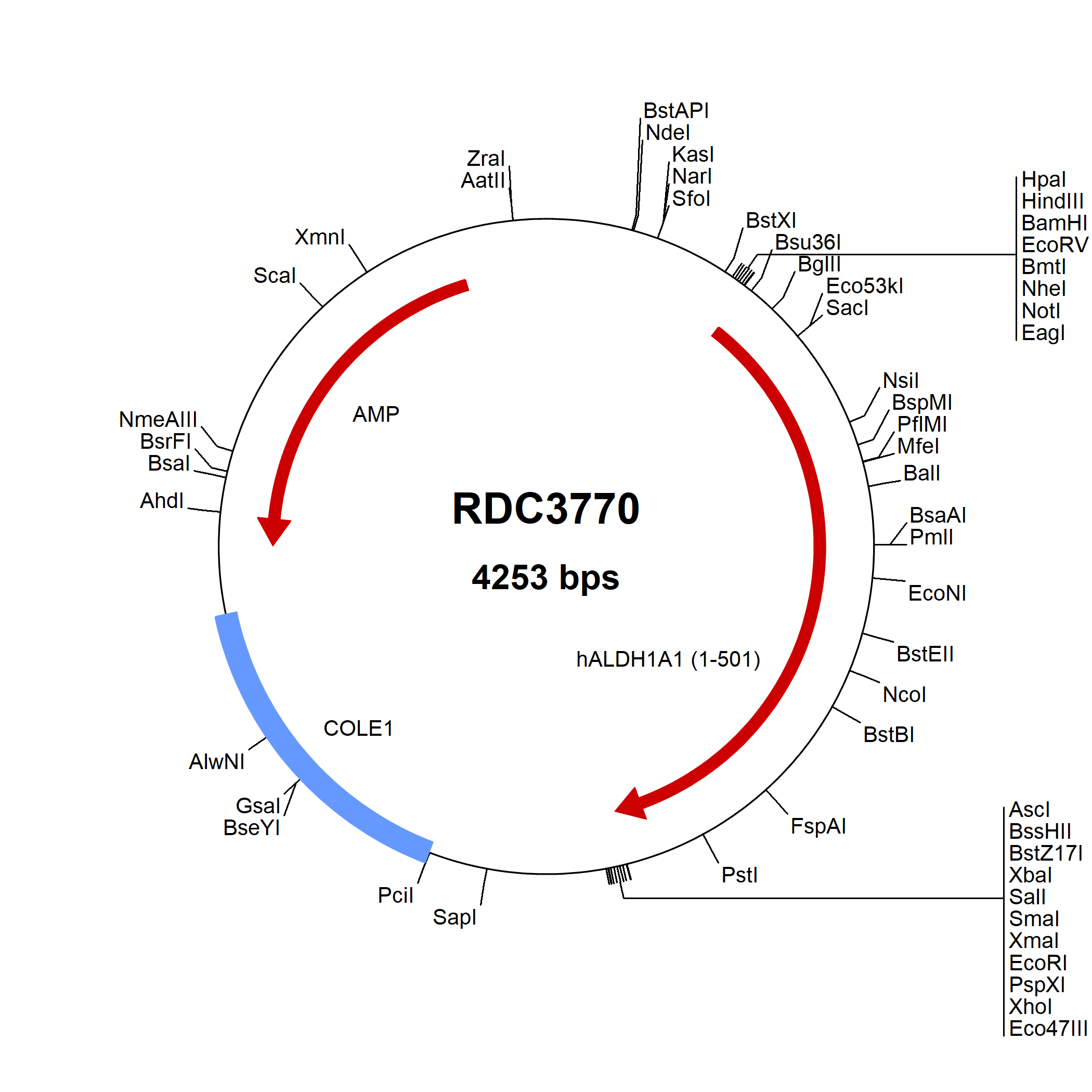
Aldehyde Dehydrogenase 1-A1/ALDH1A1: cDNA Clones
Aldehyde dehydrogenases (ALDHs) are NAD(P)+-dependent enzymes that detoxify aldehydes by oxidizing them to carboxylic acids. Nineteen ALDHs are present in humans, expressed in a variety of organelles and having different substrate preferences. ALDH1A1 is a cytosolic enzyme that preferentially oxidizes retinaldehyde to retinoic acid. ALDH1A1 is expressed in the epithelium of many organs, including brain, liver, testis, eye lens and cornea. ALDH1A1 is highly expressed in brain dopaminergic neurons, where it produces the retinoic acid required for their differentiation and development. The retinoic acid produced by ALDH1A1 is also important for the differentiation of hematopoietic stem cells. ALDH1A1 is a major enzyme in the oxidation of acetaldehyde, a toxic metabolite of ethanol.
1 result for "Aldehyde Dehydrogenase 1-A1/ALDH1A1 cDNA Clones" in Products
1 result for "Aldehyde Dehydrogenase 1-A1/ALDH1A1 cDNA Clones" in Products
Aldehyde Dehydrogenase 1-A1/ALDH1A1: cDNA Clones
Aldehyde dehydrogenases (ALDHs) are NAD(P)+-dependent enzymes that detoxify aldehydes by oxidizing them to carboxylic acids. Nineteen ALDHs are present in humans, expressed in a variety of organelles and having different substrate preferences. ALDH1A1 is a cytosolic enzyme that preferentially oxidizes retinaldehyde to retinoic acid. ALDH1A1 is expressed in the epithelium of many organs, including brain, liver, testis, eye lens and cornea. ALDH1A1 is highly expressed in brain dopaminergic neurons, where it produces the retinoic acid required for their differentiation and development. The retinoic acid produced by ALDH1A1 is also important for the differentiation of hematopoietic stem cells. ALDH1A1 is a major enzyme in the oxidation of acetaldehyde, a toxic metabolite of ethanol.