Voltage-gated Sodium Channel Inhibitors: Small Molecules and Peptides
Voltage-gated sodium channels (NaV) are accountable for potentially initiating and propagating excitable cells, including nerve, muscle, and neuroendocrine cell types. These can also be expressed at low levels in non-excitable cells, but their physiological role is unclear.
3 results for "Voltage-gated Sodium Channel Inhibitors Small Molecules and Peptides" in Products
3 results for "Voltage-gated Sodium Channel Inhibitors Small Molecules and Peptides" in Products
Voltage-gated Sodium Channel Inhibitors: Small Molecules and Peptides
Voltage-gated sodium channels (NaV) are accountable for potentially initiating and propagating excitable cells, including nerve, muscle, and neuroendocrine cell types. These can also be expressed at low levels in non-excitable cells, but their physiological role is unclear.
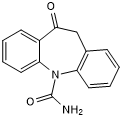
Anticonvulsant; inhibits Na+ channel activity
| Chemical Name: | 10,11-Dihydro-10-oxo-5H-dibenzo(Z)[b,f]azepine-5-carboxamide |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
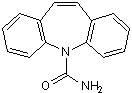
Inhibitor of neuronal NaV channels; anticonvulsant
| Alternate Names: | CBZ |
| Chemical Name: | 5H-Dibenz[b,f]azepine-5-carboxamide |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
Active metabolite of oxcarbazepine (Cat. No. 3864)
| Alternate Names: | GP 47779 |
| Chemical Name: | 10,11-Dihydro-10-hydroxy-5H-dibenz(Z)[b,f]azepin-5-carboxamide |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |