Recombinant Human FGF basic/FGF2/bFGF, 145 aa TC Grade, CF Best Seller
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # 4114-TC


Now offering a heat stable form of Recombinant Human FGF basic (Catalog # BT-FGFBHS) that retains activity at incubator temperatures and adds flexibility to your media change intervals.
Key Product Details
Product Specifications
Source
Ala144-Ser288
Endotoxin Level
N-terminal Sequence Analysis
Predicted Molecular Mass
Activity
Measured in a cell proliferation assay using NR6R-3T3 mouse fibroblast cells. Raines, E.W. et al. (1985) Methods Enzymol. 109:749.
The ED50 for this effect is 0.3-3 ng/mL.
Reviewed Applications
Read 1 review rated 5 using 4114-TC in the following applications:
Scientific Data Images for Recombinant Human FGF basic/FGF2/bFGF, 145 aa TC Grade, CF
Recombinant Human FGF basic/FGF2/bFGF (145 aa), Tissue Culture Grade Protein SEC-MALS.
Recombinant human FGF basic/FGF2/bFGF, 145 aa TC Grade (Catalog # 4114-TC) has a molecular weight (MW) of 17.2 kDa as analyzed by SEC-MALS, suggesting that this protein is a monomer. MW may differ from predicted MW due to post-translational modifications (PTMs) present (i.e. Glycosylation).iPSC-derived Cardiomyocytes Differentiated on Cultrex Stem Cell Qualified RGF BME Express Stage-specific Markers.
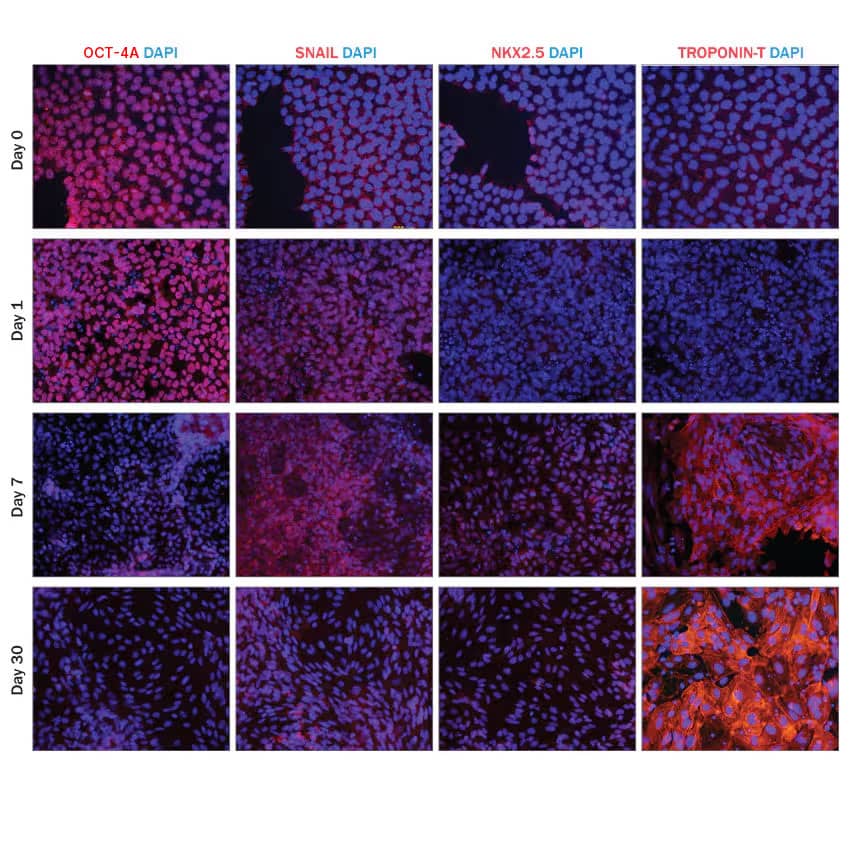
JOY6 human iPSCs were cultured in media containing Cultrex™ Stem Cell Qualified RGF BME (3434-010-02) and N21-MAX Insulin Free Media Supplement (AR010) along with Recombinant Human Activin A on day 0, Recombinant Human FGF-basic (Catalog # 4114-TC), Recombinant Human BMP-4, and CHIR99021 (4423) on days 1-5, and Recombinant Human Dkk-1 (5439-DK) on days 5-7 to induce cardiomyocyte differentiation. Cells were then cultured in media supplemented with N21-MAX Insulin Free Media Supplement (AR010) on days 7-12 and media supplemented with N21-MAX Media Supplement (AR008) from day 12 and beyond. Cells were fixed and stained for stage-specific markers at select time points during the procedure. The pluripotency marker Oct-4 was detected using a Mouse Anti-Human Oct-4A Monoclonal Antibody (MAB17591). The mesoderm marker, Snail is expressed intermediately during differentiation (Day 1). It was detected using a Goat Anti-Human Snail Polyclonal Antibody (AF3639). The cardiomyocyte markers NKX2.5 and Troponin T are not present in cells during early (Day 0) and intermediate (Day1) differentiation and become more highly expressed during the later stages of differentiation (Day 7, Day 30). NKX2.5 was detected using a Goat Anti-Human NKX2.5 Polyclonal Antibody (AF2444) and Troponin T was detected using a Mouse Anti-Human Cardiac Troponin T Monoclonal Antibody (MAB1874). Snail and NKX2.5 primary antibodies were visualized with a NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Donkey Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (NL001). Oct-4 and Troponin T were visualized with a NorthernLights 557-conjugated Donkey Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (NL007).iPSC-derived Cardiomyocytes Express Atrial and Ventricular Markers.
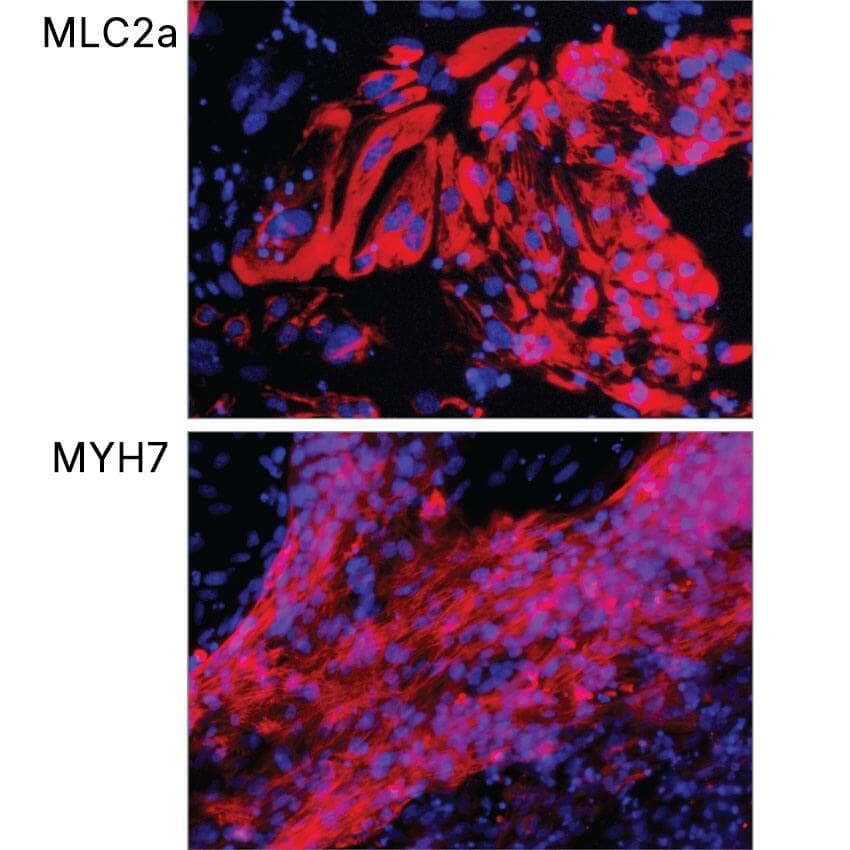
JOY6 human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) were differentiated into cardiomyocytes in media containing Cultrex™ Stem Cell Qualified Reduced Growth Factor Basement Membrane Extract (3434-010-02) and N21-MAX Insulin Free Media Supplement (AR010) along with Recombinant Human Activin A on day 0, Recombinant Human FGF-basic (Catalog # 4114-TC), Recombinant Human BMP-4, and CHIR99021 (4423) on days 1-5, and Recombinant Human Dkk-1 (5439-DK) on days 5-7. Following culture in media supplemented with N21-MAX Insulin Free Media Supplement (AR010) on days 7-12 and media supplemented with N21-MAX Media Supplement (AR008) from day 12 and beyond, cells were fixed and stained for the atrial-specific marker, MLC2a, and the ventricle-specific marker, MYH7 using a Rabbit Anti-Human MYH7 Monoclonal Antibody (MAB90961).Formulation, Preparation and Storage
4114-TC
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in Tris-HCl and NaCl. |
| Reconstitution |
Reconstitute at 0.5-1.0 mg/mL in sterile PBS.
