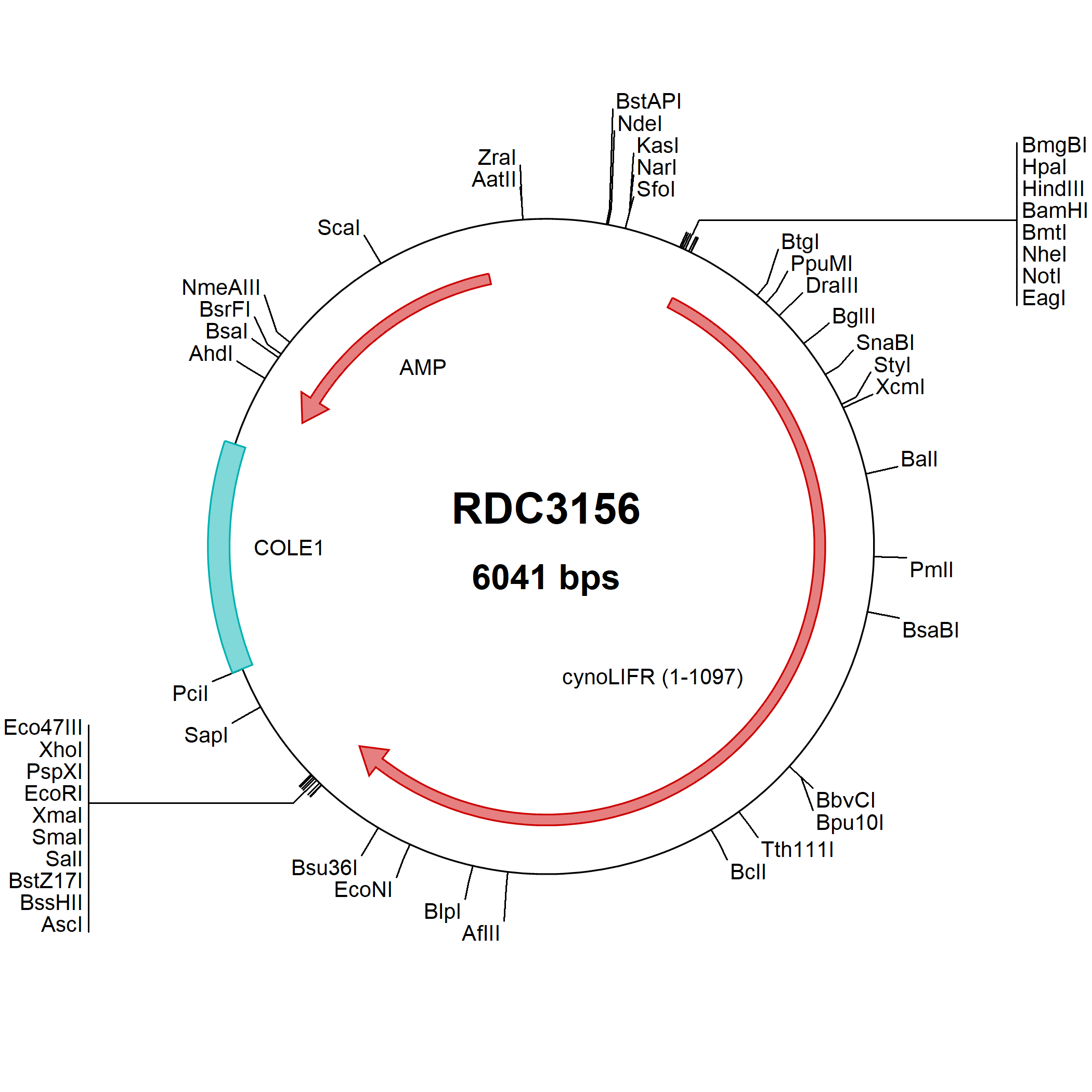
LIFR alpha: cDNA Clones
Based on its helical structure, LIF (Leukemia Inhibitory Factor) is considered a member of the Interleukin-6 family of cytokines. Functionally, it has been implicated in a many physiological processes including development, hematopoiesis, bone metabolism, and inflammation. Some cell types known to express LIF include activated T cells, monocytes, astrocytes, osteoblasts, keratinocytes, regenerating skeletal muscle, mast cells, and fibroblasts.
The activities of LIF are mediated through a high-affinity heterodimeric receptor complex consisting of two membrane glycoproteins: an alpha subunit (LIFR alpha, also known as LIFR beta and CD118) that binds LIF with low affinity and the 130 kDa (gp130) subunit that does not bind LIF by itself, but is required for high-affinity binding of LIF by the complex.
Products:
2 results for "LIFR alpha cDNA Clones" in Products
2 results for "LIFR alpha cDNA Clones" in Products
LIFR alpha: cDNA Clones
Based on its helical structure, LIF (Leukemia Inhibitory Factor) is considered a member of the Interleukin-6 family of cytokines. Functionally, it has been implicated in a many physiological processes including development, hematopoiesis, bone metabolism, and inflammation. Some cell types known to express LIF include activated T cells, monocytes, astrocytes, osteoblasts, keratinocytes, regenerating skeletal muscle, mast cells, and fibroblasts.
The activities of LIF are mediated through a high-affinity heterodimeric receptor complex consisting of two membrane glycoproteins: an alpha subunit (LIFR alpha, also known as LIFR beta and CD118) that binds LIF with low affinity and the 130 kDa (gp130) subunit that does not bind LIF by itself, but is required for high-affinity binding of LIF by the complex.
Products: