alpha-N-terminal Methyltransferase 1A/METTL11A Products
METTL11A, also named N-terminal RCC1 methyltransferase (NRMT), is an alpha-N-methyltransferase that methylates the N-terminal amino group of target proteins containing the N-terminal motif [Ala/Pro/Ser]-Pro-Lys when the initiator Met is cleaved. It is responsible for N-terminal methylation of RCC1, KLHL31, MYL2, MYL3, RB1, RPL23A and SET. NRMT lacks a SET domain but possesses a Rossman-like alpha/beta fold. The residues Asn169, Asp178, Asp181, and Ser183 of NRMT are important for substrate binding. RCC1 (Ran guanine nucleotide-exchange factor) is the first protein for which any biological function of alpha-N-methylation by NRMT has been identified. The multi-spindle phenotype associated with either NRMT knockdown or methylation-defective RCC1 mutants demonstrated the importance of alpha-N-methylation of RCC1 for normal bipolar spindle formation and chromosome aggregation. NRMT is robustly overexpressed in gastrointestinal cancers.
7 results for "alpha-N-terminal Methyltransferase 1A/METTL11A" in Products
7 results for "alpha-N-terminal Methyltransferase 1A/METTL11A" in Products
alpha-N-terminal Methyltransferase 1A/METTL11A Products
METTL11A, also named N-terminal RCC1 methyltransferase (NRMT), is an alpha-N-methyltransferase that methylates the N-terminal amino group of target proteins containing the N-terminal motif [Ala/Pro/Ser]-Pro-Lys when the initiator Met is cleaved. It is responsible for N-terminal methylation of RCC1, KLHL31, MYL2, MYL3, RB1, RPL23A and SET. NRMT lacks a SET domain but possesses a Rossman-like alpha/beta fold. The residues Asn169, Asp178, Asp181, and Ser183 of NRMT are important for substrate binding. RCC1 (Ran guanine nucleotide-exchange factor) is the first protein for which any biological function of alpha-N-methylation by NRMT has been identified. The multi-spindle phenotype associated with either NRMT knockdown or methylation-defective RCC1 mutants demonstrated the importance of alpha-N-methylation of RCC1 for normal bipolar spindle formation and chromosome aggregation. NRMT is robustly overexpressed in gastrointestinal cancers.
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Sheep IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | IHC, WB, IP |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB, ELISA, ICC/IF |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | ICC/IF |
| Applications: | AC |
| Source: | E. coli |
| Accession #: | Q9BV86 |
| Applications: | EnzAct |

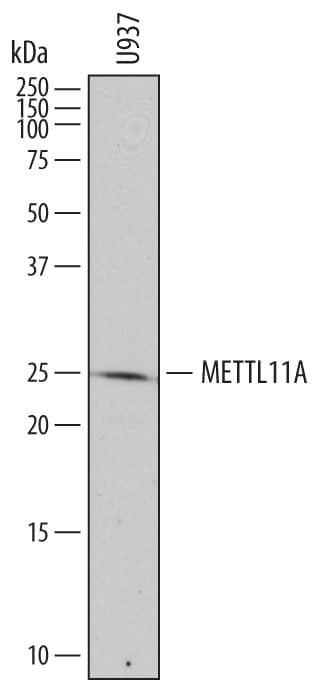

![Western Blot: alpha-N-terminal Methyltransferase 1A/METTL11A Antibody [NBP3-12704] Western Blot: alpha-N-terminal Methyltransferase 1A/METTL11A Antibody [NBP3-12704]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/alpha-N-terminal-Methyltransferase-1A-METTL11A-Antibody-Western-Blot-NBP3-12704-img0001.jpg)
![Western Blot: alpha-N-terminal Methyltransferase 1A/METTL11A AntibodyBSA Free [NBP2-92670] Western Blot: alpha-N-terminal Methyltransferase 1A/METTL11A AntibodyBSA Free [NBP2-92670]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/alpha-N-terminal-Methyltransferase-1A-METTL11A-Antibody-Western-Blot-NBP2-92670-img0002.jpg)
![Western Blot: alpha-N-terminal Methyltransferase 1A/METTL11A Antibody [H00028989-B01P] Western Blot: alpha-N-terminal Methyltransferase 1A/METTL11A Antibody [H00028989-B01P]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/alpha-N-terminal-Methyltransferase-1A-METTL11A-Antibody-Western-Blot-H00028989-B01P-img0001.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: alpha-N-terminal Methyltransferase 1A/METTL11A Antibody [NBP2-58554] Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: alpha-N-terminal Methyltransferase 1A/METTL11A Antibody [NBP2-58554]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/alpha-N-terminal-Methyltransferase-1A-METTL11A-Antibody-Immunocytochemistry-Immunofluorescence-NBP2-58554-img0001.jpg)
