Phosphoserine is an ester of serine and phosphoric acid which results from post-translational modifications. Phosphorylation is a key post-translational modification necessary for normal cellular signaling. Phosphorylated proteins mediate cell division, cellular differentiation, signal transduction and other key cellular signaling processes. Phosphorylation of serine residues on proteins is one of the keys to a cascade of reactions that are of great interest to many researchers. Phosphorylated serine residues have been detected by immunofluorescence, immunochemistry and Western blotting with phosphoserine antibodies in almost all types of cancers1, neurological disorders like Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s 2 and several other chronic diseases3.
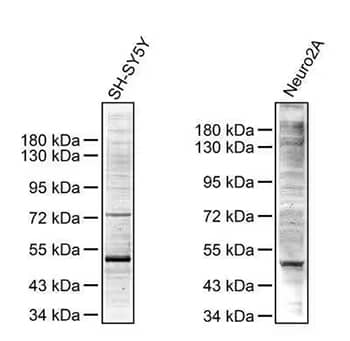
Western blot analysis showing phosphoserine expression in SH-SY5Y (left) and Neuro2A (right) whole cell lysates using Rabbit Anti-Phosphoserine Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog #NB100-1953).
Abnormal hyper-phosphorylation of pathogenic proteins is a common phenomenon that contributes to the disease process and phosphorylation of several pathological proteins at their serine residues. Researchers are now investigating if this offers a viable strategy for disease-modifying therapeutic interventions using phospho-specific antibodies.
- PMID: 6980236
- PMID: 21241799
- PMID: 22178943
Bio-Techne offers Phosphoserine reagents for your research needs including: