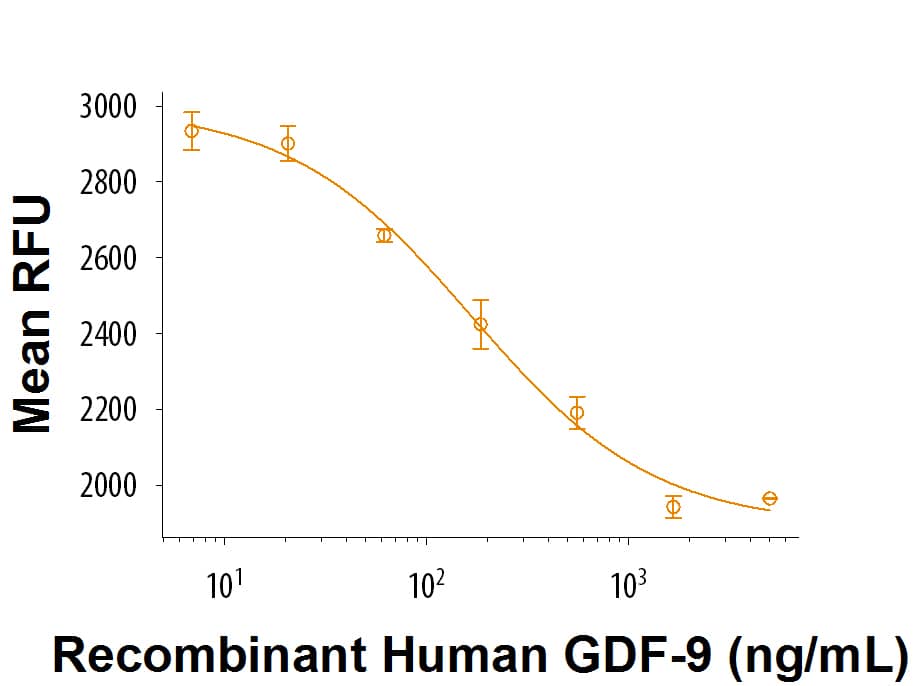
GDF-9: Proteins and Enzymes
Growth Differentiation Factor-9 (GDF-9) is an oocyte-secreted paracrine factor in the TGF-beta superfamily. It forms both non-covalent homodimers and heterodimers with BMP-15, which is coordinately expressed with GDF-9 in the oocyte. GDF-9 signals through TGF-beta RI/ALK-5 and BMPR-II while the GDF-9B/BMP-15 heterodimer is believed to signal through BMPR-II, ALK-4, -5, -7 plus BMPR-IB/ALK-6. SMAD2 and SMAD3 are phosphorylated following activation of receptor complexes by GDF-9.
GDF-9 functions as a paracrine factor in the development of primary follicles in the ovary. It is critical for the growth of granulosa and theca cells and for the differentiation and maturation of the oocyte. GDF-9 is thought to act synergistically with BMP-15 to control the development of the oocyte-cumulus cell complex. In mice, GDF-9:BMP-15 heterodimers have been shown to be more potent regulators of granulosa cell functions compared to GDF-9 homodimers. Aberrant GDF-9 expression and activation are associated with a multitude of common human ovarian disorders including premature ovarian failure and polycystic ovary syndrome.
Products:
3 results for "GDF-9 Proteins and Enzymes" in Products
3 results for "GDF-9 Proteins and Enzymes" in Products
GDF-9: Proteins and Enzymes
Growth Differentiation Factor-9 (GDF-9) is an oocyte-secreted paracrine factor in the TGF-beta superfamily. It forms both non-covalent homodimers and heterodimers with BMP-15, which is coordinately expressed with GDF-9 in the oocyte. GDF-9 signals through TGF-beta RI/ALK-5 and BMPR-II while the GDF-9B/BMP-15 heterodimer is believed to signal through BMPR-II, ALK-4, -5, -7 plus BMPR-IB/ALK-6. SMAD2 and SMAD3 are phosphorylated following activation of receptor complexes by GDF-9.
GDF-9 functions as a paracrine factor in the development of primary follicles in the ovary. It is critical for the growth of granulosa and theca cells and for the differentiation and maturation of the oocyte. GDF-9 is thought to act synergistically with BMP-15 to control the development of the oocyte-cumulus cell complex. In mice, GDF-9:BMP-15 heterodimers have been shown to be more potent regulators of granulosa cell functions compared to GDF-9 homodimers. Aberrant GDF-9 expression and activation are associated with a multitude of common human ovarian disorders including premature ovarian failure and polycystic ovary syndrome.
Products:
| Source: | CHO |
| Accession #: | AAA53035 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | O60383 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Applications: | AC |