Notch-1 Products
Notch proteins (so named for 'notches' in fly wings) are type I transmembrane glycoproteins involved in specifying cell fates and defining boundaries between different cell types during developmental processes. Notch extracellular domains are large, having 34-36 EGF-like repeats followed by three notch/Lin-12 repeats. Notch proteins interact wi...
224 results for "Notch-1" in Products
224 results for "Notch-1" in Products
Notch-1 Products
Notch proteins (so named for 'notches' in fly wings) are type I transmembrane glycoproteins involved in specifying cell fates and defining boundaries between different cell types during developmental processes. Notch extracellular domains are large, having 34-36 EGF-like repeats followed by three notch/Lin-12 repeats. Notch proteins interact wi...
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Human IgG2 Monoclonal Clone #Pfizer patent anti-Notch1 |
| Applications: | ELISA, Flow, Func |
Notch-1 Antibody (Pfizer patent anti-Notch1) - Humanized, IgG2SA - Low Endotoxin, Azide and BSA Free

Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Human IgG2 Monoclonal Clone #Pfizer patent anti-Notch1 |
| Applications: | ELISA, Flow, Func |
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Human IgG2 Monoclonal Clone #Pfizer patent anti-Notch1 |
| Applications: | ELISA, Flow, Func |
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Human IgG2 Monoclonal Clone #Pfizer patent anti-Notch1 |
| Applications: | ELISA, Flow, Func |
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Human IgG2 Monoclonal Clone #Pfizer patent anti-Notch1 |
| Applications: | ELISA, Flow, Func |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Sheep IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB, Flow, ChIP, CyTOF-ready, ICC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat (Negative) |
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 kappa Monoclonal Clone #mN1A |
| Applications: | IHC, WB, ICC/IF, Flow, IP, +2 More |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Details: | Rabbit Serum Polyclonal |
| Applications: | IHC, WB, ELISA, ICC/IF, IP |
| Reactivity: | Mouse, Rat |
| Details: | Goat IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB, Flow, IHC, Block, CyTOF-ready, +1 More |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | IHC, WB, ICC/IF, KD, Simple Western |
| Reactivity: | Mouse |
| Details: | Sheep IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB, IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Details: | Mouse IgG2B Monoclonal Clone #OTI3E12 |
| Applications: | IHC, WB, ICC/IF |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat, Canine, Bovine |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Sheep IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG2a Monoclonal Clone #433802 |
| Applications: | WB, ICC |
Contains 4 membranes - 2 spotted in duplicate with 62 different non-hematopoietic antibodies and 2 spotted in duplicate with 57 common antibodies
| Source: | NS0 |
| Accession #: | P46531 |
| Applications: | Bind |
| Reactivity: | Mouse |
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 Monoclonal Clone #N1A |
| Applications: | CyTOF-ready, ICFlow |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 Monoclonal Clone #527425 |
| Applications: | Flow, CyTOF-ready |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 Monoclonal Clone #527425 |
| Applications: | Flow |
| Source: | NS0 |
| Accession #: | Q07008.2 |
| Applications: | Bind |
| Assay Range: | 78.1 - 5,000 pg/mL |
| Applications: | ELISA |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | IHC, WB, ELISA, ICC/IF |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Sheep IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Mouse |
| Details: | Sheep IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB |


![Flow Cytometry: Notch-1 Antibody (mN1A) - BSA Free [NB100-78486] Flow Cytometry: Notch-1 Antibody (mN1A) - BSA Free [NB100-78486]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/Notch-1-Antibody-mN1A-Flow-Cytometry-NB100-78486-img0007.jpg)
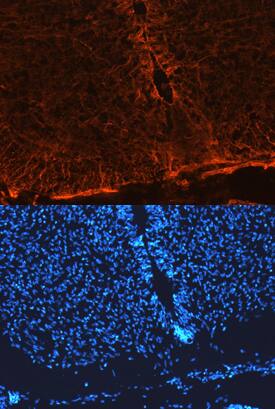
![Immunohistochemistry: Notch-1 Antibody - (Cleaved N terminal) [NB300-251] Immunohistochemistry: Notch-1 Antibody - (Cleaved N terminal) [NB300-251]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/Notch-1-Antibody-Cleaved-N-terminal-Immunohistochemistry-NB300-251-img0007.jpg)
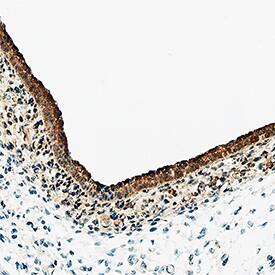
![Immunohistochemistry: Notch-1 Antibody - BSA Free [NBP1-78292] Immunohistochemistry: Notch-1 Antibody - BSA Free [NBP1-78292]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/Notch-1-Antibody-Immunohistochemistry-NBP1-78292-img0003.jpg)
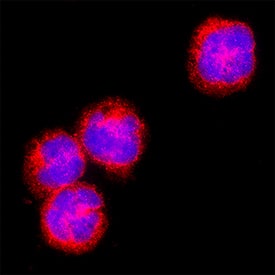
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: Notch-1 Antibody (OTI3E12) [NBP1-48289] Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: Notch-1 Antibody (OTI3E12) [NBP1-48289]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/Notch-1-Antibody-3E12-Immunocytochemistry-Immunofluorescence-NBP1-48289-img0032.jpg)
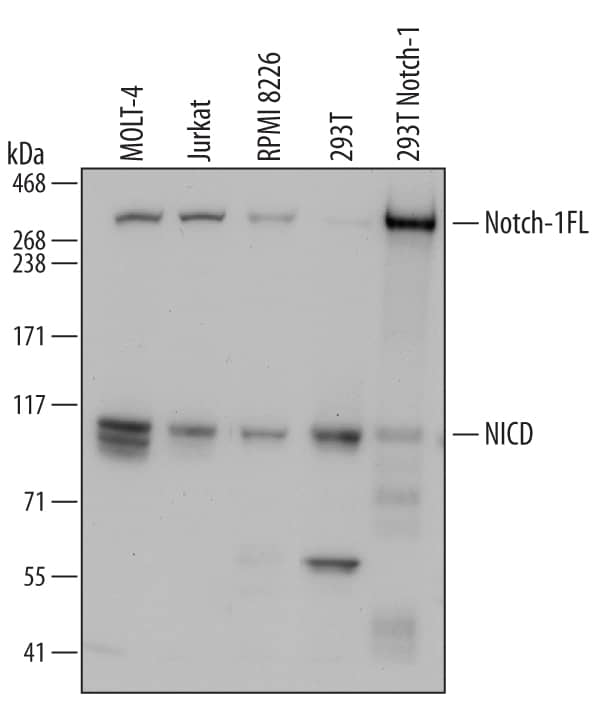
![Western Blot: Notch-1 Antibody [NBP2-24771] Western Blot: Notch-1 Antibody [NBP2-24771]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/Notch-1-Antibody-Western-Blot-NBP2-24771-img0002.jpg)






![Immunohistochemistry: Notch-1 Antibody - Azide and BSA Free [Notch-1] - Notch-1 Antibody - Azide and BSA Free](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nbp2-95105_rabbit-polyclonal-notch-1-antibody-5220251638038.jpg)