Hypoxia Signaling Modulation
Can You Induce Hypoxia in vitro?
Conventionally, the study of hypoxic responses has relied on the use of monolayer cell cultures exposed to low oxygen conditions (e.g., 0.02-5% O2) by incubation in gas-controlled chambers or incubators with a specific mixture of gases (e.g., 95% N2, 5% CO2- anoxia). However, studying hypoxia signaling using hypoxia-mimetic agents can forgo gas exchange requirements.
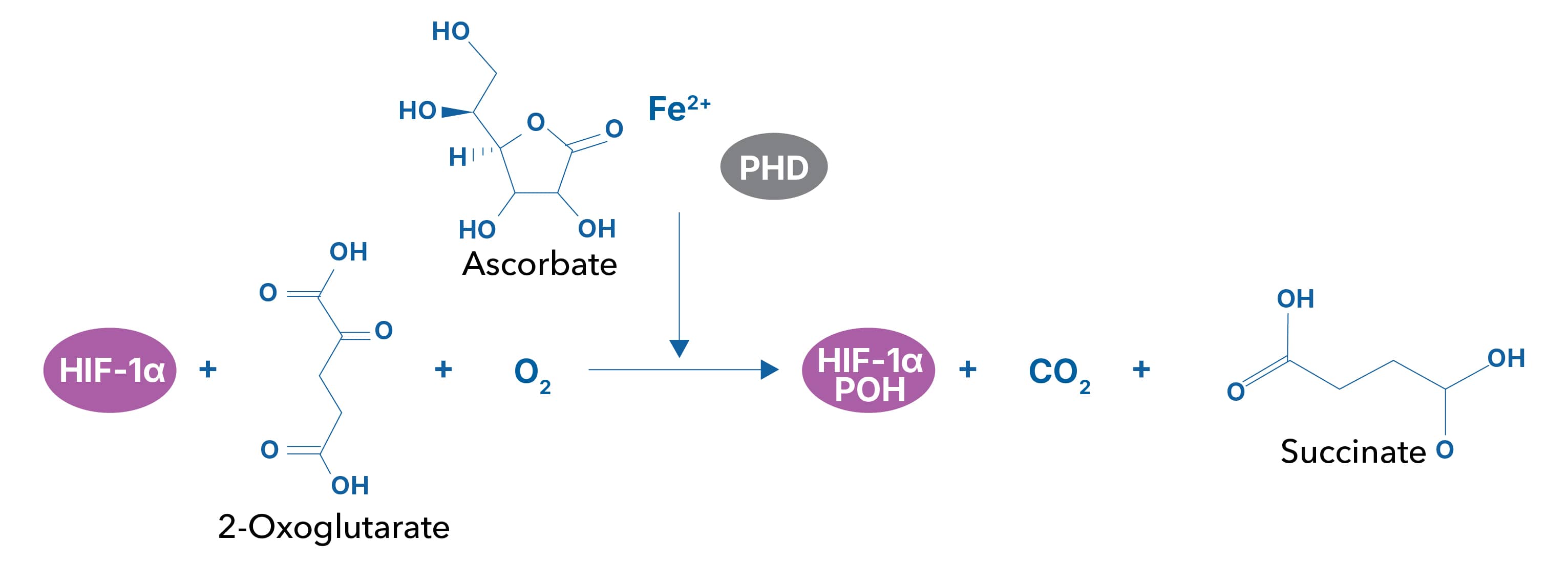
Prolyl Hydroxylase (PHD) Inhibitors Promote HIF Signaling
Under normoxic conditions, the first step of HIF degradation is proline hydroxylation in the oxygen dependent degradation domain (ODDD) by the prolyl hydroxylase (PHD) family of enzymes. Hydroxylated HIF-1 alpha will then bind to the von Hippel-Lindau protein (VHL), where HIF-1 alpha is ubiquitinated and targeted to the proteasome. Inhibiting the initial hydroxylation step by PHDs promotes HIF-1 alpha expression, independent of oxygen levels.
| Mechanism | Products | |
|---|---|---|
| Cobalt Chloride (CoCl2) | Binding to the iron-binding domain of PHD, preventing co-factor binding | CoCl2 treated lysates |
| Deferoxamine/Desferrioxamine (DFO/DFX) | Iron chelator; PHD require iron as co-factor for activity. Inhibit the activity of PHDs | Catalog # 5764 |
| Dimethyloxalylglycine (DMOG) | Competitive inhibitor of PHD enzymes | Catalog # 4408 |
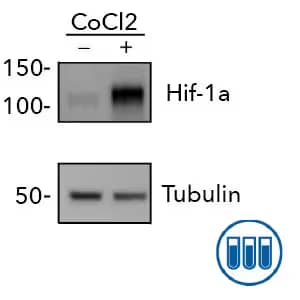
Western Blot: HeLa cells were either left untreated (-) or treated with CoCl2 and probed for HIF-1 alpha expression with Rabbit Anti-HIF-1 alpha (Catalog # NB100-134) and Tubulin expression as loading control. HIF-1 alpha expression is readily detectable in CoCl2 treated cells. Cell Lysate used is HeLa CoCl2 Treated/Untreated Cell Lysate (Catalog # NBP2-36450). The specificity of NB100-134 has been validated by both Biological and Orthogonal Strategies.
Molecules to Directly Target HIF Signaling
Other biochemical based approaches rely on the use of small molecules to target different steps in HIF signaling. Using inhibitors of key steps or enzymes involved in the regulation of HIF expression helps to uncover how hypoxia-induced signaling operates in specific systems or models under study.
Small Molecules: HIF Modulators
| Small Molecule | Mechanism | Catalog # | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitors | TAT-cyclo-CLLFVY | Selective HIF-1 dimerization inhibitor | 5582 |
| TC-S 7009 | High affinity and selective HIF-2α inhibitor | 5243 | |
| Echinomycin | Highly potent and selective HIF-1α inhibitor | 5520 | |
| Evofosfamide | Hypoxia-activated DNA alkylating agent prodrug | 7507 | |
| Inducers | VH 298 | Inhibitor of E3 ubiquitin ligase VHL, Inhibits interaction between VHL and HIF-1α | 6156 |
Molecules to Indirectly Modulate Hypoxia Signaling
Modulating proteins that play a role in HIF expression is another way to promote or inhibit the cellular response to hypoxia and modulate HIF expression. For example, STAT3 upregulates HIF1 mRNA expression, so inhibiting STAT3 would prevent HIF1 upregulation and inhibit the hypoxic response. Similarly, activating STAT3 would promote HIF1 expression and downstream targets of hypoxia signaling.
Indirect Hypoxia Modulators
| Small Molecule | Mechanism | Bio-Techne Catalog # | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitors | CGP 37157 | Antagonizes mitochondrial Na+/Ca2+ exchanger | 1114 |
| Stattic | Selective STAT3 inhibitor; STAT 3 upregulates HIF1 expression at mRNA level | 2798 | |
| Rapamycin | mTOR inhibitor; mTOR upregulates HIF1 expression at protein level | 1292 | |
| Torin 1 | Potent and selective mTOR inhibitor | 4247 | |
| LC2 | KRAS PROTAC® | 7420 | |
| Inhibitors | Colivelin | STAT3 activator | 3945 |
PROTAC® is a registered trademark of Arvinas Operations, Inc., and is used under license.