Recombinant Human SIRP alpha/CD172a Alexa Fluor® 488 Protein
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # AFG4546

Key Product Details
Source
Accession #
Structure / Form
Labeled with Alexa Fluor® 488 via amines
Excitation Wavelength: 488 nm
Emission Wavelength: 515-545 nm
Conjugate
Applications
Product Specifications
Source
| Human SIRP alpha (Gly27-Arg370) & (Glu31-Arg370) Accession # NP_542970.1 |
IEGRMD | Human IgG1 (Pro100-Lys330) |
| N-terminus | C-terminus |
Purity
Endotoxin Level
N-terminal Sequence Analysis
Predicted Molecular Mass
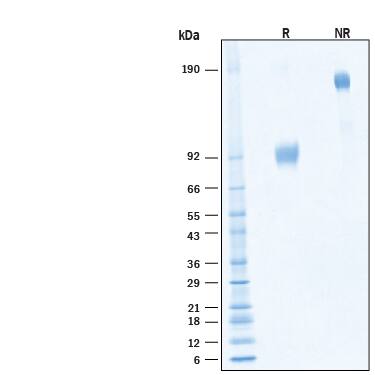
SDS-PAGE
Activity
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application.
Scientific Data Images for Recombinant Human SIRP alpha/CD172a Alexa Fluor® 488 Protein
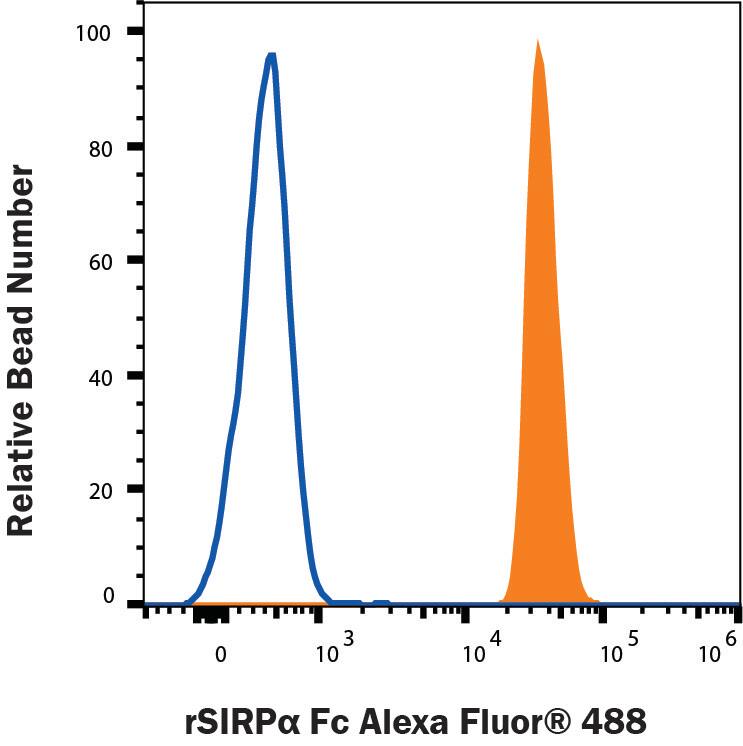
Detection of Human SIRP alpha/CD172a Antibody with Recombinant Human SIRP alpha/CD172aFc Chimera Alexa Fluor® 488 by Flow Cytometry.
Fluorescent beads conjugated to Human SIRP alpha/CD172a Antibody were stained with (A) Recombinant Human SIRP alpha/CD172aFc Chimera Alexa Fluor® 488 (Catalog # AFG4546, filled histogram) or (B) unstained (open histogram).Recombinant Human SIRP alpha/CD172aFc Chimera Alexa Fluor® 488 Protein SDS-PAGE.
