Recombinant Human SIRP alpha/CD172a Fc Biotin Protein, CF
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # BT4546B

Key Product Details
Source
Accession #
Structure / Form
Conjugate
Applications
Product Specifications
Source
| Human SIRP alpha/CD172a (Gly27-Arg370) & (Glu31-Arg370) Accession # NP_542970 |
IEGRMD | Human IgG1 (Pro100-Lys330) |
| N-terminus | C-terminus |
Purity
Endotoxin Level
N-terminal Sequence Analysis
Predicted Molecular Mass
SDS-PAGE
Activity
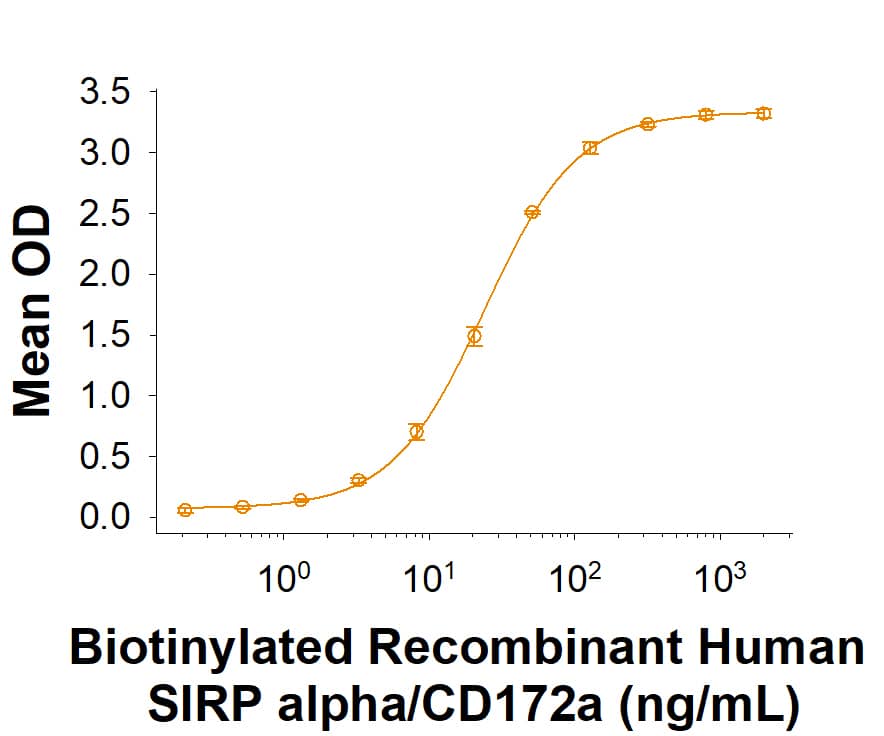
When Recombinant Human CD47 Fc Chimera (Catalog # 4670-CD) is immobilized at 0.1 µg/mL (100 µL/well), Biotinylated Recombinant SIRP alpha/CD172a Fc Chimera (Catalog # BT4546B) binds with an ED50 of 6-48 ng/mL.
Scientific Data Images for Recombinant Human SIRP alpha/CD172a Fc Biotin Protein, CF
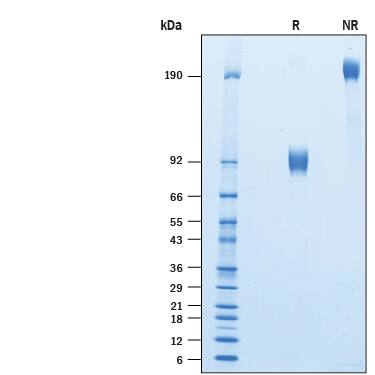
Recombinant Human SIRP alpha/CD172a Fc Chimera Protein SDS-PAGE
2 μg/lane of Biotinylated Recombinant Human SIRP alpha/CD172a Fc Chimera (Catalog # BT4546B) was resolved with SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) and non-reducing (NR) conditions and visualized by Coomassie® Blue staining, showing bands at 70-105 kDa and 140-210 kDa, respectively.Recombinant Human SIRP alpha/CD172a Fc Chimera Protein Binding Activity
When Recombinant Human CD47 Fc Chimera (Catalog # 4670-CD) is coated at 0.1 µg/mL, Biotinylated Recombinant Human SIRP alpha/CD172a Fc Chimera (Catalog # BT4546B) binds with an ED50 of 6-48 ng/mL.Formulation, Preparation and Storage
BT4546B
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS with Trehalose. |
| Reconstitution |
Reconstitute at 500 μg/mL in PBS.
