Recombinant Human Siglec-3/CD33 Fc Avi-Tag Protein, CF
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # AVI10467

Key Product Details
Source
Accession #
Structure / Form
Conjugate
Applications
Product Specifications
Source
| Human Siglec-3/CD33 (Met17-His259) Accession # P20138.2 |
IEGRMD | Human IgG1 (Pro100-Lys330) |
Avi-tag |
| N-terminus | C-terminus | ||
Purity
Endotoxin Level
N-terminal Sequence Analysis
Predicted Molecular Mass
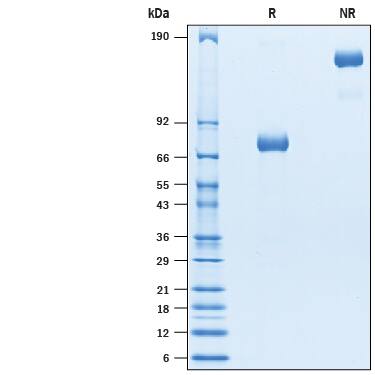
SDS-PAGE
Activity
The ED50 for this effect is 0.2-1.4 μg/mL.
Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA.
When Human Siglec-3/CD33 (6C5/2) Antibody (Catalog # MAB1137) is immobilized at 0.5 µg/mL (100 µL/well), Biotinylated Recombinant Human Siglec-3/CD33 Fc Chimera (Catalog # AVI10467) binds with an ED50 of 0.15-1.2 ng/mL.
Scientific Data Images for Recombinant Human Siglec-3/CD33 Fc Avi-Tag Protein, CF
Recombinant Human Siglec-3/CD33 Fc Avi-Tag Protein Binding Activity
Biotinylated Recombinant Human Siglec-3/CD33 Fc Chimera Avi-tag (AVI10467) supports the adhesion of human red blood cells. The ED50 for this effect is 0.2-1.4 μg/mL.Recombinant Human Siglec-3/CD33 Fc Avi-Tag Protein SDS-PAGE
2 μg/lane of Biotinylated Recombinant Siglec-3/CD33 Fc Chimera Avi-tag (Catalog # AVI10467) was resolved with SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) and non-reducing (NR) conditions and visualized by Coomassie® Blue staining, showing bands at 67-78 kDa and 130-160 kDa, respectively.Formulation, Preparation and Storage
AVI10467
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS with Trehalose. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 500 μg/mL in PBS. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped with polar packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Background: Siglec-3/CD33
Siglecs (sialic acid binding Ig-like lectins) are I-type (Ig-type) lectins belonging to the Ig superfamily. They are characterized by an N-terminal Ig-like V-type domain which mediates sialic acid binding, followed by varying numbers of Ig-like C2-type domains (1, 2). Eleven human Siglecs have been cloned and characterized. They are sialoadhesin/CD169/Siglec-1, CD22/Siglec-2, CD33/Siglec-3, Myelin-Associated Glycoprotein (MAG/Siglec-4a) and Siglecs 5 to 11 (1-3). To date, no Siglec has been shown to recognized any cell surface ligand other than sialic acids, suggesting that interactions with glycans containing this carbohydrate are important in mediating the biological functions of Siglecs. Siglecs 5 to 11 share a high degree of sequence similarity with CD33/Siglec-3 both in their extracellular and intracellular regions. They are collectively referred to as CD33-related Siglecs. One remarkable feature of the CD33-related Siglecs is their differential expression pattern within the hematopoietic system (1, 2). This fact, together with the presence of two conserved immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibition motifs (ITIMs) in their cytoplasma tails, suggests that CD33-related Siglecs are involved in the regulation of cellular activation within the immune system. Human Siglec-3 is alternatively known as myeloid cell surface antigen CD33 and GP67. Human Siglec-3 cDNA encodes a 364 amino acid (aa) polypeptide with a hydrophobic signal peptide, an N-terminal Ig-like V-type domain, one Ig-like C2-type domains, a transmembrane region and a cytoplasmic tail (1, 4). Siglec-3 expression is restricted to cells of myelomonocytic lineage (2). It binds sialic acid preferring alpha2,3- linkage over alpha2,6- linkage (5). Studies indicated that Siglec-3 recruits SHP-1 and SHP-2 to its ITIMs (6, 7). When co-crosslinking with Fc gammaR1, Siglec-3 inhibits tyrosine phosphorylation and calcium mobilization, suggesting Siglec-3 can mediate inhibitory signals (7). Our Avi-tag Biotinylated Siglec-3 features biotinylation at a single site contained within the Avi-tag, a unique 15 aa peptide. Protein orientation will be uniform when bound to streptavidin-coated surface due to the precise control of biotinylation and the rest of the protein is unchanged so there is no interference in the protein's bioactivity.
References
- Crocker, P.R. and A. Varki (2001) Trends Immunol. 22:337.
- Crocker, P.R. and A. Varki (2001) Immunology 103:137.
- Angata, T. et al. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277:24466.
- Simmons, D. and B. Seed (1988) J. Immunol. 141:2797.
- Freeman, S.D. et al. (1995) Blood 85:2002.
- Taylor, V.C. et al. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274:11505.
- Ulyanova, T. et al. (1999) Eur. J. Immunol. 29:3440.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional Siglec-3/CD33 Products
Product Documents for Recombinant Human Siglec-3/CD33 Fc Avi-Tag Protein, CF
Product Specific Notices for Recombinant Human Siglec-3/CD33 Fc Avi-Tag Protein, CF
For research use only