Recombinant Cynomolgus Monkey SIRP alpha/CD172a Protein, CF
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # 9519-SA

Key Product Details
Product Specifications
Source
Mouse myeloma cell line, NS0-derived cynomolgus monkey SIRP alpha/CD172a protein
Gly27 & Glu31-Arg369, with a C-terminal 6-His tag
Gly27 & Glu31-Arg369, with a C-terminal 6-His tag
Purity
>95%, by SDS-PAGE visualized with Silver Staining and quantitative densitometry by Coomassie® Blue Staining.
Endotoxin Level
<0.10 EU per 1 μg of the protein by the LAL method.
N-terminal Sequence Analysis
Gly27, Glu31
Predicted Molecular Mass
38 kDa
SDS-PAGE
52-67 kDa, reducing conditions
Activity
Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA.
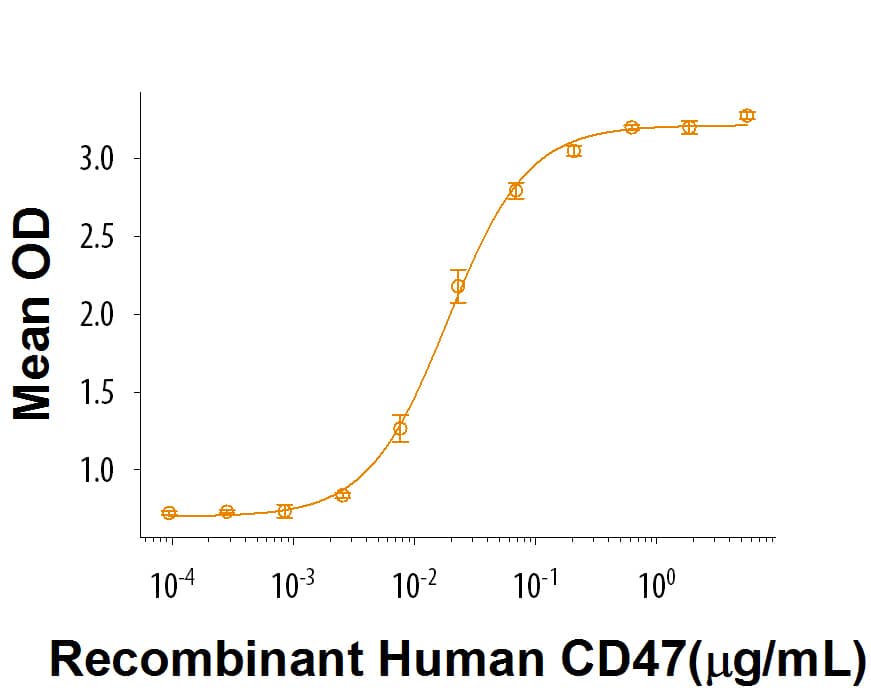
When Recombinant Cynomolgus Monkey SIRP alpha/CD172a is coated at 2 μg/mL, 100 μL/well, Recombinant Human CD47 Fc Chimera (Catalog # 4670-CD) binds with an ED50 of 10-60 ng/mL.
When Recombinant Cynomolgus Monkey SIRP alpha/CD172a is coated at 2 μg/mL, 100 μL/well, Recombinant Human CD47 Fc Chimera (Catalog # 4670-CD) binds with an ED50 of 10-60 ng/mL.
Scientific Data Images for Recombinant Cynomolgus Monkey SIRP alpha/CD172a Protein, CF
Recombinant Cynomolgus Monkey SIRP alpha/CD172a Protein Bioactivity
When Recombinant Cynomolgus Monkey SIRPa/CD172a (Catalog # 9519-SA) is immobilized at 2 µg/mL, 100 µL/well, Recombinant Human CD47 Fc Chimera (Catalog # 4670-CD) binds with an ED50 of 10-60 ng/mL.Formulation, Preparation and Storage
9519-SA
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS. |
| Reconstitution |
Reconstitute at 1 mg/mL in PBS.
|
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage |
Background: SIRP alpha/CD172a
References
- Barclay, A.N. & M.H. Brown (2006) Nat. Rev. Immunol. 6:457.
- vanBeek, E.M. et al. (2005) J. Immunol. 175:7781.
- Liu, Y. et al. (2005) J. Biol. Chem. 280:36132.
- Kharitonenkov, A. et al. (1997) Nature 386:181.
- Swissprot Accession # P7832.
- Miyashita, M. et al. (2004) Mol. Biol. Cell 15:3950.
- Wang, X.X. & K.H. Pfenninger (2005) J. Cell Sci. 119:172.
- Maile, L.A. et al. (2003) Mol. Biol. Cell 14:3519.
- Johansen, M.L. & E.J. Brown (2007) J. Biol. Chem. 282:24219.
- Takenaka, K. et al. (2007) Nat. Immunol. 8:1313.
- Ishikawa-Sekigami, T. et al. (2006) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 343:1197.
- Olsson, M. et al. (2005) Blood 105:3577.
- Ide, K. et al. (2007) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104:5062.
- Gardai, S.J. et al. (2003) Cell 115:13.
- Lundberg, P. et al. (2007) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 352:444.
Long Name
Signal-regulatory Protein alpha
Alternate Names
BIT, CD172a, MFR, MYD-1, SHPS1, SIRPA
Entrez Gene IDs
Gene Symbol
SIRPA
UniProt
Additional SIRP alpha/CD172a Products
Product Documents for Recombinant Cynomolgus Monkey SIRP alpha/CD172a Protein, CF
Product Specific Notices for Recombinant Cynomolgus Monkey SIRP alpha/CD172a Protein, CF
For research use only
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...