Recombinant Human LDLR Protein, CF
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # 9177-LD
Asp193Ala

Key Product Details
Product Specifications
Source
Human embryonic kidney cell, HEK293-derived human LDL R protein
Ala22-Arg788 (Asp193Ala), with a C-terminal 6-His tag
Ala22-Arg788 (Asp193Ala), with a C-terminal 6-His tag
Purity
>95%, by SDS-PAGE visualized with Silver Staining and quantitative densitometry by Coomassie® Blue Staining.
Endotoxin Level
<0.10 EU per 1 μg of the protein by the LAL method.
N-terminal Sequence Analysis
Ala22
Predicted Molecular Mass
86 kDa
SDS-PAGE
120-140 kDa, reducing conditions
Activity
Measured in a competitive binding assay.
When human LDL is immobilized at 1 μg/mL (100 μL/well), Recombinant Human LDL R inhibits 50% binding of Biotinylated Recombinant Human LDL R (0.5 μg/mL) at the concentration range of 0.2-1.2 μg/mL.
When human LDL is immobilized at 1 μg/mL (100 μL/well), Recombinant Human LDL R inhibits 50% binding of Biotinylated Recombinant Human LDL R (0.5 μg/mL) at the concentration range of 0.2-1.2 μg/mL.
Scientific Data Images for Recombinant Human LDLR Protein, CF
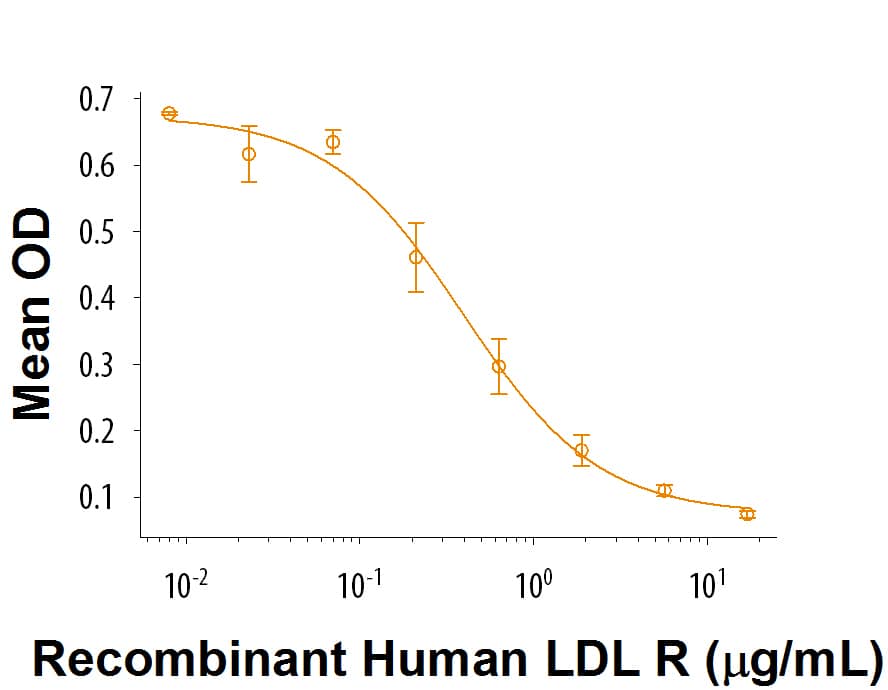
Recombinant Human LDLR Protein Bioactivity
When Human LDL is immobilized at 1 μg/mL (100 μL/well), Recombinant Human LDL R (Catalog # 9177-LD) inhibits the binding between Human LDL and Biotinylated Recombinant Human LDL R. The ED50 for this effect is 0.2-1.2 μg/mL.Formulation, Preparation and Storage
9177-LD
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS with Trehalose. |
| Reconstitution |
Reconstitute at 100 μg/mL in PBS.
|
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Background: LDLR
beta-propeller structures (class B LDL repeats) in the extracellular domain (ECD) (1-7). A membrane-proximal Ser/Thr-rich region shows extensive O-linked glycosylation (4, 8). A cytoplasmic NPxY motif links the LDL R to clathrin pits for endocytosis, and binds to select adaptor proteins (1, 4, 8). The human LDL R ECD shares 78%, 76%, 81% and 82% aa sequence identity with mouse, rat, bovine, and porcine LDL R, respectively. LDL R is constitutively and widely expressed. Its class A LDL domains near the N-terminus bind apoB and apoE, the apolipoproteins of low- and very low-density lipoproteins (LDL and VLDL), respectively (1, 2, 4, 9). Hepatocyte LDL R is responsible for endocytosis and clearing of most plasma LDL cholesterol (2, 9). At the low pH of the endocytic vesicle, it dissociates, allowing degradation of LDL and recycling of LDL R to the cell surface (1, 4). Lack of LDL R expression or function causes familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) (4, 9, 10). The protease PCSK9 (proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9) can also cause increased plasma cholesterol by promoting LDL R degradation rather than recycling to the cell surface (10-12). Soluble forms of approximately 140 kDa and 28 kDa are reported to be released by phorbol esters or interferons, respectively (6, 7).
References
- Go, G.W. and A. Mani (2012) Yale J. Biol. Med. 85:19.
- Ren, G. et al. (2010) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 107:1059.
- Bujo, H. and Y. Saito (2006) Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 26:1246.
- Gent, J. and I. Braakman (2004) Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 61:2461.
- Yamamoto, T. et al. (1984) Cell 39:27.
- Begg, M.J. et al. (2004) Eur. J. Biochem. 271:524.
- Fischer, D.G. et al. (1993) Science 262:250.
- Stolt, P.C. and H.H. Bock (2006) Cell. Signal. 18:1560.
- Defesche, J.C. (2004) Semin. Vasc. Med. 4:5.
- De Castro-Oros, I. et al. (2010) Appl. Clin Genet. 3:53.
- Zhang, D.W. et al. (2008) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105:13045.
- Tavori, H. et al. (2013) Circulation 127:2403.
Long Name
Low Density Lipoprotein Receptor
Alternate Names
LDL R
Entrez Gene IDs
Gene Symbol
LDLR
UniProt
Additional LDLR Products
Product Documents for Recombinant Human LDLR Protein, CF
Product Specific Notices for Recombinant Human LDLR Protein, CF
For research use only
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...