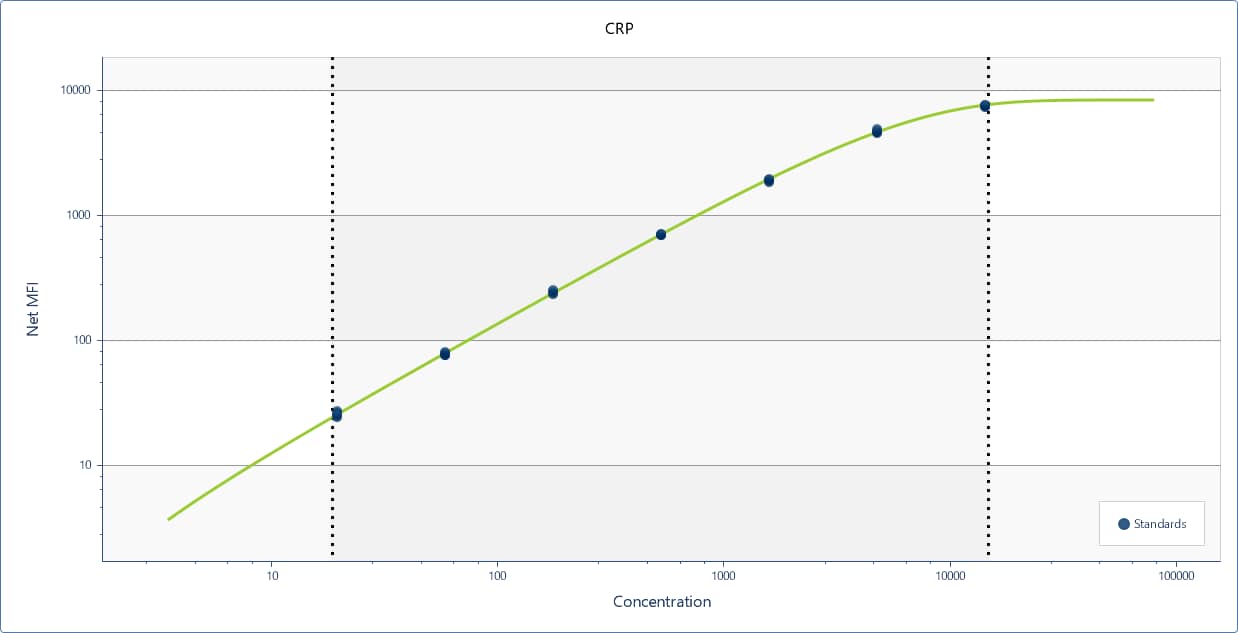
C-Reactive Protein/CRP: Luminex Assays
C-Reactive Protein (CRP), also known as Pentraxin 1, is a secreted pentameric protein that functions as a sensor and activator for the innate immune response. In humans, it is a major acute-phase protein; its circulating concentration is dramatically elevated at the onset of inflammation. In mice, however, serum CRP levels increase only slightly during inflammation, and the analogous acute phase role is filled by Pentraxin 2. CRP binds, opsonizes, and induces the phagocytosis of bacteria and apoptotic cells. It regulates activation of the classical complement pathway by binding several proteins in the complement cascade as well as Fc gamma RI, Fc gamma RIIA, and Fc gamma RIIB on macrophages and dendritic cells. It also promotes dendritic cell maturation and humoral immunity. In cardiovascular disease, CRP binds to oxidized LDL, exacerbates tissue damage in myocardial infarction, and inhibits the repair of injured vascular endothelium.
5 results for "C-Reactive Protein/CRP Luminex Assays" in Products
5 results for "C-Reactive Protein/CRP Luminex Assays" in Products
C-Reactive Protein/CRP: Luminex Assays
C-Reactive Protein (CRP), also known as Pentraxin 1, is a secreted pentameric protein that functions as a sensor and activator for the innate immune response. In humans, it is a major acute-phase protein; its circulating concentration is dramatically elevated at the onset of inflammation. In mice, however, serum CRP levels increase only slightly during inflammation, and the analogous acute phase role is filled by Pentraxin 2. CRP binds, opsonizes, and induces the phagocytosis of bacteria and apoptotic cells. It regulates activation of the classical complement pathway by binding several proteins in the complement cascade as well as Fc gamma RI, Fc gamma RIIA, and Fc gamma RIIB on macrophages and dendritic cells. It also promotes dendritic cell maturation and humoral immunity. In cardiovascular disease, CRP binds to oxidized LDL, exacerbates tissue damage in myocardial infarction, and inhibits the repair of injured vascular endothelium.
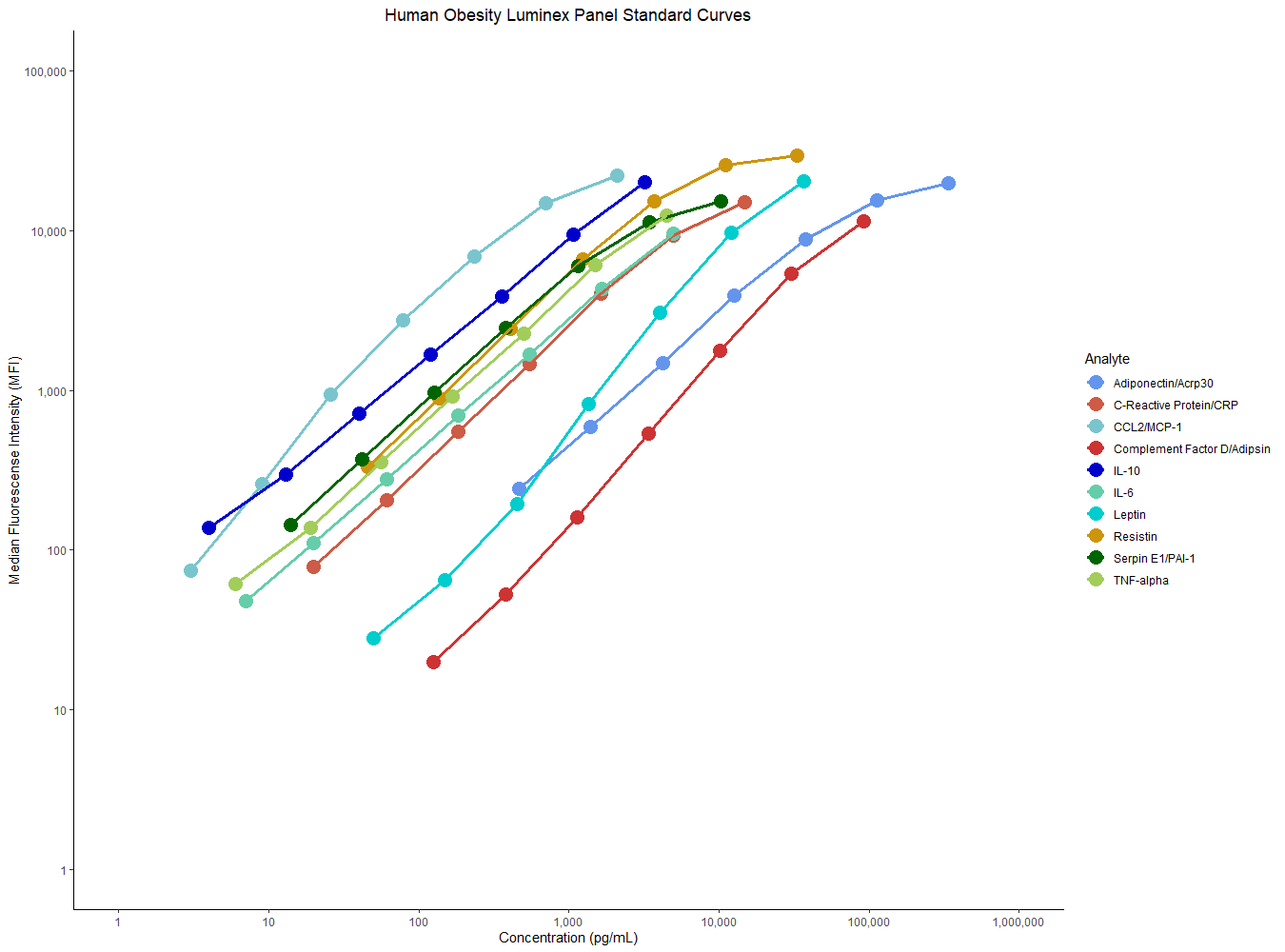
Luminex High Performance Assays go through rigorous development, validation, and quality control testing to ensure you are getting the best performance out of your multiplex assay. Panels are customizable so you can order a selection of the analytes or the entire panel.
Luminex High Performance Assays go through rigorous development, validation, and quality control testing to ensure you are getting the best performance out of your multiplex assay. Panels are customizable so you can order a selection of the analytes or the entire panel.
| Applications: | ELISA |
Luminex Discovery Assays provide the most flexible assays on the market. These panels are completely customizable using our large menu of human, mouse, and rat analytes, making them the perfect tool for biomarker discovery and screening.
Build your own Luminex Assay with our Luminex Assay Customization Tool.
Luminex Discovery Assays provide the most flexible assays on the market. These panels are completely customizable using our large menu of human, mouse, and rat analytes, making them the perfect tool for biomarker discovery and screening.
Build your own Luminex Assay with our Luminex Assay Customization Tool.
Luminex Discovery Assays provide the most flexible assays on the market. These panels are completely customizable using our large menu of human, mouse, and rat analytes, making them the perfect tool for biomarker discovery and screening.
Build your own Luminex Assay with our Luminex Assay Customization Tool.
| Applications: | NULL |