Innate Immunity Cell Identity Markers
Innate Immunity
Rapid responses to invading pathogens are mediated by the cells and humoral factors of the innate immune system. These responses are activated by the interaction between pathogen antigens and pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), localized to the surface or intracellular compartments of innate immune cells. This initial response is somewhat generic, as receptors are only able to recognize a limited repertoire of motifs from pathogen-derived molecules including lipopolysaccharides, lipoproteins and nucleic acids, collectively referred to as pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs).
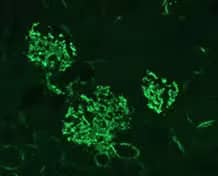
Immunohistochemistry: Complement C3 Antibody (11H9) [NB200-540] - C3 protein fragments deposited on kidney cells of MPL-lpr mouse. Staining with antibody 11H9. Glomerular staining pattern. Fixation in 4% paraformaldehyde in PBS pH 7.4. Vibratome sections of 4 μm. Pretreated with 3% hydrogen peroxide for 20 min to quench endogenous peroxidases. Microwaved in antigen unmasking solution for 2-5 min as antigen retrieval.
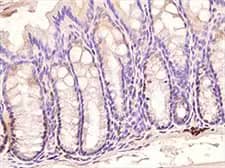
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: TLR3 Antibody (40C1285.6) [NBP2-24875] - Mouse colon using TLR3 antibody (clone 40C1285.6) at 1:500 dilution with HRP-DAB detection and hematoxylin counterstaining. Intense signal was found in subset of cells at the bases of the crypts.
Innate Cellular Mediators: Functions and Markers
| Cell Type | Function | Markers |
|---|---|---|
| Dendritic cells | Antigen presenting cells, reside in peripheral tissues where they sequester and process antigens for presentation to lymphocytes. Dendritic cells may be classified into three subsets: Myeloid- CD11c, CD13, CD33, CD11b Plasmacytoid- CD123, CD303, and CD304 Monocyte-related- CD14, all of which have high expression of MHCII (HLA-DR). |
CD11c, CLIP-170, Fascin, MADDAM, NLDC-145, MHCII (HLA-DR), CD33, CD123, CD16, CD128b Activation: CD83, CD80, CD86, CD40, MHCII (HLA-DR) |
| Macrophages (and Monocytes) | Phagocytic cells, participate in both innate and adaptive immunity, in the capture of pathogens and as antigen presenting cells. Macrophages persist and monitor tissue for prolonged periods where they demonstrate distinct tissue-specific phenotypes and origins. While some macrophages are yolk sac-derived, others differentiate from bone marrow-derived monocytes. Based on recent nomenclature, macrophages may be classified into two main subsets: M1 classically activated and M2 alternatively activated macrophages, although more subpopulations continue to be identified. | CD68, CD64, CSF-1R, F4-80 (mice), CD11b Activation: M1 classically activated- CD68, CD80, CD86, CD38, CD11c M2 alternatively activated- CD68, CD163, MMR/CD206, MGL1 , MGL2, Egr2 Monocytes: CD14, CD16, CD115 (mice), Ly-6C (mice) |
| Mast cells | Mature mast cells are found in association with a variety of tissues including those with high environmental influence (e.g., mucosal and skin tissues). Mast cells degranulate following stimulation through IgE-dependent and independent mechanisms and release several products including proteases, TNF-alpha, GM-CSF and cytokines. | CD34 (mice), Chymase, CD117/c-kit, Fc epsilon RI Activation: LAMP-I (CD1-7a), LAMP-2 (CD107b) |
| Natural killer cells (NK) | NK cells recognize infected or transformed cells and target them for lysis via the release of perforins and granzymes. Activated NK cells secrete various cytokines including IL-1, IL-2 and INF-gamma. Two main subsets are identifiable for their differential expression of CD16 and CD56. | CD56, CD16, CD57, CD161, NKp46, NKp30, CD25 Activation: CD69, CD107a, NKp46, NKp30, CD95 |
|
Granulocytes |