|
| Shipping | The product is shipped with polar packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Background: FGF basic/FGF2/bFGF
FGF basic (also known as FGF2 and HBGF-2) is an 18-34 kDa, heparin-binding member of the FGF superfamily of molecules (1-3). Superfamily members are characterized by the presence of a centrally placed beta-trefoil structure. FGF acidic (FGF1) and FGF basic (FGF2) were the first two identified FGFs, and the designations acidic and basic refer to their relative isoelectric points. Human FGF basic is 288 amino acids (aa) in length. There are multiple start sites, four of which utilize atypical CUG codons, and one that initiates at an AUG start site (4-6). The four CUG start sites generate high molecular weight (HMW) FGF basic. There is a 34 kDa, 288 aa form, a 24 kDa, 210 aa form, a 22.5 kDa, 201 aa form, and a 22 kDa, 196 aa form. All are retained intracellularly, undergo extensive methylation, and possess one or more nuclear localization signals (NLS) (7-9). The AUG initiating form is 18 kDa and 155 aa in length. There is no signal sequence (ss). It is, however, secreted directly through the plasma membrane via a mechanism that appears to be dependent upon tertiary structure (10). In place of a ss, there is purportedly a 9 aa N-terminal prosegment that precedes a 146 aa mature segment (11). Early isolations of 18 kDa bovine FGF basic yielded 146 aa molecules, an effect attributed to the presence of acid proteases (12). The molecule contains a heparin-binding site (aa residues 128-144), and undergoes phosphorylation at Ser117 (13). There is also an ill-defined C-terminal NLS that may be more “functional” (or 3-dimensional) than structural (7). Human 146 aa FGF basic is 97% aa identical to mouse FGF basic (14).
References
- Sorenson, V. et al. (2006) BioEssays 28:504.
- Kardami, E. et al. (2004) Cardiovasc. Res. 63:458.
- Nugent, M.A. and R.V. Lozzo (2000) Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 32:115.
- Abraham, J.A. et al. (1986) EMBO J. 5:2523.
- Prats, H. et al. (1989) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86:1836.
- Arnaud, E. et al. (1999) Mol. Cell. Biol. 19:505.
- Foletti, A. et al. (2003) Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 60:2254.
- Arese, M. et al. (1999) Mol. Biol. Cell 10:1429.
- Pintucci, G. et al. (1996) Mol. Biol. Cell 7:1249.
- Nickel, W. (2005) Traffic 6:607.
- SwissProt # P09038.
- Klagsbrun, M. et al. (1987) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84:1839.
- Bailly, K. et al. (2000) FASEB J. 14:333.
- Hebert, J.M. et al. (1990) Dev. Biol. 138:454.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional FGF basic/FGF2/bFGF Products
Product Documents for Recombinant Human FGF basic/FGF2/bFGF, 145 aa TC Grade, CF
Product Specific Notices for Recombinant Human FGF basic/FGF2/bFGF, 145 aa TC Grade, CF
For research use only