Recombinant Human DPPIV/CD26 (High Purity Dimer) Protein, CF
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # 9168-SE

Discontinued Product
9168-SE has been discontinued.
An alternative/replacement product is available:
11244-SE. View all DPPIV/CD26 products.
Key Product Details
Source
NS0
Accession #
Structure / Form
Noncovalently-linked homodimer
Conjugate
Unconjugated
Applications
Enzyme Activity
Product Specifications
Source
Mouse myeloma cell line, NS0-derived human DPPIV/CD26 protein
Asn29-Pro766, with a C-terminal Asp-Ile and 6-His tag
Asn29-Pro766, with a C-terminal Asp-Ile and 6-His tag
Purity
>95%, by SDS-PAGE visualized with Silver Staining and quantitative densitometry by Coomassie® Blue Staining.
Endotoxin Level
<1.0 EU per 1 μg of the protein by the LAL method.
N-terminal Sequence Analysis
Asn29
Predicted Molecular Mass
86 kDa
SDS-PAGE
95-110 kDa, reducing condtions
Activity
Measured by its ability to cleave the fluorogenic peptide substrate, Gly-Pro-7-amido-4-methylcoumarin (GP-AMC).
The specific activity is >8500 pmol/min/µg as measured under the described conditions.
The specific activity is >8500 pmol/min/µg as measured under the described conditions.
Scientific Data Images for Recombinant Human DPPIV/CD26 (High Purity Dimer) Protein, CF
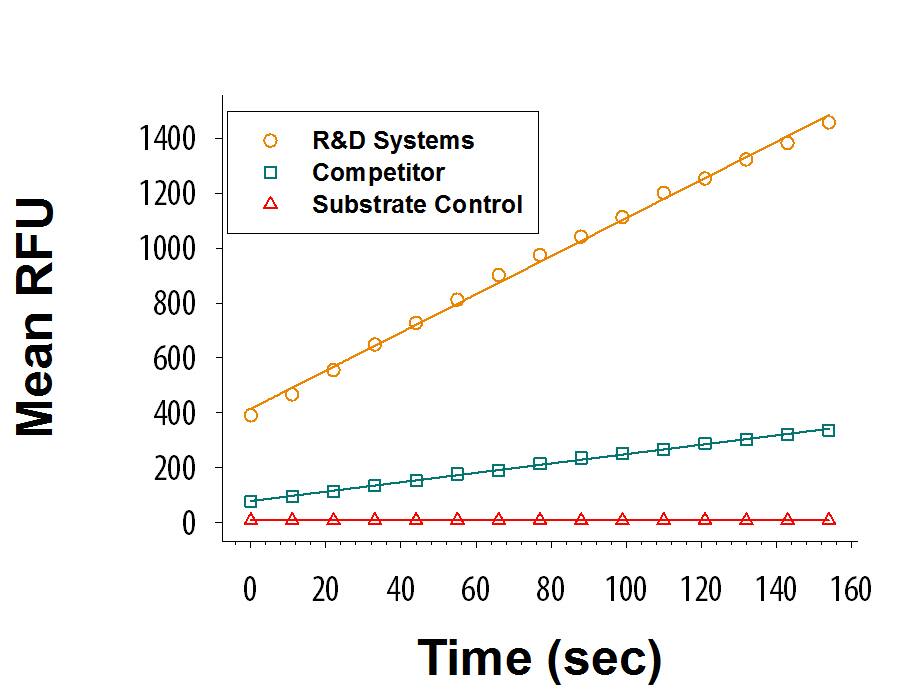
Recombinant Human DPPIV/CD26 (High Purity Dimer) Protein Enzyme Activity
Recombinant Human DPPIV/CD26 (Catalog # 9168-SE) is measured by its ability to cleave the fluorogenic peptide substrate, Gly-Pro-7-amido-4-methylcoumarin (GP-AMC). The activity (orange) is approximately 4-fold greater than the competitor's DPPIV/CD26 (green).Formulation, Preparation and Storage
9168-SE
| Formulation | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution in MES and NaCl. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped with dry ice or equivalent. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Background: DPPIV/CD26
References
- Klemann, C. et al. (2016) Clin. Exp. Immunol. Epub PMID 26919392.
- Mortier, A. et al. (2016) J. Leukoc. Biol. Epub PMID 26744452.
- Tanaka, T. et al. (1992) J. Immunol. 149:481.
- Rohrborn, D. et al. (2014) FEBS Lett. 588:3870.
- Waumans, Y. et al. (2015) Front. Immunol. 6:387.
- Lamers, D. et al. (2011) Diabetes 60:1917.
- Proost, P. et al. (1998) J. Biol. Chem. 273:7222.
- Proost, P. et al. (2001) Blood 98:3554.
- Ohtsuki, T. et al. (1998) FEBS Lett. 431:236.
- Barreira da Silva, R. et al. (2015) Nat. Immunol. 16:850.
- Guan, E. et al. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277:32348.
- Callebaut, C. et al. (1993) Science 262:2045.
- Raj, V.S. et al. (2013) Nature 495:251.
- Broxmeyer, H.E. et al. (2012) Nat. Med. 18:1786.
- Christopherson II, K.W. et al. (2004) Science 305:1000.
- Kameoka, J. et al. (1993) Science 261:466.
- Ohnuma, K. et al. (2007) J. Biol. Chem. 282:10117.
- Hatano, R. et al. (2013) Immunology 138:165.
Long Name
Dipeptidyl-peptidase IV
Alternate Names
CD26, DPP4
Gene Symbol
DPP4
UniProt
Additional DPPIV/CD26 Products
Product Documents for Recombinant Human DPPIV/CD26 (High Purity Dimer) Protein, CF
Product Specific Notices for Recombinant Human DPPIV/CD26 (High Purity Dimer) Protein, CF
For research use only
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...