Exosomes in Cancer and Inflammatory Diseases
Exosomes and other EVs are associated with many aspects of cancer. Tumor cells secrete exosomes and other EVs containing messages related to tumor initiation, growth, progression, metastasis, and drug resistance.
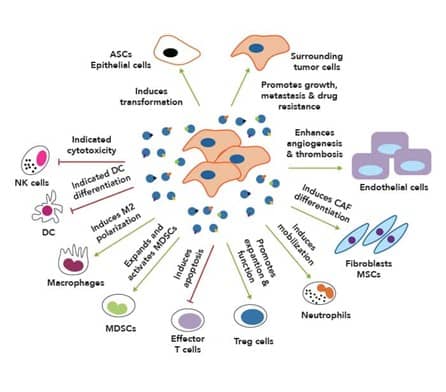
Broadly, the role of exosomes and other EVs in cancer can be divided into four categories:
- Tumor Growth and Metastasis
- Therapy Resistance
- Immunosuppression
- Biomarkers
Figure adapted from Zhang, X., et al. (2015) Exosomes in cancer: small particle, big player. J Hematol Oncol 8, 83 (PMID: 26156517). License provided by CC License.
In cancer cells, exosomes and other EVs transport cargo that is implicated in each stage of tumor growth and metastasis. For instance, cancerous cells can secrete EVs containing growth factors that have multiple roles in tumor growth and metastasis, including the induction of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), the transformation of normal cells into malignant cells, and the increased stemness of cancer cells.
Additionally, oncogenic cells can secrete EVs containing anti-apoptotic factors, like Survivin, to prevent cell death, and growth factors, like VEGF, to increase angiogenesis in the tumor microenvironment (TME).
| Exosome Cargo | Cancers Reported | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| KRAS c-MET MIF EGFR/EGFRvIII |
Colon, Melanoma, Pancreatic, Breast | Inhibits apoptosis of tumor cells |
| Survivin | Cervical, Breast, Lung | Enhances angiogenesis and thrombosis |
| VEGF Angiogenin |
NSCLC, Renal, Colon, Glioblastoma | Involved in epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) |
| Vimentin Rab3D TGF-β |
NSCLC, Prostate, Bladder, Colorectal, Breast, Gastric | Induces myofibroblast differentiation |
| TGF-β HIF-1α c-KIT Wnt3a |
NSCLC, NPC, GIST, Diffuse large B cell lymphoma | Enhancing tumor cell migration and invasion, establishing pre-metastatic niche, remodeling extra cellular matrix |
NSCLC, Non small-cell lung cancer; NPC, Nasopharyngeal carcinoma; GIST, Gastrointestinal stromal tumor
To be successful, tumors need to evade and suppress the immune response of the host. Some mechanisms of immunosuppression in the tumor microenvironment (TME) include cytotoxic inhibition of NK cells and effector T cells, expansion and activation of T regulatory (Treg) cells, and polarization of M2 macrophages. EVs including exosomes play an important role in each of these immunosuppressive processes.
| Exosome Cargo | Cancers Reported | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| NKG2D DNAM-1 Galectin-9 PD-L1 FasL CD39, CD73 |
Ovarian, NPC Melanoma, Bladder, Colorectal, Prostate, Breast | Inhibits cytotoxicity of NK cells and effector T cells Promotes apoptosis of effector cells |
| HSP70 | NSCLC, Renal, Breast, Colon | Activates and expands myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) |
| EGFR TGF-β CCL20 |
NSCLC, Melanoma, NPC | Promotes expansion and function of regulatory T cells (Tregs) |
| EGFR | NSCLC | Inhibits dendritic cell (DC) differentiation |
NSCLC, non-small cell lung cancer; NPC, nasopharyngeal carcinoma
In addition to tumor metastasis and immunosuppression, exosomes and other EVs can contribute to tumor growth and disease progression by directly promoting resistance to anti-cancer therapy. EVs can transfer material, such as multi-drug resistant (MDR)-associated proteins and miRNAs to susceptible cells, transforming them into therapy-resistant cells. Additionally, drugs and drug metabolites can be encapsulated within EVs to facilitate transport out of the tumor cell, rendering the drug ineffective. Finally, due to their expression of cell surface markers that are also targets for therapy, such as CD20, Her-2, and PD-L1, EVs can serve as decoy targets, limiting therapeutic efficacy.
In general, a biomarker is a biological characteristic that can be measured and monitored. Biomarkers are an especially useful tool for the diagnosis and monitoring of cancer when the primary tumor site is in a hard-to-reach place, such as the brain or other solid organ.
EVs are under investigation as biomarkers to:
- diagnose disease,
- determine disease burden, and
- monitor disease progression and/or treatment efficacy.
Learn more about Bio-Techne's Exosome Platform for diagnostic biomarker discovery and development.
| Cancer | Exosome Markers |
|---|---|
| Colon | VSIG3, GPA33, CD147 |
| Ovarian | CD147, EpCAM, CA125/MUC16 |
| Breast | EGFR |
| Pancreatic | Glypican-1, MIF |
| Lung | CD151, L1CAM/CD171, Tetraspanin 8, (NSCLC-EGFR, LRG-1) |
| Glioblastoma | Syndecan-1, EGFRvIII |
| Prostate | PSA, PSMA, PTEN |
| Melanoma | TRP2, VLA-4, HSP70, PD-L1 |
Exosomes and other EVs are implicated in the pathogenesis of many inflammatory diseases including cardiovascular disease, kidney disease, autoimmune disorders, and viral infections. Thus far, much of this work has investigated the role of various microRNAs (miRNAs) and protein cargo, the role of exosomes in inflammatory disease is being increasingly studied.
| Disease | Exosome/EV Cargo |
|---|---|
| Cardiovascular Disease | Cystatin C, Serpin F2, CD14, PolyIg Receptor, C5a, Tissue Factor, CD31, CD62e |
| Renal Disease | AQP1, AQP2, Aminopeptidase N |
| Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) | IFN-α, TNF-α, C1q, CD54 |
| Type 1 Diabetes | GAD65, Proinsulin |
| HIV | HMGB1, NF-L, HIV gp120 |
Zheng H, et al. (2018) The roles of tumor-derived exosomes in non-small cell lung cancer and their clinical implications. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 37 226. https://doi.org/10.1186/S13046-018-0901-5.
Zhang X, et al. (2015) Exosomes in cancer: small particle, big player. J Hematol Oncol 8 83. https://doi.org/10.1186/S13045-015-0181-X.
Bălașa A, et al. (2020) The involvement of exosomes in glioblastoma development, diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment. Brain Sci 10 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10080553.
Liu H, et al. (2021) Role of exosomes in pancreatic cancer (Review). Oncol Lett 21 298. https://doi.org/10.3892/OL.2021.12559.
Bellin G, et al. (2019) Exosome in cardiovascular diseases: a complex world full of hope. Cells 8 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8020166.
Dickhout A and Koenen RR (2018) Extracellular vesicles as biomarkers in cardiovascular disease; chances and risks. Front Cardiovasc Med 5 113. https://doi.org/10.3389/FCVM.2018.00113.
Wu W-C, et al. (2020) Role of extracellular vesicles in autoimmune pathogenesis. Front Immunol 11 579043. https://doi.org/10.3389/FIMMU.2020.579043.
Chung IM, et al. (2020) Exosomes: current use and future applications. Clin Chim Acta 500 226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2019.10.022.
Jansen F, et al. (2017) Extracellular vesicles in cardiovascular disease. Circ Res 120 1649. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.310752.
Xu K, et al. (2020) Extracellular vesicles as potential biomarkers and therapeutic approaches in autoimmune diseases. J Transl Med 18 432. https://doi.org/10.1186/S12967-020-02609-0.