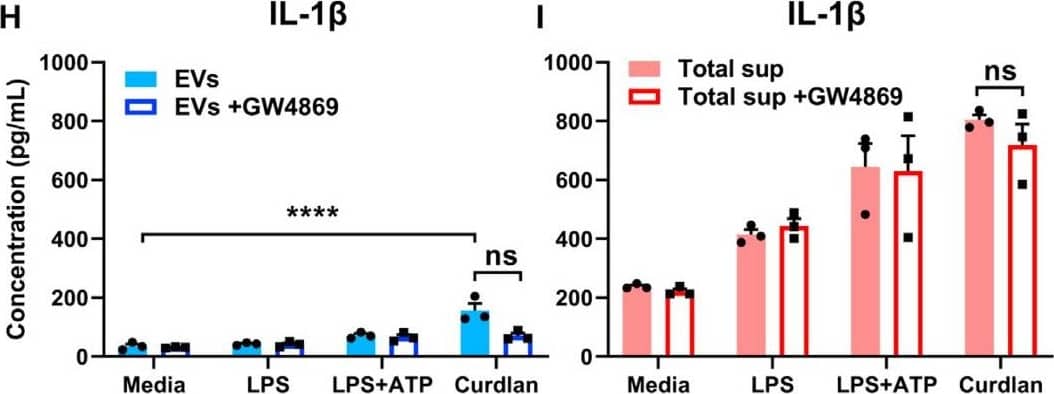
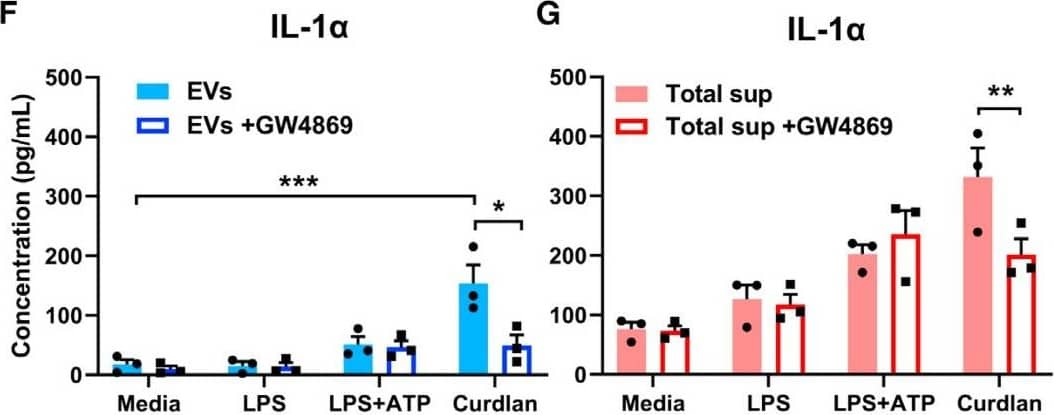
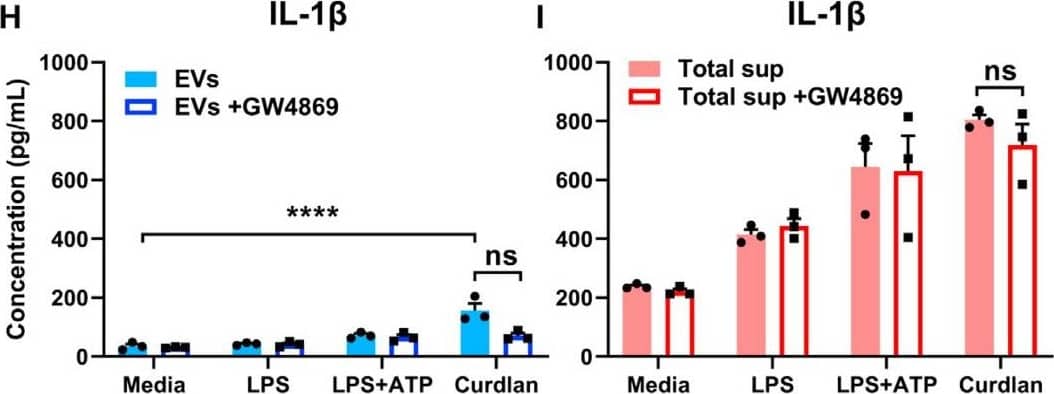
Exosomal release of IL-1 alpha by neutrophils(A) Representative confocal images of peritoneal neutrophils stimulated with LPS or curdlan for 6 h.(B) Quantification of IL-1 alpha and CD63 co-localization using ImageJ (each data point represents a single cell).(C) NTA of EV size distribution and concentration.(D–G) Neutrophils were stimulated in the presence of exosome inhibitor GW4869, and IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta were quantified by ELISA in isolated EVs following lysis (D and F) and in total cell-free supernatants (E and G).(H) Inhibition of EV secretion shown by NTA.(I) Bioactive IL-1 signaling through IL-1R1 reporter cells was measured in isolated exosomes in the absence of detergent lysis (n = 4). Neutralizing antibodies (Abs) to IL-1 alpha, IL-1 beta, or both cytokines were included in the reporter assay, and bioactive cytokine concentration was calculated based on a standard curve using recombinant IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta.Two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. Experiments in (A) and (B) were repeated three times; (C)–(G) are biological replicates from repeat experiments. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34010648), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Detection of Mouse IL-1 beta/IL-1F2 by ELISA
Exosomal release of IL-1 alpha by neutrophils(A) Representative confocal images of peritoneal neutrophils stimulated with LPS or curdlan for 6 h.(B) Quantification of IL-1 alpha and CD63 co-localization using ImageJ (each data point represents a single cell).(C) NTA of EV size distribution and concentration.(D–G) Neutrophils were stimulated in the presence of exosome inhibitor GW4869, and IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta were quantified by ELISA in isolated EVs following lysis (D and F) and in total cell-free supernatants (E and G).