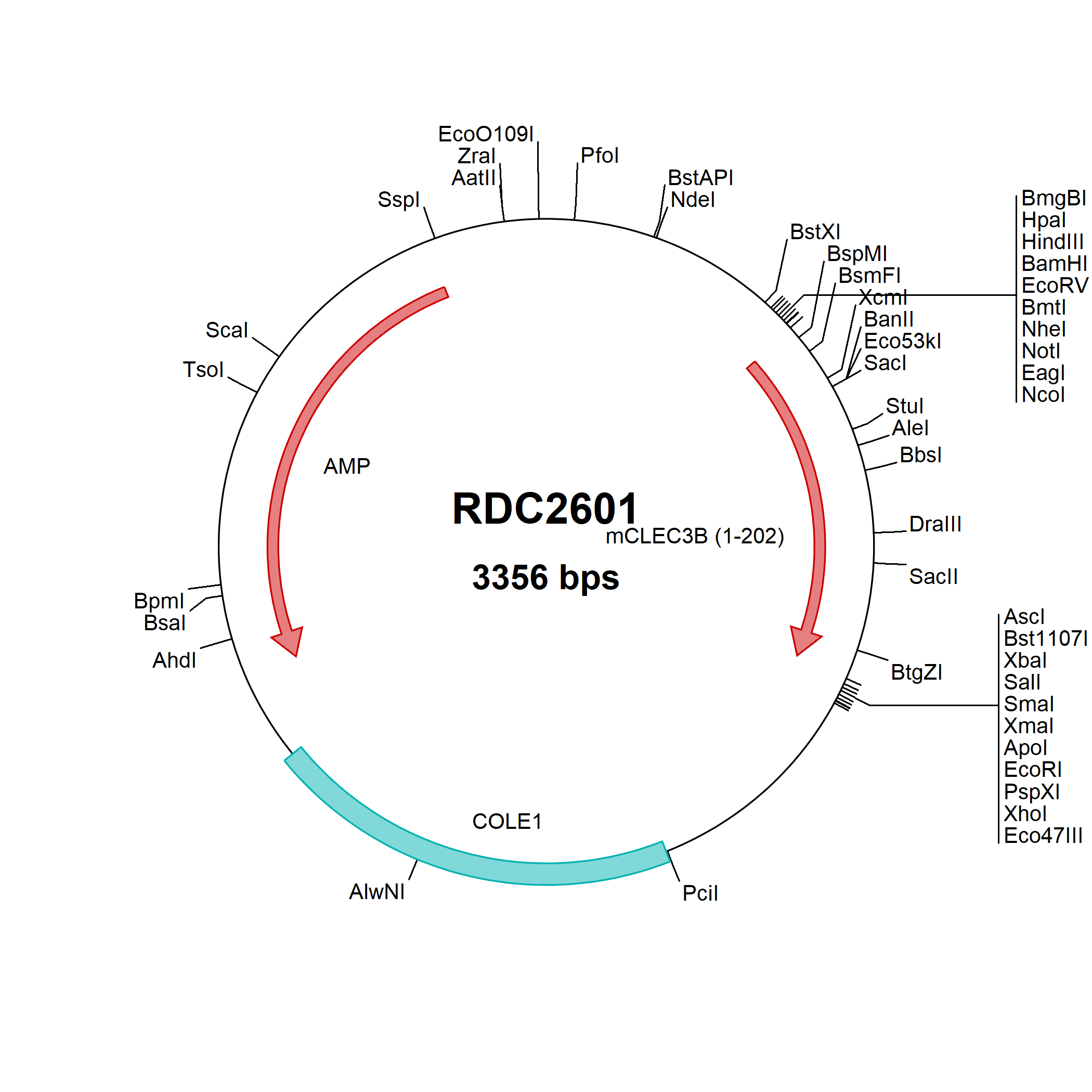
CLEC3B/Tetranectin: cDNA Clones
CLEC3B (C-type lectin domain family 3 member B), also known as Tetranectin, is a 17 kDa O-glycosylated member of the C-type lectin superfamily. Mature human CLEC3B consists of an alpha-helical coiled-coil region followed by one C-type lectin domain (CTLD). It shares 81% amino acid sequence identity with mouse and rat CLEC3B. CLEC3B associates into non-covalent homotrimers, although it was named Tetranectin based on the proposal that it formed tetramers. CLEC3B is secreted by endocrine, epithelial, endothelial, and mesenchymal cells including several hematopoietic cell types. It shows binding selectivity for heparan sulfate, fucoidan, and chondroitin sulfates A, B, and C. CLEC3B binds the Kringle domain-containing proteins Plasminogen, tPA, and HGF, and it enhances the tPA-mediated activation of Plasminogen. It also reduces the ability of Angiostatin (a Plasminogen fragment) to inhibit vascular endothelial cell proliferation. In mouse, CLEC3B is involved in the development and repair of muscle, spine, and skin. CLEC3B is upregulated in stromal cells surrounding various tumors but not in the tumor cells themselves. It is concentrated in the extracellular matrix at the leading edge of malignant tumors, a pattern that overlaps that of Plasminogen.
2 results for "CLEC3B/Tetranectin cDNA Clones" in Products
2 results for "CLEC3B/Tetranectin cDNA Clones" in Products
CLEC3B/Tetranectin: cDNA Clones
CLEC3B (C-type lectin domain family 3 member B), also known as Tetranectin, is a 17 kDa O-glycosylated member of the C-type lectin superfamily. Mature human CLEC3B consists of an alpha-helical coiled-coil region followed by one C-type lectin domain (CTLD). It shares 81% amino acid sequence identity with mouse and rat CLEC3B. CLEC3B associates into non-covalent homotrimers, although it was named Tetranectin based on the proposal that it formed tetramers. CLEC3B is secreted by endocrine, epithelial, endothelial, and mesenchymal cells including several hematopoietic cell types. It shows binding selectivity for heparan sulfate, fucoidan, and chondroitin sulfates A, B, and C. CLEC3B binds the Kringle domain-containing proteins Plasminogen, tPA, and HGF, and it enhances the tPA-mediated activation of Plasminogen. It also reduces the ability of Angiostatin (a Plasminogen fragment) to inhibit vascular endothelial cell proliferation. In mouse, CLEC3B is involved in the development and repair of muscle, spine, and skin. CLEC3B is upregulated in stromal cells surrounding various tumors but not in the tumor cells themselves. It is concentrated in the extracellular matrix at the leading edge of malignant tumors, a pattern that overlaps that of Plasminogen.