Mouse/Rat/Porcine/Equine CD44 Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # AF6127

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Gln25-Thr224
Accession # NP_033981
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Endotoxin Level
Scientific Data Images for Mouse/Rat/Porcine/Equine CD44 Antibody
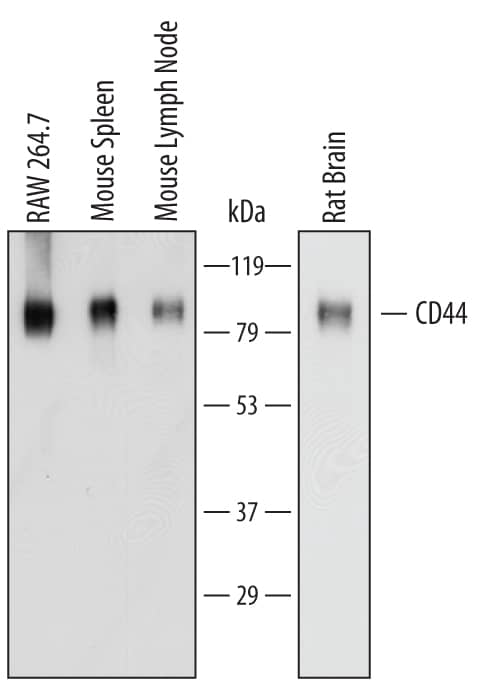
Detection of Mouse and Rat CD44 by Western Blot.
Western blot shows lysates of RAW 264.7 mouse monocyte/macrophage cell line, mouse spleen tissue, mouse lymph node tissue, and rat brain tissue. PVDF membrane was probed with 1 µg/mL of Sheep Anti-Mouse/Rat/Porcine/Equine CD44 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF6127) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Sheep IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF016). Specific bands were detected for CD44 at approximately 80 to 100 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 1.Detection of CD44 in Mouse Splenocytes by Flow Cytometry.
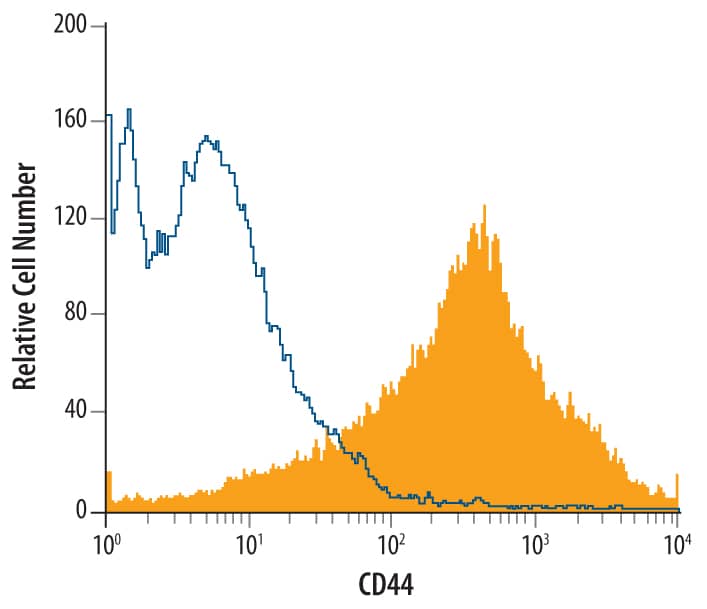
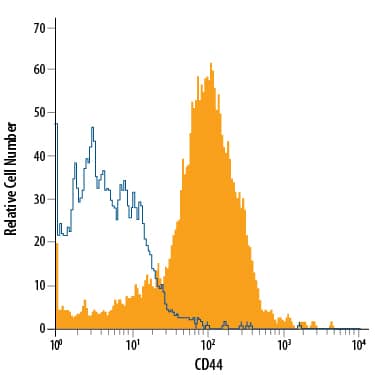
Mouse splenocytes were stained with Sheep Anti-Mouse/Rat/Porcine/Equine CD44 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF6127, filled histogram) or control antibody (Catalog # 5-001-A, open histogram), followed by Allophycocyanin-conjugated Anti-Sheep IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # F0127).Detection of CD44 in Rat Splenocytes by Flow Cytometry.
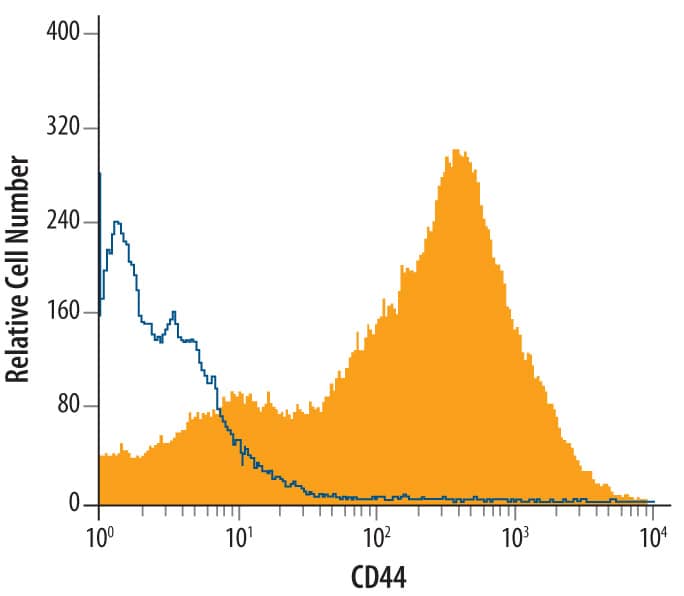
Rat splenocytes were stained with Sheep Anti-Mouse/Rat/Porcine/Equine CD44 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF6127, filled histogram) or control antibody (Catalog # 5-001-A, open histogram), followed by Allophycocyanin-conjugated Anti-Sheep IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # F0127).Applications for Mouse/Rat/Porcine/Equine CD44 Antibody
Blockade of Receptor-ligand Interaction
CyTOF-ready
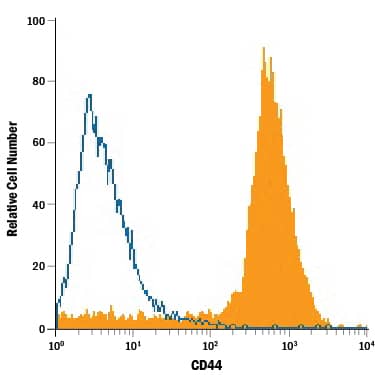
Flow Cytometry
Sample: Mouse splenocytes, rat splenocytes, porcine mesenchymal stem cells, and equine peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs)
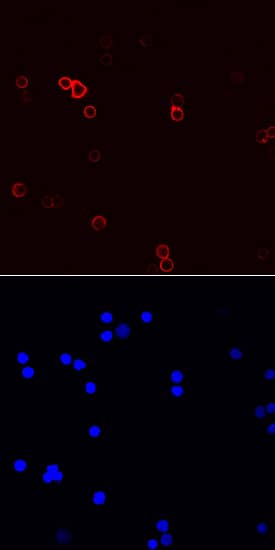
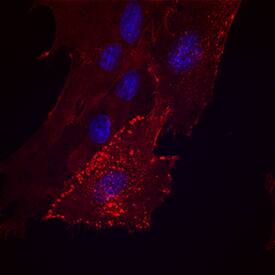
Immunocytochemistry
Sample: Immersion fixed mouse splenocytes and porcine mesenchymal stem cells
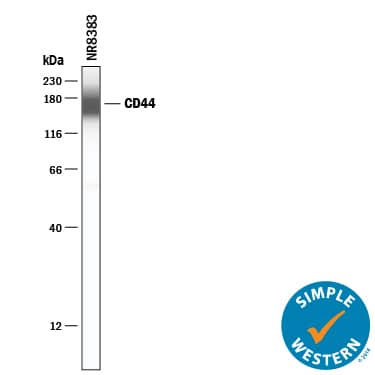
Simple Western
Sample: NR8383 rat alveolar macrophage cell line
Western Blot
Sample: RAW 264.7 mouse monocyte/macrophage cell line, mouse spleen tissue, mouse lymph node tissue, and rat brain tissue
Reviewed Applications
Read 2 reviews rated 4.5 using AF6127 in the following applications:
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: CD44
CD44 is a ubiquitously expressed protein that is the major receptor for hyaluronan and exerts control over cell growth and migration (1 - 5). Mouse CD44 has a 22 amino acid (aa) signal sequence, an extracellular domain (ECD) with a 100 aa hyaluronan-binding disulfide-stabilized link region and a 48-463 aa stem region, a 21 aa transmembrane domain, and a 72 aa cytoplasmic domain. Within the stem, ten variably spliced exons (v1-10, exons 6-15) produce multiple protein isoforms (1-5). The standard or hematopoietic form, CD44H, does not include the variable segments (1‑5). Cancer aggressiveness and T cell activation have been correlated with expression of specific isoforms (2, 4). With variable N- and O-glycosylation and splicing within the stalk, CD44 can range from 80 to 200 kDa (1, 2). Within the N‑terminal invariant portion of the ECD (aa 23-222), mouse CD44 shares 92%, 77%, 77%, 79% and 71% identity with corresponding rat, human, equine, canine and bovine CD44, respectively. The many reported functions of CD44 fall within three categories (1, 2). First, CD44 binds hyaluronan and other ligands within the extracellular matrix and can function as a "platform" for growth factors and metalloproteinases. Second, CD44 is a co-receptor that modifies activity of receptors including MET and the ErbB family of tyrosine kinases. Third, the CD44 intracellular domain links the plasma membrane to the actin cytoskeleton via the ERM proteins, ezrin, radixin and moesin. CD44 can be synthesized in a soluble form (4) or may be cleaved at multiple sites by either membrane-type matrix metalloproteinases, or ADAM proteases to produce soluble ectodomains (6, 7). The cellular portion may then undergo gamma secretase-dependent intramembrane cleavage to form an A beta‑like transmembrane portion and a cytoplasmic signaling portion that affects gene expression (8, 9). These cleavage events are thought to promote metastasis by enhancing tumor cell motility and growth (1, 2, 6).
References
- Pure, E. and R.K. Assoian (2009) Cell. Signal. 21:651.
- Ponta, H. et al. (2003) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 4:33.
- Screaton, G.R. et al. (1992) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89:12160.
- Lynch, K.W. (2004) Nat. Rev. Immunol. 4:931.
- Yu, Q. and B.P. Toole (1996) J. Biol. Chem. 271:20603.
- Nagano, O. and H. Saya (2004) Cancer Sci. 95:930.
- Nakamura, H. et al. (2004) Cancer Res. 64:876.
- Murakami, D. et al. (2003) Oncogene 22:1511.
- Lammich, S. et al. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277:44754.
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional CD44 Products
Product Documents for Mouse/Rat/Porcine/Equine CD44 Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Mouse/Rat/Porcine/Equine CD44 Antibody
For research use only