Phagocytic cells with short life span (days) characterized by the presence of cytosolic granules containing a variety of immunologically active substances which are microbicidal, cytotoxic, or inflammatory. | Neutrophils: CD16, CD11b, CD16b, CD66c, CD66b, Ly-6G/Gr-1 (mice) Basophils: CD49b (mice), CD41 (mice), Fc epsilon RI, CD203c, CD123 , CCR3/CD193 Eosinophils: CD11b, CCR3/CD193, F4/80 (mice), Siglec-F (mice), EMR1, Siglec-8 Activation: Neutrophil: CD11b, CD88, CD18, L-selectin (CD62L), CD32, CD54, CD66b Basophil: CD41 (mice), CD200R, CD63, CD203c, CD69, CD13, CD164, CD107a, CRTH2/DP2 Eosinophils: CD69, CD63, CD44 |
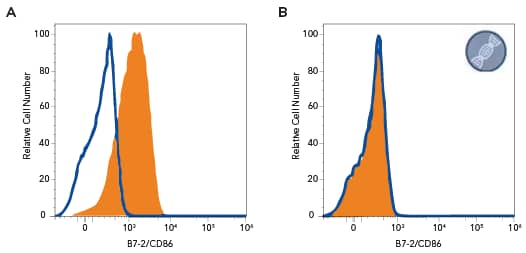
Human Ramos lymphoma cell line was stained with: A. Mouse Anti-Human B7-2/CD86 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog #MAB141, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (Catalog # MAB002, open histogram) followed by PE-conjugated Goat Anti-Mouse IgG secondary antibody (Catalog # F0102B); B. B7-2/CD86 knockout Ramos human lymphoma cell line was stained with Mouse Anti-Human B7-2/CD86 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog #MAB141, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (Catalog #MAB002, open histogram) followed by PE-conjugated Goat anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog #F0102B). No staining in the B7-2/CD86 knockout Ramos cell line was observed. View our protocol for Staining Membrane-associated Proteins.
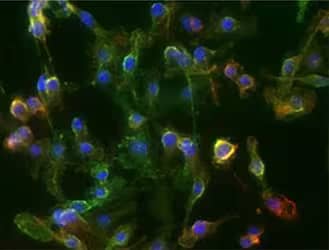
Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence: CD11b Antibody (M1/70.15) [NB600-1327] - ICC/IF analysis of RAW264.7 cells using CD11b antibody (clone M1/70.15) with Dylight 488 conjugated secondary (green). Nuclei and tubulin were stained with DAPI (Catalog # 5748, blue) and Dylight 550 (red), respectively.
Amano, H., Amano, E., Santiago-Raber, M. L., et al. (2005). Selective expansion of a monocyte subset expressing the CD11c dendritic cell marker in the Yaa model of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis and Rheumatism. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.21365
Baaten, B. J., Li, C. R., & Bradley, L. M. (2010). Multifaceted regulation of T cells by CD44. Communicative & integrative biology, 3 (6), 508-12. doi: [10.4161/cib.3.6.13495]
Boumiza, R., Debard, A. L., & Monneret, G. (2005). The basophil activation test by flow cytometry: Recent developments in clinical studies, standardization and emerging perspectives. Clinical and Molecular Allergy. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-7961-3-9
Breel, M., Laman, J., & Kraal, G. (1988). Murine Hybrid Cell Lines Expressing the NLDC-145 Dendritic Cell Determinant. Immunobiology. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0171-2985(88)80062-7
Chávez-Galán, L., Olleros, M. L., Vesin, D., & Garcia, I. (2015). Much more than M1 and M2 macrophages, there are also CD169+and TCR+macrophages. Frontiers in Immunology. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2015.00263
Collin, M., Mcgovern, N., & Haniffa, M. (2013). Human dendritic cell subsets. Immunology. https://doi.org/10.1111/imm.12117
De Clerck, L. S., De Gendt, C. M., Bridts, C. H., Van Osselaer, N., & Stevens, W. J. (1995). Expression of neutrophil activation markers and neutrophil adhesion to chondrocytes in rheumatoid arthritis patients: relationship with disease activity. Research in Immunology. https://doi.org/10.1016/0923-2494(96)80241-0
Drew, E., Merkens, H., Chelliah, S., Doyonnas, R., & McNagny, K. M. (2002). CD34 is a specific marker of mature murine mast cells. Experimental Hematology. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-472X(02)00890-1
Ehrnsperger, A., Rehli, M., Thu-Hang, P., & Kreutz, M. (2005). Epigenetic regulation of the dendritic cell-marker gene ADAM19. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.04.149
Fortunati, E., Kazemier, K. M., Grutters, J. C., Koenderman, L., & Van Den Bosch, V. J. M. M. (2009). Human neutrophils switch to an activated phenotype after homing to the lung irrespective of inflammatory disease. Clinical and Experimental Immunology. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2249.2008.03791.x
Grützkau, A., Smorodchenko, A., Lippert, U., Kirchhof, L., Artuc, M., & Henz, B. M. (2004). LAMP-1 and LAMP-2, but not LAMP-3, are reliable markers for activation-induced secretion of human mast cells. Cytometry Part A. https://doi.org/10.1002/cyto.a.20068
