Mouse AHR Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # AF6697

Key Product Details
Validated by
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Asn706-Ser805 (Thr758Ala)
Accession # P30561
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Mouse AHR Antibody
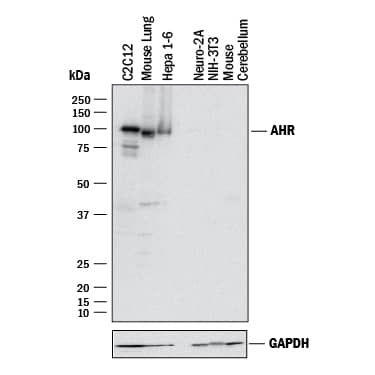
Detection of Mouse AHR by Western Blot.
Western blot shows lysates of C2C12 mouse myoblast cell line, mouse lung tissue, Hepa 1-6 mouse hepatoma cell line, Neuro-2A mouse neuroblastoma cell line (negative control), NIH-3T3 mouse embryonic fibroblast cell line (negative control), and mouse cerebellum tissue (negative control). PVDF membrane was probed with 1 µg/mL of Sheep Anti-Mouse AHR Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF6697) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Sheep IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF016). A specific band was detected for AHR at approximately 110 kDa (as indicated). GAPDH(Catalog # AF5718) is shown as a loading control. This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 1.AHR in C2C12 Mouse Cell Line.
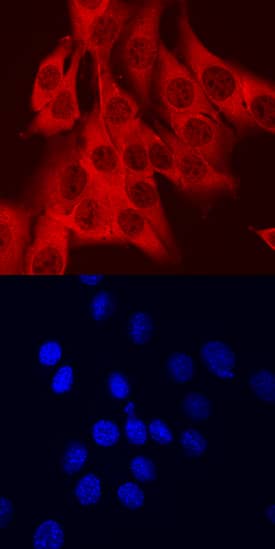
AHR was detected in immersion fixed C2C12 mouse myoblast cell line using Sheep Anti-Mouse AHR Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF6697) at 10 µg/mL for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained using the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Sheep IgG Secondary Antibody (red, upper panel; Catalog # NL010) and counterstained with DAPI (blue, lower panel). Specific staining was localized to nuclei and cytoplasm. View our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Cells on Coverslips.Detection of Mouse AHR by Western Blot
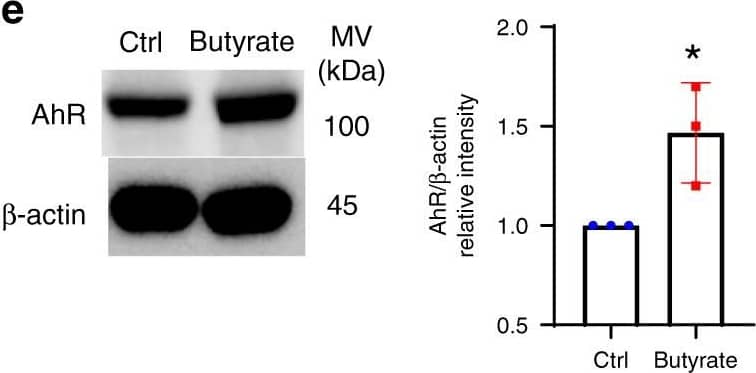
HIF1 alpha and AhR mediate butyrate induction of IL-22 in CD4+ T cells.a WT CD4+ T cells were activated with anti-CD3/CD28 mAbs under Th1 conditions ± butyrate (0.5 mM) for 2 days (n = 3 biologically independent samples per group). RNA sequencing was performed. Hif1 alpha, Ahr, and Prdm1 were shown in heatmap. b–f CD4+ T cells were activated with anti-CD3/CD28 mAbs ± butyrate (0.5 mM) under Th1 conditions (n = 3/group). Hif1a (b) and Ahr (c) were analyzed by qRT-PCR. HIF1 alpha (d) and AhR (e) protein was analyzed by western blot on day 2. HIF1 alpha activity was measured using HIF1 alpha Transcription Factor Assay Kit (f). g Raw 264.7 cells were transduced with XRE/AhR Luciferase Reporter Gene Lentivirus, and treated ± butyrate (0.5 mM) 3 days post transduction. AhR activity was assessed by luciferase. h–j Cbir1 Tg CD4+ T cells were activated with APCs and Cbir1 peptide under Th1 conditions with butyrate (0.5 mM) ± YC-1 (5 µM) or/and CH-223191 (3 µM) for 60 h (n = 3/group). IL-22 mRNA (h) and protein (i) were measured by qRT-PCR and ELISA. j IL-22 was measured by flow cytometry on