CD16 is a lymphocyte Fc gamma type III low-affinity receptor for IgG and is represented by two similar genes, CD16A (Fc gamma RIII A) and CD16B (Fc gamma RIIIB). CD16A exists as a heterooligomeric polypeptide-anchored form in macrophages and NK cells. CD16B exists as a monomeric glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored form in neutrophils. CD16 binds IgG in the form of immune complexes or free antibody. It exhibits preferential binding to IgG1 and IgG3 isotypes, with minimal binding of IgG2 and IgG4. Upon IgG binding, both CD16 isoforms initiate signaling cascades that produce a diverse variety of responses including antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), phagocytosis, degranulation, and proliferation. CD16 is expressed on macrophages, natural killer (NK) cells and neutrophils. Their expression is constitutive, although cytokines and lymphokines can modulate their expression levels.
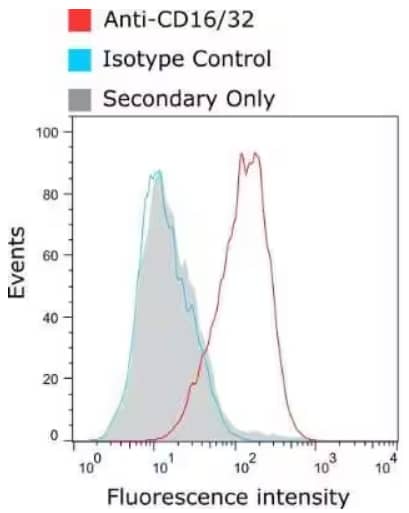
Flow Cytometry: CD16/CD32 Antibody (2.4G2) [NBP2-52644] - Staining of murine macrophages Murine bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) were stained with anti-CD16/32 antibody (as well as isotype control) and bound antibody detected using goat IgG anti-rat IgG (H&L-chain) polyclonal antibody directly conjugated to Alexa Fluor 647(AF647) commercially available from a competitor. Compared to the isotype control and secondary-only control, a CD16/32-positive population is apparent.
Initial molecular studies on CD16 used the CD16 antibody to characterize ligand and receptor binding sites and assist in molecular modeling1. deHaas’ group from the Netherlands relied upon the CD16 antibody to assess the implications of polymorphisms in the CD16A gene among a donor pool2. Their studies suggest that their triallelic polymorphism affects resultant CD16A binding to IgG counterparts. Additionally, Gasdaska et al used the CD16 antibody in their characterization studies of a novel afucosylated rituximab (BLX-300)3. Their toxicity experiments compared the performance of this compound to rituximab itself, where they found it exhibited not only higher levels of antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), but also B-cell depletion.
PMIDs
- 8759741
- 8609432
- 22305040