Recombinant Human Hip Protein, CF
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # 9280-HP

Key Product Details
Product Specifications
Source
Chinese Hamster Ovary cell line, CHO-derived human Hip protein
| Human Hip (Phe18-Asp670) Accession # Q96QV1 |
HP | GGGSGGGSGGGS | HHHHHH |
| N-terminus | C-terminus | ||
Purity
>95%, by SDS-PAGE visualized with Silver Staining and quantitative densitometry by Coomassie® Blue Staining.
Endotoxin Level
<0.10 EU per 1 μg of the protein by the LAL method.
N-terminal Sequence Analysis
Lys24
Predicted Molecular Mass
75 kDa
SDS-PAGE
77-89 kDa, reducing conditions
Activity
Measured by its ability to inhibit Sonic Hedgehog (Shh) induction of alkaline phosphatase production in C3H10T1/2 mouse embryonic fibroblast cells.
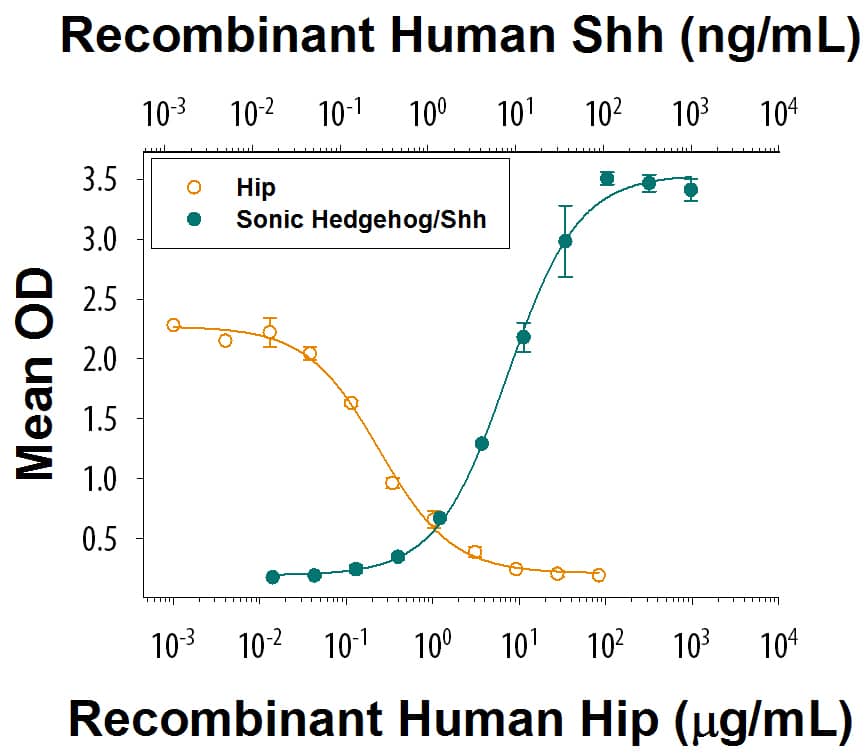
Recombinant Human Hip (Catalog # 9280-HP) inhibits a constant dose of 20 ng/mL of Recombinant Human Sonic Hedgehog/Shh Protein, High Activity (Catalog # 8908-SH) in a C3H10T1/2 mouse embryonic fibroblast cell alkaline phosphatase induction assay with an
ED50 = 0.1-0.6 µg/mL.
Recombinant Human Hip (Catalog # 9280-HP) inhibits a constant dose of 20 ng/mL of Recombinant Human Sonic Hedgehog/Shh Protein, High Activity (Catalog # 8908-SH) in a C3H10T1/2 mouse embryonic fibroblast cell alkaline phosphatase induction assay with an
ED50 = 0.1-0.6 µg/mL.
Scientific Data Images for Recombinant Human Hip Protein, CF
Recombinant Human Hip Protein Bioactivity
Recombinant Human Sonic Hedgehog/Shh (Catalog # 8908-SH) induces alkaline phosphatase production in C3H10T1/2 cells (green line). Recombinant Human Hip (Catalog # 9280-HP) inhibits a constant dose of 20 ng/mL of Recombinant Human Sonic Hedgehog/Shh Protein, High Activity (Catalog # 8908-SH) in C3H10T1/2 mouse embryonic fibroblasts with an ED50 = 0.1-0.6 µg/mL (orange line).Formulation, Preparation and Storage
9280-HP
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS and NaCl. |
| Reconstitution |
Reconstitute at 500 μg/mL in PBS.
|
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Background: Hip
References
- Ramsbottom, S.A. and M.E. Pownall (2016) J. Dev. Biol. 4:23.
- Chuang, P-T. and A.P. McMahon (1999) Nature 397:617.
- Bishop, B. et al. (2009) Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 16:698.
- Bak, M. et al. (2001) Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 92:300.
- Coulombe, J. et al. (2004) Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 25:323.
- Chuang, P-T. et al. (2003) Genes Dev. 17:342.
- Olsen, C.L. et al. (2004) BMC Cancer 4:43.
- Tada, M. et al. (2008) Clin. Cancer Res. 14:3768.
Long Name
Hedgehog-interacting Protein
Alternate Names
HHIP
Gene Symbol
HHIP
UniProt
Additional Hip Products
Product Documents for Recombinant Human Hip Protein, CF
Product Specific Notices for Recombinant Human Hip Protein, CF
For research use only
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...