day 5. k WT and HIF1 alpha−/− CD4+ T cells were activated with anti-CD3/CD28 mAbs ± butyrate (0.5 mM) for 5 days (n = 3/group). IL-22 was assessed by flow cytometry. l, m CD4+ T cells were activated with anti-CD3/CD28 mAbs under Th1 conditions with or without butyrate (0.5 mM), AR420626 (5 µM), or TSA (10 nM) for 60 h (n = 3/group). Hif1a (l) and Ahr (m) were measured by qRT-PCR. One representative of three independent experiments was shown (b–m). Data were expressed as mean ± SD. Statistical significance was tested by two-tailed unpaired Student t-test (b–g) or two-tailed one-way ANOVA (h–m). b **p = 0.0033 (24 h), ***p = 0.0002 (36 h), **p = 0.0032 (48 h), *p = 0.0310 (60 h); c *p = 0.0338 (24 h), **p = 0.0054 (36 h), ***p = 0.0003 (48 h), ***p = 0.0007 (60 h); d *p = 0.0178; e *p = 0.0325; f *p = 0.0273; g *p = 0.0435; h ****p < 0.0001; i ****p < 0.0001, ***p = 0.0002 (butyrate + YC-1 vs butyrate), ***p = 0.0006; j ****p < 0.0001; k **p = 0.0015, *p = 0.0325; l **p = 0.0014 (butyrate vs control) and 0.0036 (AR429626 vs control); m ****p < 0.0001, ***p = 0.0009. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32901017), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Applications for Mouse AHR Antibody
Immunocytochemistry
Sample: Immersion fixed C2C12 mouse myoblast cell line
Western Blot
Sample: C2C12 mouse myoblast cell line, mouse lung tissue, and Hepa 1‑6 mouse hepatoma cell line
Reviewed Applications
Read 1 review rated 5 using AF6697 in the following applications:
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: AHR
AHR (Aryl-hydrocarbon receptor; also bHLHE76) is a 100-105 kDa member of the bHLH/PAS transcription factor family. It is widely expressed and serves many functions. First, it binds multiple xenobiotic chemicals in the cytoplasm. This induces dimerization with ARNT, translocation to the nucleus, and activation of P450 genes such as CYP1A1 and UGT1A6. Second, it appears to block cell cycle progression, possibly via a downregulation of CDK proteins. And third, it blocks apoptosis by interacting with E2F1, thus silencing Tap73 and Apaf1 genes. Mouse AHR precursor is 848 amino acids (aa) in length. It contains a nine aa prosegment, plus an 839 aa mature molecule that contains a DNA binding motif (aa 12-39), a bHLH region (aa 40-80), two PAS domains (aa 116-336) and one PAC segment that stabilizes the PAS domains (aa 342-383). There are multiple alleles for mouse AHR. One 95-97 kDa allele shows a premature truncation after Ser805, while a second 112 kDa allele shows a 41 aa substitution for aa 843-848. Over aa 706-805, mouse AHR shares 87% and 63% aa identity with rat and human AHR, respectively.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional AHR Products
Product Documents for Mouse AHR Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Mouse AHR Antibody
For research use only