2 μg/lane of Recombinant Human SIRP alpha/CD172aFc Chimera Alexa Fluor® 488 Protein (Catalog # AFG4546) was resolved with SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) and non-reducing (NR) conditions and visualized by Coomassie® Blue staining, showing bands at 70-105 kDa and 140-210 kDa, respectively.Formulation, Preparation and Storage
AFG4546
| Formulation | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS with BSA as a carrier protein. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped with dry ice or equivalent. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Protect from light. Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Background: SIRP alpha/CD172a
Signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRP alpha, designated CD172a), also called SHPS-1 (SHP substrate 1) and previously, MyD-1 (Myeloid/Dendritic-1), is a monomeric ~90 kDa type I transmembrane glycoprotein that belongs to the SIRP/SHPS (CD172) family of the immunoglobulin superfamily (1 - 4). SIRPs are paired receptors, with similar extracellular domains but differing C-termini and functions (1, 2). The 503 amino acid (aa) human SIRP alpha contains a 342 aa extracellular domain (ECD), with one V-type, and two C1 type Ig domains, and three potential N glycosylation sites. It has a 110 aa cytoplasmic sequence with ITIM motifs that recruit tyrosine phosphatases SHP-1 and SHP-2 when phosphorylated (4). Human SIRP alpha has more than 40 described polymorphisms, including the prominent BIT (Brain Ig like molecule with Tyrosine-based activation motifs, also called SIRP alpha2 or PTPNS) (5). One reported isoform lacks aa 1 - 101, which eliminates most of the V type Ig domain. Human SIRP alpha ECD shares 61%, 60%, 71%, 72% and 73% aa identity with mouse, rat, porcine, bovine and equine SIRP alpha, respectively; it shares 84% and 76% aa identity with human SIRP beta1 and SIRP gamma, respectively (2). SIRP alpha is expressed mainly on myeloid cells, including macrophages, neutrophils, dendritic and Langerhans cells (3 - 6). It is also found on neurons, smooth muscle and endothelial cells (7 - 9). SIRP alpha shows adhesion to the ubiquitous CD47/IAP (integrin associated protein), while SIRP gamma binds more weakly and SIRP alpha1 does not bind at all (1, 2). Mouse and human SIRP alpha-CD47 binding only cross-reacts for specific polymorphisms and influences engraftment of xenotransplanted stem cells (6, 10). SIRP alpha engagement generally produces a negative regulatory signal (4). Low SIRP alpha recognition of CD47, which occurs on aged erythrocytes or platelets or xenogenic cells, promotes clearance of CD47low cells from circulation (11, 13). SIRP alpha recognition of surfactants SP-A and SP-D in the lung can inhibit alveolar macrophage cytokine production (14). The CD47 integrin-SIRP alpha interaction is reported to promote macrophage fusion during osteoclastogenesis (15).
References
- Barclay, A.N. & M.H. Brown (2006) Nat. Rev. Immunol. 6:457.
- vanBeek, E.M. et al. (2005) J. Immunol. 175:7781.
- Liu, Y. et al. (2005) J. Biol. Chem. 280:36132.
- Kharitonenkov, A. et al. (1997) Nature 386:181.
- Swissprot Accession # P78324.
- Miyashita, M. et al. (2004) Mol. Biol. Cell 15:3950.
- Wang, X.X. & K.H. Pfenninger (2005) J. Cell Sci. 119:172.
- Maile, L.A. et al. (2003) Mol. Biol. Cell 14:3519.
- Johansen, M.L. & E.J. Brown (2007) J. Biol. Chem. 282:24219.
- Takenaka, K. et al. (2007) Nat. Immunol. 8:1313.
- Ishikawa-Sekigami, T. et al. (2006) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 343:1197.
- Olsson, M. et al. (2005) Blood 105:3577.
- Ide, K. et al. (2007) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104:5062.
- Gardai, S.J. et al. (2003) Cell 115:13.
- Lundberg, P. et al. (2007) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 352:444.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Entrez Gene IDs
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional SIRP alpha/CD172a Products
Product Documents for Recombinant Human SIRP alpha/CD172a Alexa Fluor® 488 Protein
Product Specific Notices for Recombinant Human SIRP alpha/CD172a Alexa Fluor® 488 Protein
This product is provided under an agreement between Life Technologies Corporation and R&D Systems, Inc, and the manufacture, use, sale or import of this product is subject to one or more US patents and corresponding non-US equivalents, owned by Life Technologies Corporation and its affiliates. The purchase of this product conveys to the buyer the non-transferable right to use the purchased amount of the product and components of the product only in research conducted by the buyer (whether the buyer is an academic or for-profit entity). The sale of this product is expressly conditioned on the buyer not using the product or its components (1) in manufacturing; (2) to provide a service, information, or data to an unaffiliated third party for payment; (3) for therapeutic, diagnostic or prophylactic purposes; (4) to resell, sell, or otherwise transfer this product or its components to any third party, or for any other commercial purpose. Life Technologies Corporation will not assert a claim against the buyer of the infringement of the above patents based on the manufacture, use or sale of a commercial product developed in research by the buyer in which this product or its components was employed, provided that neither this product nor any of its components was used in the manufacture of such product. For information on purchasing a license to this product for purposes other than research, contact Life Technologies Corporation, Cell Analysis Business Unit, Business Development, 29851 Willow Creek Road, Eugene, OR 97402, Tel: (541) 465-8300. Fax: (541) 335-0354.
For research use only