Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 E484K N501Y Spike RBD His Protein, CF
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # 10788-CV

Key Product Details
Product Specifications
Source
Human embryonic kidney cell, HEK293-derived sars-cov-2 Spike RBD protein
Arg319-Phe541 (Glu484Lys, Asn501Tyr), with a C-terminal 6-His tag
Arg319-Phe541 (Glu484Lys, Asn501Tyr), with a C-terminal 6-His tag
Purity
>95%, by SDS-PAGE visualized with Silver Staining and quantitative densitometry by Coomassie® Blue Staining.
Endotoxin Level
<0.10 EU per 1 μg of the protein by the LAL method.
N-terminal Sequence Analysis
Arg319
Predicted Molecular Mass
26 kDa
SDS-PAGE
32-40 kDa, under reducing conditions
Activity
Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA with Recombinant
Human ACE-2 His-tag
(Catalog #
933-ZN).
Scientific Data Images for Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 E484K N501Y Spike RBD His Protein, CF
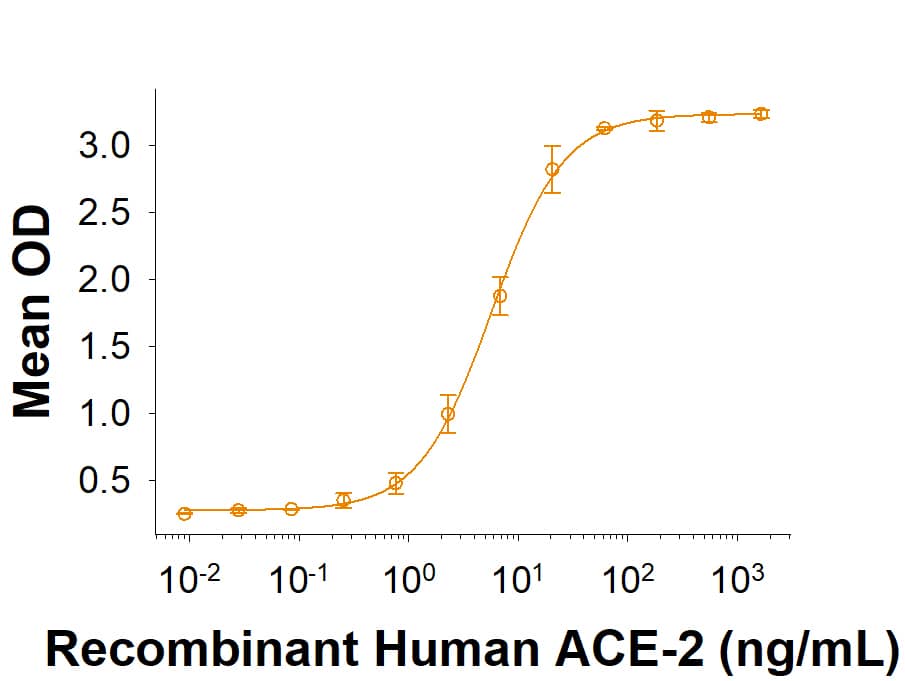
Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 E484K N501Y Spike RBD His-tag Protein Binding Activity.
Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 E484K N501Y Spike RBD His-tag (Catalog # 10788-CV) binds Recombinant Human ACE-2 His-tag (933-ZN) in a functional ELISA.Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 E484K N501Y Spike RBD His-tag Protein SDS-PAGE.
2 μg/lane of Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 E484L N501Y Spike RBD His-tag (Catalog # 10788-CV) was resolved with SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) and non-reducing (NR) conditions and visualized by Coomassie® Blue staining, showing bands at 32-40 kDa.Formulation, Preparation and Storage
10788-CV
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS with Trehalose. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 500 μg/mL in PBS. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Background: Spike RBD
References
- Wu, F. et al. (2020) Nature 579:265.
- Tortorici, M.A. and D. Veesler (2019) Adv. Virus Res. 105:93.
- Bosch, B.J. et al. (2003). J. Virol. 77:8801.
- Belouzard, S. et al. (2009) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 106:5871.
- Millet, J.K. and G.R. Whittaker (2015) Virus Res. 202:120.
- Li, W. et al. (2003) Nature 426:450.
- Wong, S.K. et al. (2004) J. Biol. Chem. 279:3197.
- Kozlov, Max (2020) TheScientist https://www.the-scientist.com/news-opinion/new-sars-cov-2-variant-spreading-rapidly-in-uk-68292.
- Wise, J. (2020) B.M.J 371:m4857.
- Tang, J.W. et al. (2020) J. Infect. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2020.12.024.
- Davies, N.G. (2020) medRxiv doi:10.1101/2020.12.24.20248822.
Long Name
Spike Receptor Binding Domain
Gene Symbol
S
UniProt
Additional Spike RBD Products
Product Documents for Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 E484K N501Y Spike RBD His Protein, CF
Product Specific Notices for Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 E484K N501Y Spike RBD His Protein, CF
For research use only
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...