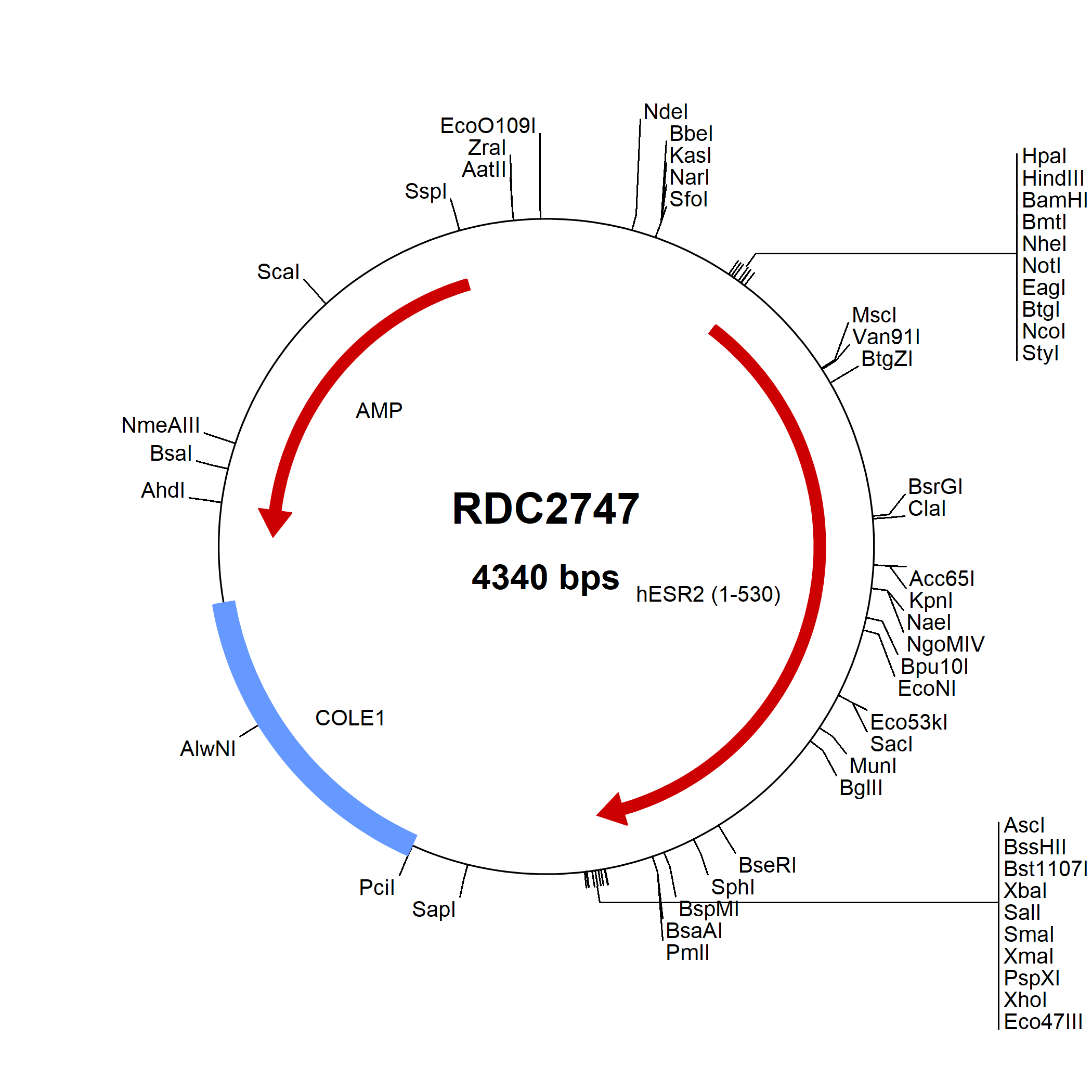
ER beta/NR3A2: cDNA Clones
Estrogen Receptor beta (ERβ,NR3A2) is a member of the steroid receptor family. The natural ligand for ER is the classical estrogenic compound 17β-estradiol. ERβ is expressed in the granulosa cell layer of primary, secondary and mature follicles in the ovary, in bone, bladder, uterus, testis, epididymis, gastrointestinal tract, kidney, breast, heart, vessel wall, immune system, lung, pituitary, hippocampus and hypothalamus. Roles for ERβ in the reproductive and cardiovascular systems have been reported, although these are the subject of conflicting reports. ERβ has been postulated to act primarily as a modulator of ERα function. ER&beta has been shown to form homodimers as well as heterodimers with ERα. Both ERα and ERβ can give rise to numerous isoforms.
1 result for "ER beta/NR3A2 cDNA Clones" in Products
1 result for "ER beta/NR3A2 cDNA Clones" in Products
ER beta/NR3A2: cDNA Clones
Estrogen Receptor beta (ERβ,NR3A2) is a member of the steroid receptor family. The natural ligand for ER is the classical estrogenic compound 17β-estradiol. ERβ is expressed in the granulosa cell layer of primary, secondary and mature follicles in the ovary, in bone, bladder, uterus, testis, epididymis, gastrointestinal tract, kidney, breast, heart, vessel wall, immune system, lung, pituitary, hippocampus and hypothalamus. Roles for ERβ in the reproductive and cardiovascular systems have been reported, although these are the subject of conflicting reports. ERβ has been postulated to act primarily as a modulator of ERα function. ER&beta has been shown to form homodimers as well as heterodimers with ERα. Both ERα and ERβ can give rise to numerous isoforms.