Human/Mouse Caspase-8 Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # AF705

Key Product Details
Validated by
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Ser234-Asp496
Accession # AAC50645
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Human/Mouse Caspase-8 Antibody
Detection of Human and Mouse Caspase‑8 by Western Blot.
Western blot shows lysates of Jurkat human leukemic T cell line and DA3 mouse myeloma cell line treated with 1 µM staurosporine for the indicated time. PVDF membrane was probed with 0.5 µg/mL Goat Anti-Human/Mouse Caspase-8 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF705) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF017). Specific bands for Caspase-8 precursor were detected at approximately 60 kDa (as indicated in upper panal) and specific bands for cleaved Caspase-8 were detected at approximately 14-18 kDa (as indicated in lower panal). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 4.Western Blot Shows Human Caspase‑8 Specificity by Using Knockout Cell Line.
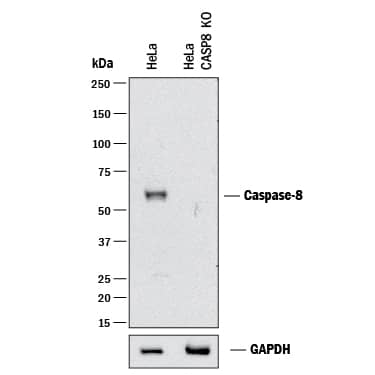
Western blot shows lysates of HeLa human cervical epithelial carcinoma parental cell line and Caspase-8 knockout HeLa cell line (KO). PVDF membrane was probed with 0.5 µg/mL of Goat Anti-Human/Mouse Caspase-8 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF705) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF017). A specific band was detected for Caspase-8 at approximately 58 kDa (as indicated) in the parental HeLa cell line, but is not detectable in knockout HeLa cell line. GAPDH (Catalog # AF5718) is shown as a loading control. This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 1.Detection of Human Caspase‑8 by Simple WesternTM.
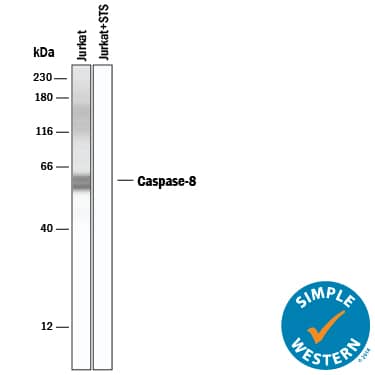
Simple Western lane view shows lysates of Jurkat human acute T cell leukemia cell line untreated or treated with Staurosporine (STS) for 2 hours, loaded at 0.2 mg/mL. Specific bands were detected for Caspase-8 at approximately 59 kDa (as indicated) using 5 µg/mL of Goat Anti-Human/Mouse Caspase-8 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF705) followed by 1:50 dilution of HRP-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF109). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using the 12-230 kDa separation system.Applications for Human/Mouse Caspase-8 Antibody
Knockout Validated
Simple Western
Sample: Jurkat human acute T cell leukemia cell line
Western Blot
Sample: Jurkat human leukemic T cell line and DA3 mouse myeloma cell line treated with 1 µM staurosporine
Reviewed Applications
Read 1 review rated 3 using AF705 in the following applications:
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Caspase-8
Caspase-8 (Cysteine-aspartic acid protease 8/Casp8a; also named MCH5, FLICA and MACH alpha1) is a 28 kDa member of the peptidase C14A family of enzymes (1, 2, 3). It is widely expressed and is considered an initiating caspase for the apoptotic cascade (4). Caspase-8 acts on a wide variety of substrates, including procaspases-3, 4, 6, 7, 9 and 10, c-FLIPL and procaspase‑8 itself (1, 5, 6). Human procaspase-8a is a 54‑56 kDa, 479 amino acid (aa) protein (4, 7, 8, 9). It contains two N-terminal death domains (aa 1‑177), followed by a catalytic site that utilizes His317Gly318 plus Cys360. Normally, it is an inactive, cytosolic monomer (1, 10, 11). But following death-domain (DD) containing receptor oligomerization, Caspase-8 is recruited to the death-inducing signaling complex (DISC) that forms around the death domains of the oligomerized receptor (12). FADD/CAP-1 is recruited first, followed by procaspase-8/CAP-4 and, possibly, c-FLIPL and procaspase-10 (12). The recruitment, or concentration, of procaspase-8 induces homodimerization. This act alone is sufficient for activation. However, the activity level is modest at best, and appears to be directed towards either itself, or c-FLIPL, which is known to form a functional heterodimer with procaspase-8 (5, 11). When directed towards itself, autocleavage occurs first between Asp374Ser375, generating a 43 kDa (p43) N-terminal (aa 1‑374) and an 11 kDa C‑terminal (aa 375‑479) fragment. The C-terminus is further cleaved between Asp384Leu385 to generate a mature p10 subunit (aa 385‑479). The p43 subunit is next cleaved twice, once between Asp216Ser217, and again between Asp210Ser211 to generate a 26 kDa DD-containing prodomain (aa 1‑210) with an additional 18 kDa mature p18 subunit (aa 217‑374) (12). p18 and p10 noncovalently associate to form a 28 kDa heterodimer, which subsequently associates with another p18:p10 heterodimer to form an active, mature Caspase-8 molecule. This leaves the DISC to act on downstream apoptotic procaspases. In the event procaspase-8 comes to the DISC complexed with c‑FLIPL, c‑FLIPL will be cleaved by procaspase-8, generating a p43 fragment that is analogous to the Caspase-8 p43 subunit. This fragment, however, appears not to be an intermediate in a proteolytic cascade. Rather, it serves as a functional subunit, interacting with TRAF2 and activating NF kappaB. This may account for many of the nonapoptotic activities associated with Caspase-8 (5, 6, 13). Mature human and mouse Caspase-8a heterodimers are 73% aa identical (14).
References
-
Chowdhury, I. et al. (2008) Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B 151:10.
-
Boatright, K.M. & G.S. Salvesen (2003) Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 15:725.
-
Launay, S. et al. (2005) Oncogene 24:5137.
-
Srinivasula, S.M. et al. (1996) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93:14486.
-
Hughes, M.A. et al. (2009) Mol. Cell 35:265.
-
Lamkanfi, M. et al. (2007) Cell Death Differ. 14:44.
-
Fernandes-Alnemri, T. et al. (1996) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93:7464.
-
Boldin, M.P. et al. (1996) Cell 85:803.
-
Muzio, M. et al. (1996) Cell 85:817.
-
Donepudi, M. et al. (2003) Mol. Cell 11:543.
-
Boatright, K.M. et al. (2003) Mol. Cell 11:529.
-
Golks, A. et al. (2006) Cell Death Differ. 13:489.
-
Scaffidi, C. et al. (1997) J. Biol. Chem. 272:26953.
-
Sakamaki, K. et al. (1998) Eur. J. Biochem. 253:399.
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional Caspase-8 Products
Product Documents for Human/Mouse Caspase-8 Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human/Mouse Caspase-8 Antibody
For research use only