Recombinant Human Dkk-1 Biotinylated Protein
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # BT5439

Key Product Details
Source
Accession #
Structure / Form
Conjugate
Applications
Product Specifications
Source
Thr32-His266
Purity
Endotoxin Level
N-terminal Sequence Analysis
Predicted Molecular Mass
SDS-PAGE
Activity
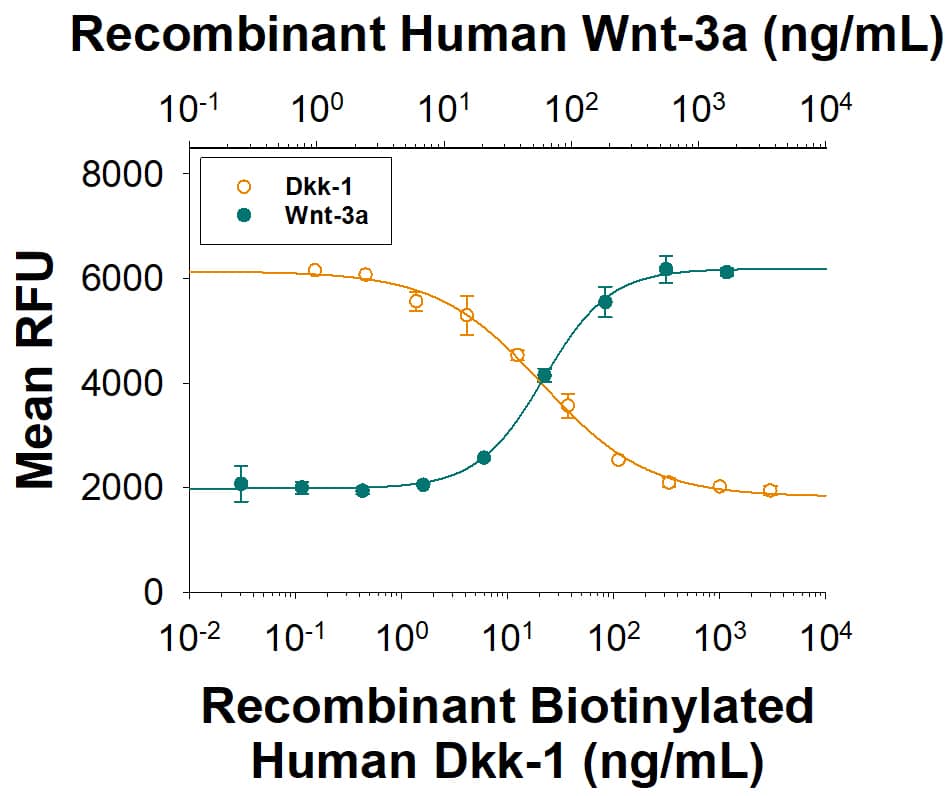
Biotinylated Recombinant Human Dkk-1 (Catalog # BT5439) inhibits a constant dose of 500 ng/mL of Recombinant Human Wnt‑3a (Catalog # 5036-WN). The ED50 for this effect is 10-60 ng/mL.
Scientific Data Images for Recombinant Human Dkk-1 Biotinylated Protein
Recombinant Human Dkk-1 Biotinylated Protein Bioactivity
Recombinant Human Wnt-3a (Catalog # 5036-WN) induces a dose responsive increase in Wnt reporter activity in HEK293 cells (green circles). Recombinant Biotinylated Human Dkk-1 (Catalog # BT5439) inhibits a constant dose of 500 ng/mL of Recombinant Human Wnt-3a. The ED50 for this effect is 10-60 ng/mL (orange circles).Formulation, Preparation and Storage
Carrier Free
What does CF mean?CF stands for Carrier Free (CF). We typically add Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a carrier protein to our recombinant proteins. Adding a carrier protein enhances protein stability, increases shelf-life, and allows the recombinant protein to be stored at a more dilute concentration. The carrier free version does not contain BSA.
