Human Dkk-2 Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # MAB6628

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Applications
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Met1-Ile259
Accession # NP_055236
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Human Dkk-2 Antibody
Dkk‑2 in SH-SY5Y Human Cell Line.
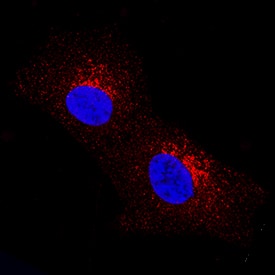
Dkk-2 was detected in immersion fixed SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cell line using Mouse Anti-Human Dkk-2 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB6628) at 8 µg/mL for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained using the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (red; Catalog # NL007) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Specific staining was localized to cytoplasm. View our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Cells on Coverslips.Dkk‑2 in Human Kidney.
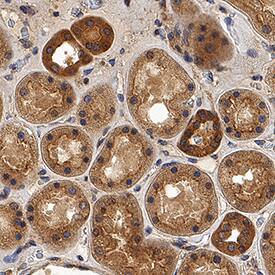
Dkk-2 was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human kidney using Mouse Anti-Human Dkk-2 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB6628) at 5 µg/mL for 1 hour at room temperature followed by incubation with the Anti-Mouse IgG VisUCyte™ HRP Polymer Antibody (Catalog # VC001). Before incubation with the primary antibody, tissue was subjected to heat-induced epitope retrieval using Antigen Retrieval Reagent-Basic (Catalog # CTS013). Tissue was stained using DAB (brown) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to cytoplasm in convoluted tubules. View our protocol for IHC Staining with VisUCyte HRP Polymer Detection Reagents.Detection of DKK-2 in Human SHSY-5Y Cells by Flow Cytometry
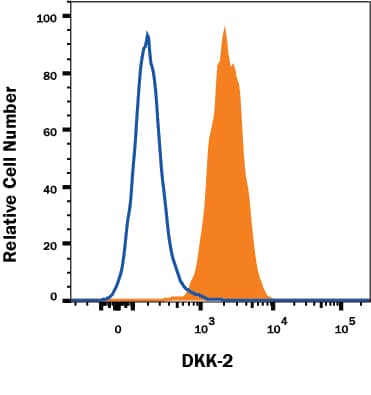
Human SHSY-5Y neuroblastoma cell line was stained with Mouse Anti-Human DKK-2 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB6628, filled histogram) or Mouse IgG2A Isotype Control Antibody (Catalog # MAB003, open histogram) followed by Goat anti-Mouse IgG PE-conjugated Secondary Antibody (Catalog # F0102B). To facilitate intracellular staining, cells were fixed and permeabilized with FlowX FoxP3 Fixation & Permeabilization Buffer Kit (Catalog # FC012). View our protocol for Staining Intracellular Molecules.Applications for Human Dkk-2 Antibody
Immunocytochemistry
Sample: Immersion fixed SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cell line
Immunohistochemistry
Sample:
Immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human kidney
Intracellular Staining by Flow Cytometry
Sample: Human SHSY-5Y neuroblastoma cell line fixed and permeabilized with FlowX FoxP3 Fixation & Permeabilization Buffer Kit (Catalog # FC012)
Reviewed Applications
Read 1 review rated 5 using MAB6628 in the following applications:
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Dkk-2
Dickkopf related protein 2 (Dkk-2) is a member of the Dickkopf family of secreted Wnt modulators (1-3). Dkk proteins contain a signal peptide and two conserved cysteine-rich domains that are separated by a linker region. The second cysteine-rich domain mediates Dkk-2 binding activities, and its interaction with beta-propeller domains of LRP‑5/6 has been mapped (2-4, 7). The 226 amino acid (aa), ~35 kDa mature human Dkk-2 shares 96%, 97%, 97%, 97%, 97% and 98% aa identity with mouse, rat, canine, equine, bovine and porcine Dkk-2, respectively. Mouse Dkk-2 can activate the canonical Wnt signaling pathway in Xenopus embryos, showing evolutionary conservation of function (5). Dkk proteins modify Wnt engagement of a receptor complex composed of a Frizzled protein and a low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein, either LRP‑5 or LRP‑6 (3). Also, Kremen-1 and Kremen-2 are high affinity receptors for Dkk-1 and Dkk-2 (9). When LRP‑6 is over-expressed, direct high‑affinity binding of Dkk-2 to LRP can enhance canonical Wnt signaling (6-8). However, when Dkk‑2 and LRP‑6 form a ternary complex with Kremen‑2, Wnt signaling is inhibited due to internalization of Dkk‑2/LRP6/Krm2 complexes (9, 10). Thus, depending on the cellular context, Dkk‑2 can either activate or inhibit canonical Wnt signaling (3). In contrast, binding of Dkk-1 or Dkk-4 to LRP is consistently antagonistic (3). Dkk proteins are expressed in mesenchymal tissues and control epithelial transformations. Dkk-2 expression has been studied most in bone and eye, although it is expressed as early as periimplantation in mice (11). Mouse Dkk-1 or Dkk-2 deficiencies have opposite effects on bone homeostasis, despite down‑regulating Wnt antagonism in both cases (12, 13). Dkk-2 expression is induced by Wnts in bone, and is thought to enhance bone density by promoting terminal differentiation of osteoblasts and mineral deposition (12). In contrast, Dkk-1 negatively regulates late osteoblast proliferation, which limits bone density (13). Dkk-2-deficient mice are blind, exhibiting faulty differentiation of corneal epithelium and ectopic blood vessels in the periocular mesenchyme (14, 15).
References
- Monaghan, A.P. et al. (1999) Mech. Dev. 87:45.
- Krupnik, V.E. et al. (1999) Gene 238:301.
- Niehrs, C. (2006) Oncogene 25:7469.
- Chen, L. et al. (2008) J. Biol. Chem. 283:23364.
- Wu, W. et al. (2000) Current Biol. 10:1611.
- Mao, B. et al. (2001) Nature 411:321.
- Li, L. et al. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277:5977.
- Brott, B. and S.Y. Sokol (2002) Mol. Cell. Biol. 22:6100.
- Mao, B. et al. (2002) Nature 417:664.
- Mao, B. and C. Niehrs (2003) Gene 302:179.
- Zhang, Y. et al. (2009) J. Reprod. Dev. 55:17.
- Li, X. et al. (2005) Nat. Genet. 37:945.
- van der Horst, G. et al. (2005) J. Bone Miner. Res. 20:1867.
- Mukhopadhyay, M. et al. (2006) Development 133:2149.
- Gage, P.J. et al. (2008) Dev. Biol. 317:310.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional Dkk-2 Products
Product Documents for Human Dkk-2 Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human Dkk-2 Antibody
For research use only