|
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Background: SIRP alpha/CD172a
Signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRP alpha, designated CD172a), also called SHPS-1 (SHP substrate 1) and previously, MyD-1 (Myeloid/Dendritic-1), is a monomeric ~90 kDa type I transmembrane glycoprotein that belongs to the SIRP/SHPS (CD172) family of the immunoglobulin superfamily (1 - 4). SIRPs are paired receptors, with similar extracellular domains but differing C-termini and functions (1, 2). The 503 amino acid (aa) human SIRP alpha contains a 342 aa extracellular domain (ECD), with one V-type, and two C1 type Ig domains, and three potential N glycosylation sites. It has a 110 aa cytoplasmic sequence with ITIM motifs that recruit tyrosine phosphatases SHP-1 and SHP-2 when phosphorylated (4). Human SIRP alpha has more than 40 described polymorphisms, including the prominent BIT (Brain Ig like molecule with Tyrosine-based activation motifs, also called SIRP alpha2 or PTPNS) (5). One reported isoform lacks aa 1 - 101, which eliminates most of the V type Ig domain. Human SIRP alpha ECD shares 61%, 60%, 71%, 72% and 73% aa identity with mouse, rat, porcine, bovine and equine SIRP alpha, respectively; it shares 84% and 76% aa identity with human SIRP beta1 and SIRP gamma, respectively (2). SIRP alpha is expressed mainly on myeloid cells, including macrophages, neutrophils, dendritic and Langerhans cells (3 - 6). It is also found on neurons, smooth muscle and endothelial cells (7 - 9). SIRP alpha shows adhesion to the ubiquitous CD47/IAP (integrin associated protein), while SIRP gamma binds more weakly and SIRP alpha1 does not bind at all (1, 2). Mouse and human SIRP alpha-CD47 binding only cross-reacts for specific polymorphisms and influences engraftment of xenotransplanted stem cells (6, 10). SIRP alpha engagement generally produces a negative regulatory signal (4). Low SIRP alpha recognition of CD47, which occurs on aged erythrocytes or platelets or xenogenic cells, promotes clearance of CD47low cells from circulation (11, 13). SIRP alpha recognition of surfactants SP-A and SP-D in the lung can inhibit alveolar macrophage cytokine production (14). The CD47 integrin-SIRP alpha interaction is reported to promote macrophage fusion during osteoclastogenesis (15).
References
- Barclay, A.N. & M.H. Brown (2006) Nat. Rev. Immunol. 6:457.
- vanBeek, E.M. et al. (2005) J. Immunol. 175:7781.
- Liu, Y. et al. (2005) J. Biol. Chem. 280:36132.
- Kharitonenkov, A. et al. (1997) Nature 386:181.
- Swissprot Accession # P78324.
- Miyashita, M. et al. (2004) Mol. Biol. Cell 15:3950.
- Wang, X.X. & K.H. Pfenninger (2005) J. Cell Sci. 119:172.
- Maile, L.A. et al. (2003) Mol. Biol. Cell 14:3519.
- Johansen, M.L. & E.J. Brown (2007) J. Biol. Chem. 282:24219.
- Takenaka, K. et al. (2007) Nat. Immunol. 8:1313.
- Ishikawa-Sekigami, T. et al. (2006) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 343:1197.
- Olsson, M. et al. (2005) Blood 105:3577.
- Ide, K. et al. (2007) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104:5062.
- Gardai, S.J. et al. (2003) Cell 115:13.
- Lundberg, P. et al. (2007) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 352:444.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Entrez Gene IDs
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional SIRP alpha/CD172a Products
Product Documents for Recombinant Human SIRP alpha/CD172a Fc Biotin Protein, CF
Product Specific Notices for Recombinant Human SIRP alpha/CD172a Fc Biotin Protein, CF
For research use only