Human CD45 Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # MAB14302

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Applications
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Thr24-Asn575
Accession # P08575
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Human CD45 Antibody
CD45 in Human PBMCs and MCF-7 Cell Line.
CD45 was detected in immersion fixed human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (positive staining; left panel) and MCF-7 human breast cancer cell line (negative staining; right panel) using Mouse Anti-Human CD45 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB14302) at 8 µg/mL for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained using the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (red; Catalog # NL007) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Specific staining was localized to cell surfaces. View our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Non-adherent Cells.CD45 in Human Tonsil.
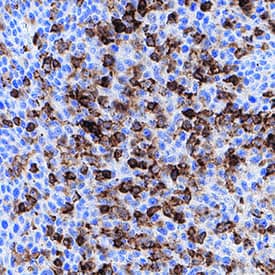
CD45 was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human tonsil using Mouse Anti-Human CD45 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB14302) at 15 µg/mL for 1 hour at room temperature followed by incubation with the Anti-Mouse IgG VisUCyte™ HRP Polymer Antibody (Catalog # VC001). Before incubation with the primary antibody, tissue was subjected to heat-induced epitope retrieval using Antigen Retrieval Reagent-Basic (Catalog # CTS013). Tissue was stained using DAB (brown) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to cytoplasm in lymphocytes. View our protocol for IHC Staining with VisUCyte HRP Polymer Detection Reagents.Detection of Mouse CD45 by Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence
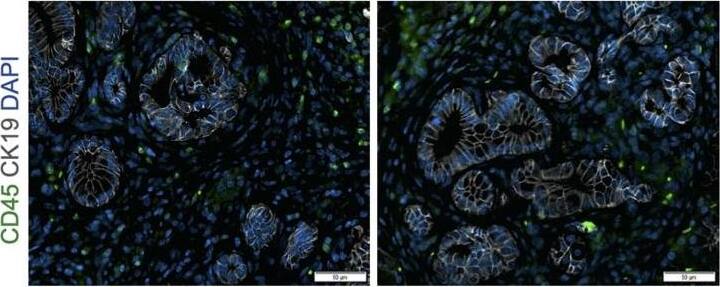
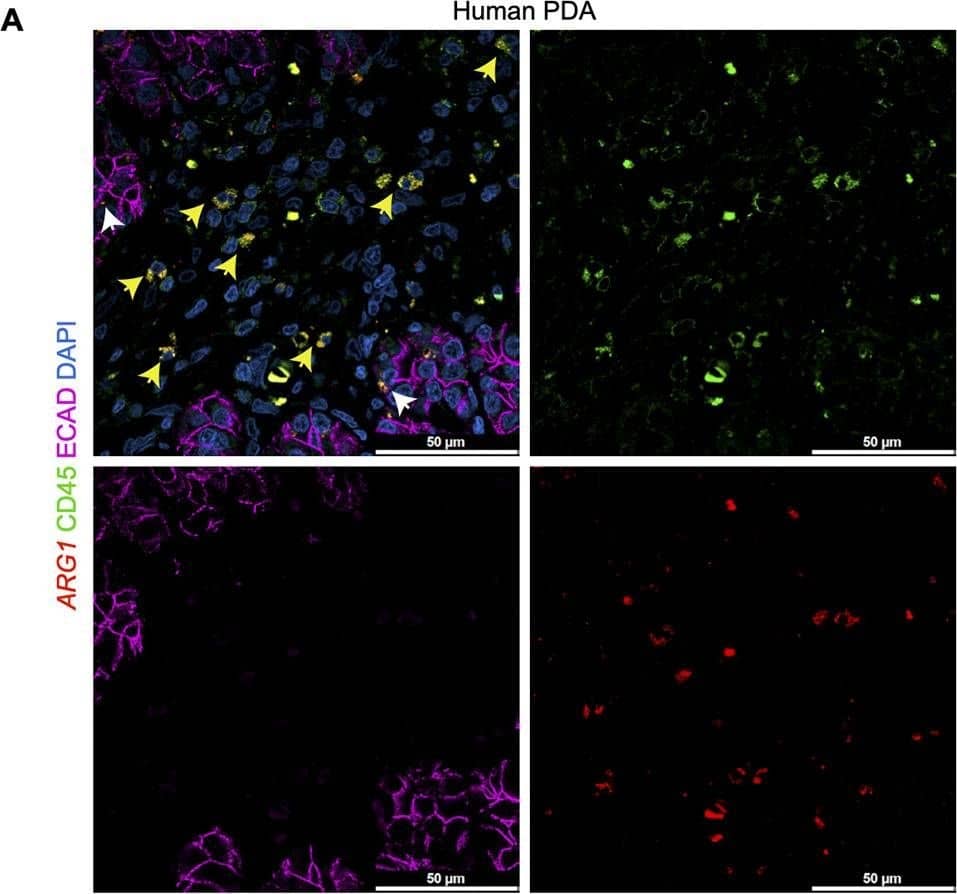
Deletion of Arginase 1 (Arg1) in myeloid cells decreases cell proliferation and cell death during early stages of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.(A) Experimental design for KF and KFCA mice aged to 2 mo. (B) Representative images of co-immunofluorescence staining for ARG1 (red), macrophages (F4/80, green), epithelial (CK19, gray), and DAPI (blue) in KF and KFCA pancreata at 2 mo. Yellow staining shows co-localization of ARG1 and F4/80. Scale bar, 50 μm. Quantification on the right, n=4–6/group (C) Representative hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) images for KF and KFCA mice at 2 mo, n=6–7/group. Scale bar, 100 μm. On the right, percentage of ADM/PanIN lesions area in KF and KFCA tissue at 2 mo, n=6–7/group. (D) Representative immunohistochemistry staining for total cell proliferation (Ki67) and total cell death (cleaved caspase-3 [CC3]). Scale bar, 100 μm. Quantification on the right, n=6–7/group. (E) Representative immunofluorescence staining for immune cells (CD45, green) and epithelial cells (CK19, gray). Scale bar, 50 μm. Quantification on the right, n=4/group. (F) Representative immunohistochemistry staining for macrophages (F4/80) and CD8+ T cells (CD8) in KF and KFCA tissue at 2 mo. Scale bar, 100 μm. Positive staining quantification is shown on the right. Student’s t test was used to determine significance. Statistically significant when p<0.005. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36727849), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Applications for Human CD45 Antibody