What formulation is right for me?In general, we advise purchasing the recombinant protein with BSA for use in cell or tissue culture, or as an ELISA standard. In contrast, the carrier free protein is recommended for applications, in which the presence of BSA could interfere.
Carrier: BT5439
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS with BSA as a carrier protein. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 100 μg/mL in PBS containing at least 0.1% human or bovine serum albumin. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Carrier Free: BT5439/CF
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 100 μg/mL in PBS. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Background: Dkk-1
Dickkopf related protein 1 (Dkk-1) is the founding member of the Dickkopf family of proteins that includes Dkk-1, -2, -3, -4, and a related protein, Soggy (1, 2). Dkk proteins are secreted proteins that contain two conserved cysteine-rich domains (CRDs) separated by a linker region. Each domain contains ten cysteine residues (1-3). Mature human Dkk-1 is a 40 kDa glycosylated protein that shares 83% amino acid sequence identity with mouse and rat Dkk-1. Dkk-1 is a well-characterized antagonist of Wnt/beta-Catenin signaling (1, 2, 4, 5). This pathway is activated by Wnt engagement of a receptor complex composed of the Frizzled proteins and one of two low-density lipoprotein receptor-related proteins, LRP-5 or LRP-6 (4). Crystallographic studies have shown that Dkk-1 interacts with LRP-6 as a bipartite inhibitor, with both CRDs binding the extracellular domain of LRP-6 simultaneously (4, 6-8). Dkk-1/LRP-6/Krm2 complex internalization has been shown to down-regulate Wnt signaling (4, 9). Dkk-1 is expressed throughout development and antagonizes Wnt-7a during limb development (10, 11). Other sites of expression include developing neurons, hair follicles, and the retina (12, 13). The balance between Wnt signaling and Dkk-1 inhibition is critical for bone formation and homeostasis (14). Insufficient or excess Dkk-1 activity in bone results in increased or decreased bone density, respectively (12, 15). In adults, Dkk-1 is expressed in osteoblasts and osteocytes, and neurons. Cerebral ischemia induces Dkk-1 expression, which contributes to neuronal cell death (16). Dkk-1 also likely has a complex role in cancer, as it has been shown to act as a tumor suppressor and also to promote metastasis (17-19).
References
- Krupnik, V.E. et al. (1999) Gene 238:301.
- Niehrs, C. (2006) Oncogene 25:7469.
- Bullock, C.M. et al. (2004) Mol. Pharmacol. 65:582.
- Mao, B. et al. (2001) Nature 411:321.
- Brott, B.K. and S.Y. Sokol (2002) Mol. Cell. Biol. 22:6100.
- Chen, S. et al. (2011) Dev. Cell 21:848.
- Bourhis, E. et al. (2011) Structure 19:1433.
- Cheng, Z. et al. (2011) Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 18:1204.
- Mao, B. et al. (2002) Nature 417:664.
- Kemp, C. et al. (2005) Dev. Dyn. 233:1064.
- Adamska, M. et al. (2004) Dev. Biol. 272:134.
- Li, J. et al. (2006) Bone 39:754.
- Verani, R. et al. (2007) J. Neurochem. 100:242.
- Pinzone, J.J. et al. (2009) Blood 113:517.
- Morvan, F. et al. (2006) J. Bone Miner. Res. 21:934.
- Cappuccio, I. et al. (2005) J. Neurosci. 25:2647.
- Menezes, M.E. et al. (2012) Int. J. Cancer 130:1477.
- Li, S. et al. (2013) PLoS One 8:e84944.
- Chen, L. et al. (2013) Mol. Cancer 12:157.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional Dkk-1 Products
Product Documents for Recombinant Human Dkk-1 Biotinylated Protein
Product Specific Notices for Recombinant Human Dkk-1 Biotinylated Protein
For research use only