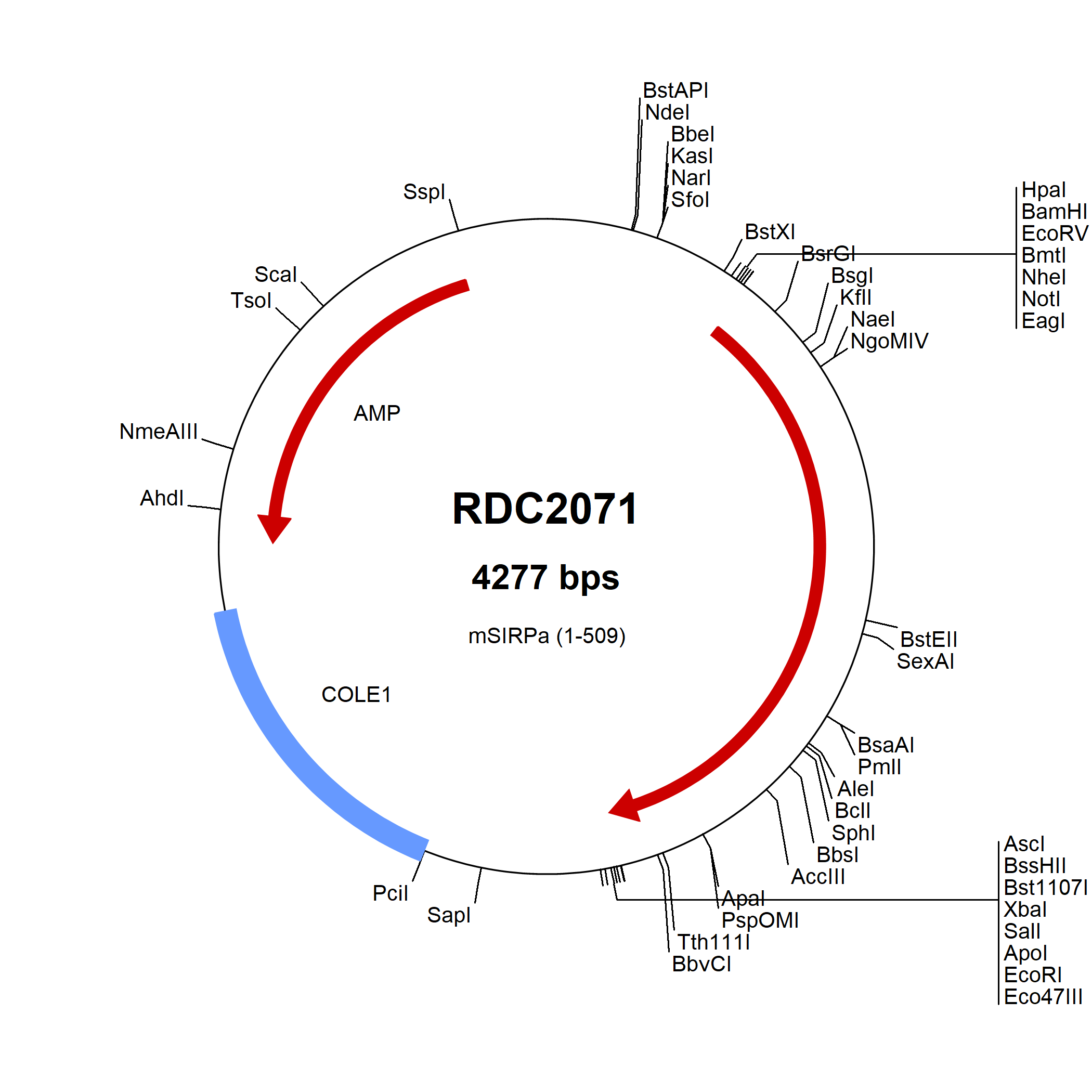
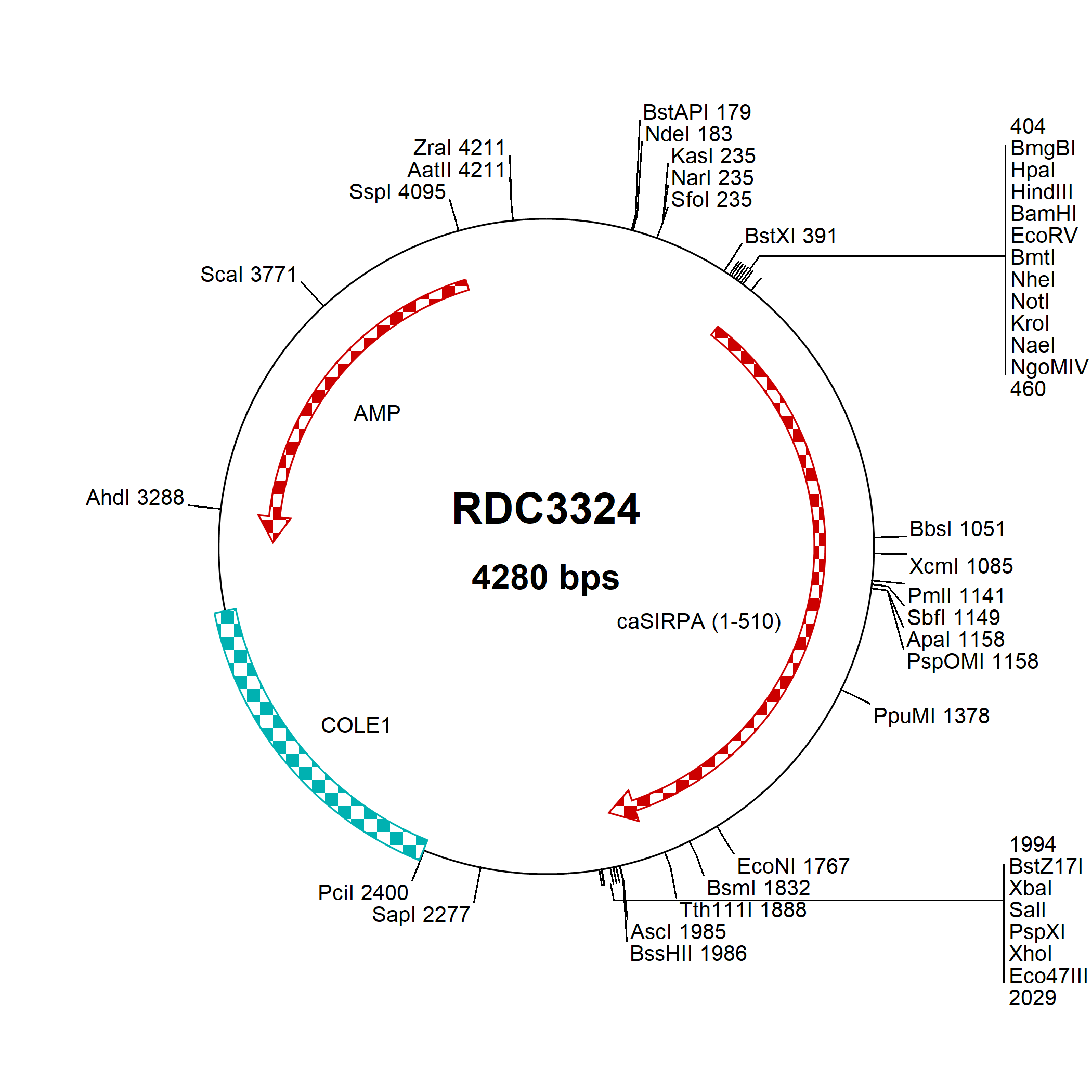
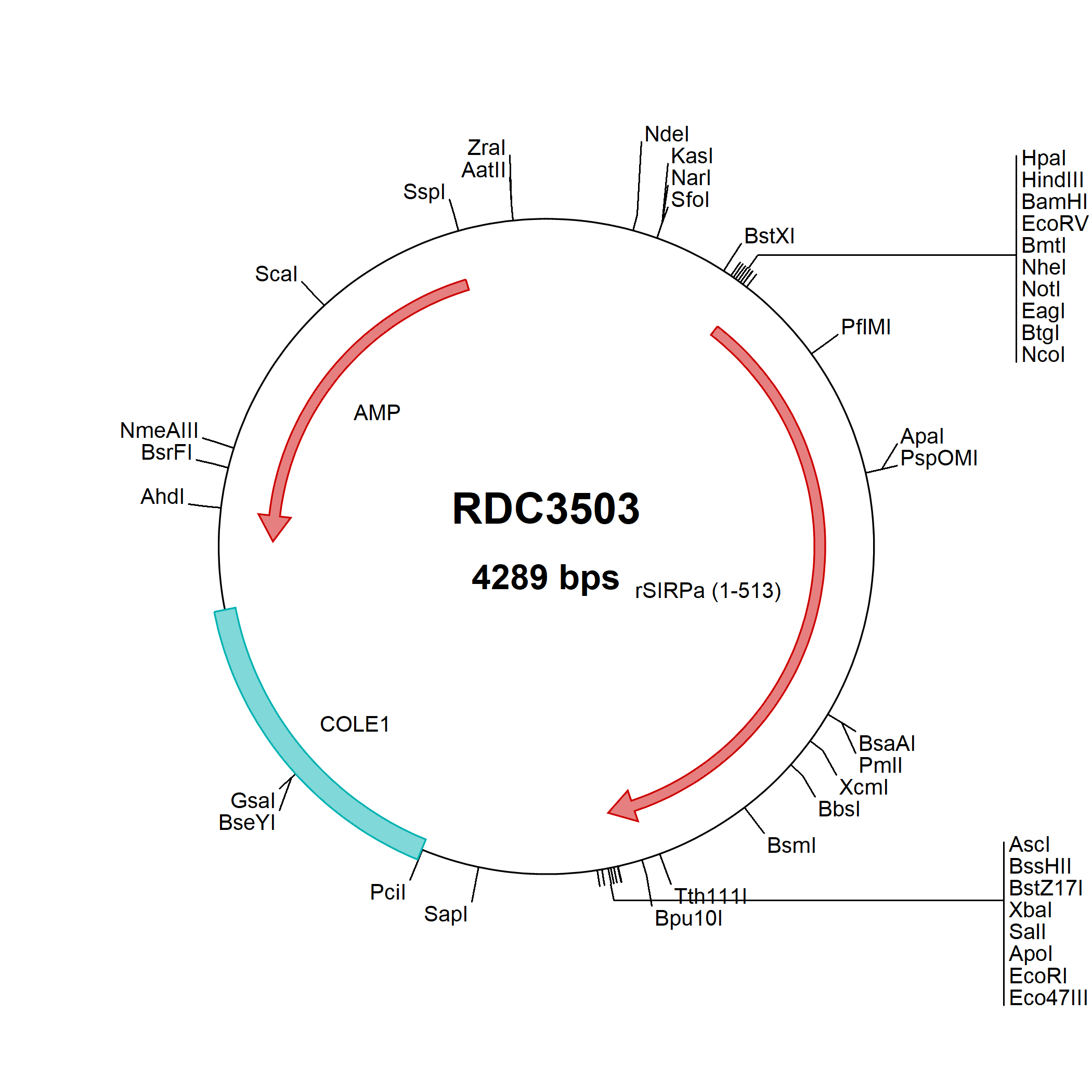
SIRP alpha/CD172a: cDNA Clones
Signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRP alpha, designated CD172a), also called SHPS-1 (SHP substrate 1), BIT (Brain Ig-like molecule with Tyrosine-based activation motifs) and previously, MyD-1 (Myeloid/Dendritic-1), is a transmembrane glycoprotein belonging to the SIRP/SHPS (CD172) family within the immunoglobulin superfamily. SIRP alpha contains cytoplasmic ITIM domains and produces negative regulatory signals. Through adhesion to CD47/IAP (integrin-associated protein), SIRP alpha inhibits clearance of CD47high young erythrocytes and platelets and promotes macrophage fusion during osteoclastogenesis. SIRP alpha recognition of surfactants SP-A and SP-D in the lung can inhibit alveolar macrophage cytokine production.
6 results for "SIRP alpha/CD172a cDNA Clones" in Products
6 results for "SIRP alpha/CD172a cDNA Clones" in Products
SIRP alpha/CD172a: cDNA Clones
Signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRP alpha, designated CD172a), also called SHPS-1 (SHP substrate 1), BIT (Brain Ig-like molecule with Tyrosine-based activation motifs) and previously, MyD-1 (Myeloid/Dendritic-1), is a transmembrane glycoprotein belonging to the SIRP/SHPS (CD172) family within the immunoglobulin superfamily. SIRP alpha contains cytoplasmic ITIM domains and produces negative regulatory signals. Through adhesion to CD47/IAP (integrin-associated protein), SIRP alpha inhibits clearance of CD47high young erythrocytes and platelets and promotes macrophage fusion during osteoclastogenesis. SIRP alpha recognition of surfactants SP-A and SP-D in the lung can inhibit alveolar macrophage cytokine production.