(H) Inhibition of EV secretion shown by NTA.(I) Bioactive IL-1 signaling through IL-1R1 reporter cells was measured in isolated exosomes in the absence of detergent lysis (n = 4). Neutralizing antibodies (Abs) to IL-1 alpha, IL-1 beta, or both cytokines were included in the reporter assay, and bioactive cytokine concentration was calculated based on a standard curve using recombinant IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta.Two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. Experiments in (A) and (B) were repeated three times; (C)–(G) are biological replicates from repeat experiments. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34010648), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Kit Contents for Mouse IL-1 beta/IL-1F2 DuoSet ELISA
- Capture Antibody
- Detection Antibody
- Recombinant Standard
- Streptavidin conjugated to horseradish-peroxidase (Streptavidin-HRP)
Other Reagents Required
DuoSet Ancillary Reagent Kit 2 (5 plates): (Catalog # DY008) containing 96 well microplates, plate sealers, substrate solution, stop solution, plate coating buffer (PBS), wash buffer, and Reagent Diluent Concentrate 2.
The components listed above may be purchased separately:
PBS: (Catalog # DY006), or 137 mM NaCl, 2.7 mM KCl, 8.1 mM Na2HPO4, 1.5 mM KH2PO4, pH 7.2 - 7.4, 0.2 µm filtered
Wash Buffer: (Catalog # WA126), or 0.05% Tween® 20 in PBS, pH 7.2-7.4
Reagent Diluent: (Catalog # DY995), or 1% BSA in PBS, pH 7.2-7.4, 0.2 µm filtered
Substrate Solution: 1:1 mixture of Color Reagent A (H2O2) and Color Reagent B (Tetramethylbenzidine) (Catalog # DY999)
Stop Solution: 2 N H2SO4 (Catalog # DY994)
Microplates: R&D Systems (Catalog # DY990)
Plate Sealers: ELISA Plate Sealers (Catalog # DY992)
Preparation and Storage
Shipping
Stability & Storage
Background: IL-1 beta/IL-1F2
Long Name
Alternate Names
Entrez Gene IDs
Gene Symbol
Additional IL-1 beta/IL-1F2 Products
Product Documents for Mouse IL-1 beta/IL-1F2 DuoSet ELISA
Product Specific Notices for Mouse IL-1 beta/IL-1F2 DuoSet ELISA
For research use only