Spatial Multiomic Assay for Studying Interneuron Heterogeneity in the Brain
by Chengxin Zhou, Debia Wakhloo, Anushka Dikshit, and Li-Chong Wang.
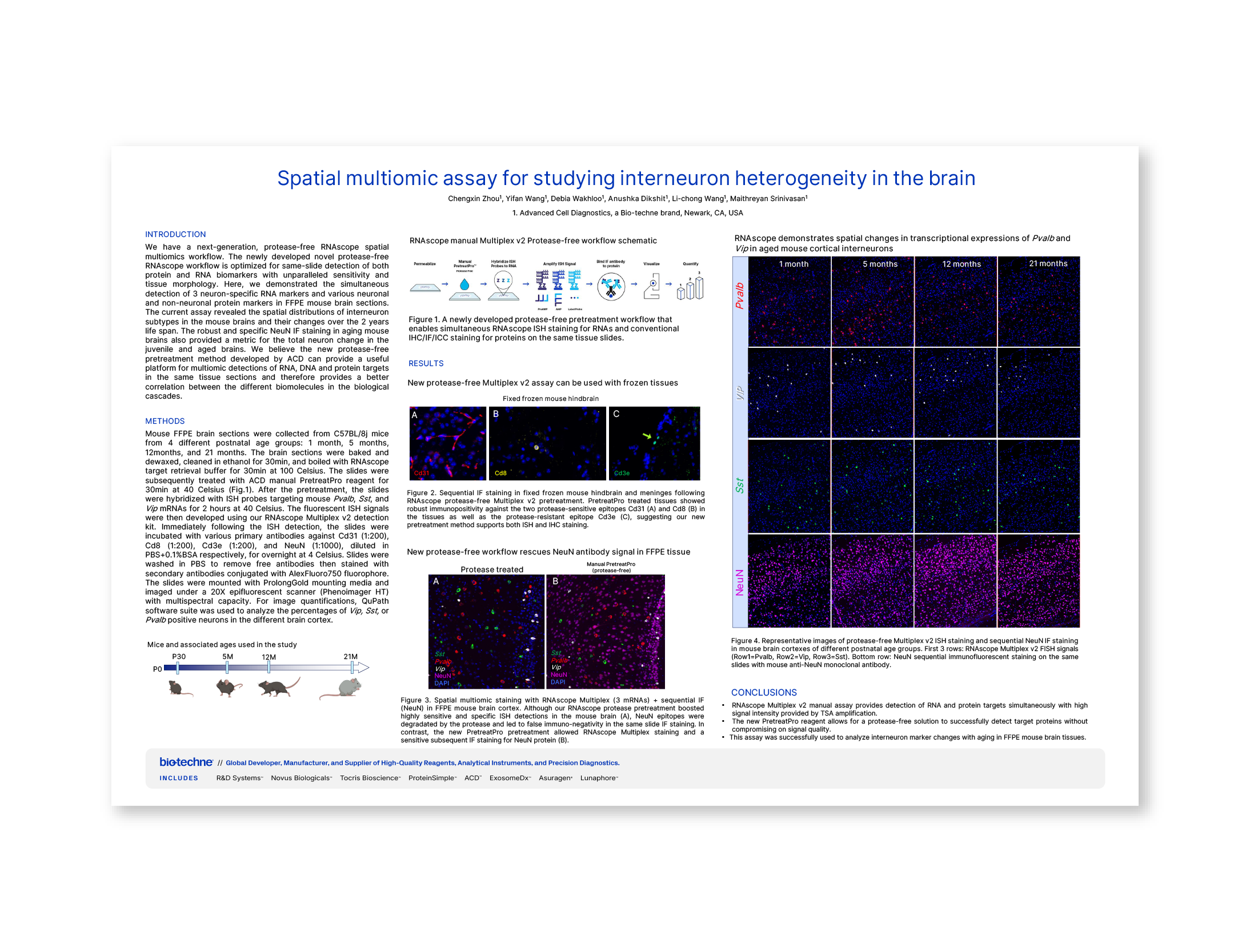
Scientific Meeting PostersInterneurons, a diverse group of inhibitory neurons, play a critical role in maintaining the balance and function of neural circuits within the brain. Certain groups of interneurons are also heavily involved in memory formation, learning, and sensory processing.
Disruptions in this balance can lead to complex neurological disorders, age-related cognitive decline, and psychiatric disorders. Studying interneuron diversity in the brain provides valuable insights into these disorders.
To optimize protein detection alongside RNA, we have developed a new protease-free workflow for the RNAscope™ Multiplex Fluorescent V2 assay. This assay uses a TSA-amplification strategy that boosts the probe signals, enabling the detection of up to four RNA targets alongside proteins, while preserving antigen integrity and tissue morphology.
We used this assay to study interneuron diversity by visualizing target RNAs and protein markers in brain tissue sections.
Download this spatial multiomics poster to explore:
- The use of RNA probes (Pvalb, Vip, and Sst) to study interneuron diversity in the aging brain
- How this protease free multiomic workflow enhances the understanding of complex brain tissue while preserving antigen integrity and tissue morphology
This poster was presented at the Society for Neuroscience (SfN)’s Neuroscience 2024 meeting in October 2024.