Haldar, M., & Murphy, K. M. (2014). Origin, development, and homeostasis of tissue-resident macrophages. Immunological reviews, 262(1), 25-35. doi: 10.1111/imr.12215
Hellman, P., & Eriksson, H. (2007). Early Activation Markers of Human Peripheral Dendritic Cells. Human Immunology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humimm.2007.01.018
Jablonski, K. A., Amici, S. A., Webb, L. M., Ruiz-Rosado, J. D. D., Popovich, P. G., Partida-Sanchez, S., & Guerau-De-arellano, M. (2015). Novel markers to delineate murine M1 and M2 macrophages. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0145342
Lakschevitz, F. S., Hassanpour, S., Rubin, A., Fine, N., Sun, C., & Glogauer, M. (2016). Identification of neutrophil surface marker changes in health and inflammation using high-throughput screening flow cytometry. Experimental Cell Research. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2016.03.007
Mahanonda, R., Sa-Ard-Iam, N., Yongvanitchit, K., Wisetchang, M., Ishikawa, I., Nagasawa, T., … Pichyangkul, S. (2002). Upregulation of co-stimulatory molecule expression and dendritic cell marker (CD83) on B cells in periodontal disease. Journal of Periodontal Research. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0765.2002.00664.x
Mahnke, K., Becher, E., Ricciardi-Castagnoli, P., Luger, T. A., Schwarz, T., & Grabbe, S. (1997). CD14 is expressed by subsets of murine dendritic cells and upregulated by lipopolysaccharide. Adv Exp Med Biol.
Matsumoto, K., Appiah-Pippim, J., Schleimer, R. P., Bickel, C. A., Beck, L. A., & Bochner, B. S. (1998). CD44 and CD69 represent different types of cell-surface activation markers for human eosinophils. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology. https://doi.org/10.1165/ajrcmb.18.6.3159
McLennan, I. S. (1993). Resident macrophages (ED2- and ED3-positive) do not phagocytose degenerating rat skeletal muscle fibres. Cell & Tissue Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00323586
Nishikawa, K., Morii, T., Ako, H., Hamada, K., Saito, S., & Narita, N. (1992). In vivo expression of CD69 on lung eosinophils in eosinophilic pneumonia: CD69 as a possible activation marker for eosinophils. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. https://doi.org/10.1016/0091-6749(92)90068-D
Piccioli, D., Tavarini, S., Borgogni, E., Steri, V., Nuti, S., Sammicheli, C., … Wack, A. (2007). Functional specialization of human circulating CD16 and CD1c myeloid dendritic-cell subsets. Blood. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2006-08-038422
Pinkus, G. S., Lones, M. A., Matsumura, F., Yamashiro, S., Said, J. W., & Pinkus, J. L. (2002). Langerhans cell histiocytosis: Immunohistochemical expression of fascin, a dendritic cell marker. American Journal of Clinical Pathology. https://doi.org/10.1309/N2TW-ENRB-1N1C-DWL0
Sahashi, K., Ibi, T., & Zhang, G. (1997). Immunohistochemical localization of chymase; a mast cell marker and clinical significance in diseased human skeletal muscle. Clinical Neurology.
Sahin, U., Neumann, F., Türeci, Ö., Schmits, R., Perez, F., & Pfreundschuh, M. (2002). Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cell–associated autoantigen CLIP-170/restin is a marker for dendritic cells and is involved in the trafficking of macropinosomes to the cytoskeleton, supporting a function-based concept of Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells. Blood, 100(12), 4139-4145. Accessed November 30, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.V100.12.4139.
Tang, D., Kang, R., Coyne, C. B., Zeh, H. J., & Lotze, M. T. (2012). PAMPs and DAMPs: signal 0s that spur autophagy and immunity. Immunological reviews, 249(1), 158-75. doi: [10.1111/j.1600-065X.2012.01146.x]
Yoshimura, C., Yamaguchi, M., Iikura, M., Izumi, S., Kudo, K., Nagase, H., … Hirai, K. (2002). Activation markers of human basophils: CD69 expression is strongly and preferentially induced by IL-3. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. https://doi.org/10.1067/mai.2002.123532