Human HVEM/TNFRSF14 Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # MAB3561

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Pro37-Val202 (predicted)
Accession # Q92956.3
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Human HVEM/TNFRSF14 Antibody
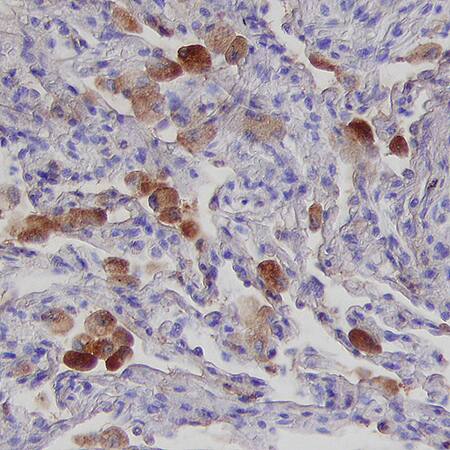
HVEM/TNFRSF14 in Human Lung.
Herpesvirus Entry Mediator (HVEM/TNFRSF14) was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human lung using Mouse Anti-Human HVEM/TNFRSF14 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB3561) at 15 µg/mL for 1 hour at room temperature followed by incubation with the Anti-Mouse IgG VisUCyte™ HRP Polymer Antibody (Catalog # VC001). Tissue was stained using DAB (brown) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to cytoplasm. View our protocol for IHC Staining with VisUCyte HRP Polymer Detection Reagents.Applications for Human HVEM/TNFRSF14 Antibody
Immunohistochemistry
Sample: Immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human lung
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: HVEM/TNFRSF14
Herpesvirus entry mediator (HVEM), also referred to as TR2 (TNF receptor-like molecule) and ATAR (another TRAF-associated receptor), is a type I membrane protein belonging to the TNF/NGF receptor superfamily. In the TNF superfamily nomenclature, HVEM is referred to as TNFRSF14. Human HVEM cDNA encodes a 283 amino acid (aa) residue protein with a probable 36 aa residue signal peptide, a 166 aa residue extracellular domain, a 23 aa residue transmembrane region and a 58 aa residue cytoplasmic region. The extracellular domain of HVEM contains several cysteine-rich repeats characteristic of TNF receptor superfamily members. The short cytoplasmic region lacks a death domain present in some TNF receptor family members, but contains a TRAF (TNF receptor-associated factor) interaction domain. HVEM expression has been detected in peripheral blood T cells, B cells, monocytes and in various tissues enriched in lymphoid cells. The extracellular domain of HVEM has been shown to interact directly with the herpes simplex virus envelope glycoprotein D. Two TNF superfamily ligands, including the secreted TNF‑ beta (lymphotoxin alpha) and the membrane protein LIGHT (lymphotoxins, exhibits inducible expression, and competes with HSV glycoprotein D for HVEM, a receptor expressed by T lymphocytes), have been shown to be the cellular ligands for HVEM. Besides HVEM, LIGHT can also interact with LT betaR, the receptor for lymphotoxin alpha beta heterotrimer. The role of the HVEM-LIGHT/LT beta receptor-ligand pair in immune function and herpesvirus pathobiology remains to be elucidated.
References
- Hsu, H. et al. (1997) J. Biol. Chem. 272:13471.
- Mauri, D.N. et al. (1998) Immunity 8:21.
- Montgomery, R.I. et al. (1996) Cell 87:427.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional HVEM/TNFRSF14 Products
Product Documents for Human HVEM/TNFRSF14 Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human HVEM/TNFRSF14 Antibody
For research use only