CD31/PECAM-1, or platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule 1, is a 130-kDa glycoprotein expressed on vascular and hematopoietic cells. Depending on the cell type, CD31/PECAM-1 expression can be largely localized to cell junctions, playing a role in cell adhesion. Aside from its role in cellular adhesion, CD31/PECAM-1 is also a large player in a variety of signaling pathways, such as angiogenesis, cell migration, leukocyte transmigration and more. Specifically, the association and indication of angiogenesis in breast cancer is of interest, given that extensive research shows angiogenesis is involved in breast cancer development, invasion and metastasis. The use of a CD31/PECAM-1 primary antibody in experimental studies to quantify tumor neovascularization is a popular approach to measure microvessel density.
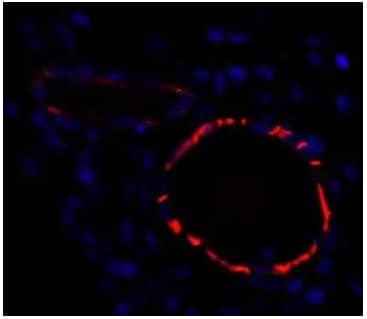
CD31/PECAM-1 Antibody (Catalog # NB100-2284) - FFPE section of human breast carcinoma. Antibody: Affinity purified rabbit anti-CD31/PECAM (NB100-2284) used at a dilution of 1:100. Detection: Red-fluorescent goat anti-rabbit IgG-Hilyte Plus™ 555
Kalet et al. used a CD31/PECAM-1 antibody in their study of the role transcription factor Ets1 in estrogen receptor alpha positive breast cancer progression. Their results found that Ets1 expression increases cellular proliferation, migration and invasion in Ets1-expressing MCF7 cell clones. In order to measure angiogenesis, a MCF7 orthotopic tumor model was developed and subsequent immunohistochemistry was performed using a standard protocol and the application of a CD31/PECAM-1 antibody. Ultimately no difference in proliferation blood vascular endothelial cells was found between Ets1 tumors and control MCF7 tumors. Alongside the CD31/PECAM-1 antibody staining, cellular proliferation was also measured using a Ki67 primary antibody, however both types of cell models yielded a 14% increase in cell growth (no marked change was observed). While CD31 and Ki67 expression levels did not exhibit a change between cell models, it was determined that Ets1 expression increased the sensitivity of MCF7 cells to estradiol signaling.
Another study using a CD31/PECAM-1 antibody was performed by Haxho et al. to determine the effect of oseltamivir phosphate (OP) monotherapy in triple negative breast cancer. The level of host endothelial CD31/PECAM-1 cell expression was measured using CD31/PECAM-1 antibody on 5 μm thickness sections of triple negative breast cancer cell line, MDA-MB-231 at a 1:300 dilution. It was observed that OP monotherapy ablates tumor vascularization after dose dependent treatment was applied to tumors through immunohistochemical staining with a CD31/PECAM-1 antibody on paraffin-embedded samples.
-
Woodfin, A. et al. () PECAM-1: a multi-functional molecule in inflammation and vascular biology PMID: 17872453.
-
Kalet, B.T. et al. () Transcription factor Ets1 cooperates with estrogen receptor α to stimulate estradiol-dependent growth in breast cancer cells and tumors PMID: 23874775.
-
Haxho, F. et al. () Oseltamivir phosphate monotherapy ablates tumor neovascularization, growth, and metastasis in mouse model of human triple-negative breast adenocarcinoma PMID: 25525387.