Immunocytochemistry
Sample: Immersion fixed human peripheral blood mononuclear cells and MCF‑7 human breast cancer cell line
Immunohistochemistry
Sample: Immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human tonsil
Reviewed Applications
Read 1 review rated 5 using MAB14302 in the following applications:
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: CD45
CD45, previously called LCA (leukocyte common antigen), T200, or Ly5 in mice, is member C of the class 1 (receptor‑like) protein tyrosine phosphatase family (PTPRC) (1, 2). It is a variably glycosylated 180‑220 kDa transmembrane protein that is abundantly expressed on all nucleated cells of hematopoietic origin (1‑3). CD45 has several isoforms, expressed according to cell type, developmental stage and antigenic exposure (1‑5). The longest form, CD45RABC (called B220 in mouse), is expressed on B lymphocytes (5). The CD45RABC cDNA encodes 1304 amino acids (aa), including a 23 aa signal sequence, a 552 aa extracellular domain containing the splicing region, a cysteine‑rich region and two fibronectin type III domains, a 22 aa transmembrane sequence, and a 707 aa cytoplasmic domain that contains two phosphatase domains, D1 and D2. Only D1 has phosphatase activity. CD45R0 is the shortest form, lacking exons 4, 5 and 6 which encode aa 32‑191. It is expressed on memory cells, while intermediate sizes are expressed on other T cells (3, 4, 6). CD45 has been best studied in T cells, where it determines T cell receptor signaling thresholds (3, 6‑8). CD45 is moved into or out of the immunological synapse (IS) membrane microdomain depending on the relative influence of interaction with the extracellular galectin lattice or the intracellular actin cytoskeleton (9, 10). Galectin interaction can be fine‑tuned by varying usage of the heavily O‑glycosylated spliced regions and sialylation of N‑linked carbohydrates (4, 9). Within the IS, CD45 dephosphorylates and negatively regulates the Src family kinase, Lck (8‑10). In other leukocytes, CD45 influences differentiation and links immunoreceptor signaling with cytokine secretion and cell survival, partially overlapping in function with DEP‑1/CD148 (11‑14). CD45 deletion causes in severe immunodeficiency, while point mutations may be associated with autoimmune disorders (6, 7).
References
- Anderson, J.N. et al. (2004) FASEB J. 18:8.
- Streuli, M. et al. (1987) J. Exp. Med. 166:1548.
- Hermiston, M.L. et al. (2003) Annu. Rev. Immunol. 21:107.
- Earl, L.A. and L.G. Baum (2008) Immunol. Cell Biol. 86:608.
- Ralph, S.J. et al. (1987) EMBO J. 6:1251.
- Falahti, R. and D. Leitenberg (2008) J. Immunol. 181:6082.
- Tchilian, E.Z. and P.C.L. Beverley (2006) Trends Immunol. 27:146.
- McNiell, L. et al. (2007) Immunity 27:425.
- Chen, I-J. et al. (2007) J. Biol. Chem. 282:35361.
- Freiberg, B.A. et al. (2002) Nat. Immunol. 3:911.
- Zhu, J.W. et al. (2008) Immunity 28:183.
- Huntington, N.D. et al. (2006) Nat. Immunol. 7:190.
- Hesslein, D.G. et al. (2006) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103:7012.
- Cross, J.L. et al. (2008) J. Immunol. 180:8020.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional CD45 Products
Product Documents for Human CD45 Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human CD45 Antibody
For research use only