What is Dual ISH-IHC?
On their own, both in situ hybridization (ISH) and immunohistochemistry (IHC) are informative, but when paired together they become even more powerful. ISH is a technique to localize and detect specific nucleic acid sequences, while IHC determines the expression and localization of target proteins in tissues. Both techniques require experienced eyes. ISH results often have less subjectivity, but compared to IHC, ISH is slower, more expensive, and difficult to administer. Dual ISH-IHC overcomes the challenges posed by the individual techniques by making ISH and IHC complementary to one another. Using dual ISH-IHC, one can study both RNA and protein expression on the same section without any co-localization.
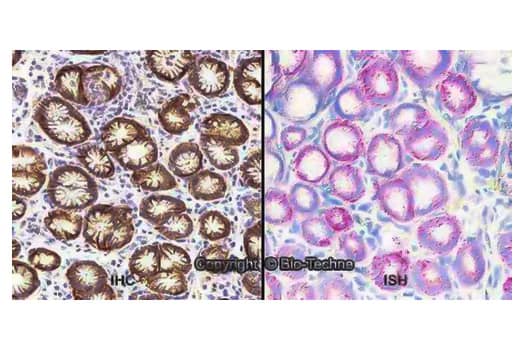
Orthogonal Strategies Validation. Dual RNAscope ISH-IHC: Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue sections of human stomach were probed for Carbonic Anhydrase IX/CA9 mRNA (RNAscope Probe, catalog # 559348; Fast Red chromogen, catalog # 322750). IHC was performed on adjacent tissue section using Rabbit Polyclonal anti-Carbonic Anhydrase IX/CA9 Antibody (Catalog # NB100-417) followed by incubation with Goat anti-Rabbit IgG VisUCyte HRP Polymer Antibody (Catalog # VC003) and DAB chromogen (yellow-brown). Hematoxylin was used to counterstain tissue (blue; Catalog # 5222). Specific staining was localized to glandular cells.
Practical Applications and Utilization of Dual RNAscope ISH-IHC
There are several applications of this combined approach. ISH can identify cells that produce a secreted protein or enzyme, while IHC can inform where that protein is localized. Dual ISH-IHC can give insight into the cellular localization and regulation of receptors. For example, Grill et al. performed RNAscope ISH-IHC on mouse models of inflammation to show cell-specific distribution and regulation of cannabinoid receptor (CB1, CB2), G protein-coupled receptor 55 (GPR55), and monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL) mRNA in the immune cells. RNAscope, a multiplex nucleic acid technology, is an advanced ISH technique to simultaneously suppress noise and amplify signal to detect even tiny amounts of RNA in individual cells.
For heterogenous tumors like diffuse large B-cell lymphomas (DLBLs), combination of ISH-IHC is particularly beneficial in diagnosis and prognosis. As an example, Annese et al. used RNAscope ISH to detect STAT3 mRNA and IHC to determine FVIII protein expression in DLBLs. By delineating tumor endothelial characterization, new prognostic markers could be developed for patient selection in antiangiogenic treatments. Likewise, Marino et al. carried out Human papillomavirus (HPV) RNA ISH and classic p16 IHC on the same slide to detect HPV E6/E7 transcripts and p16INK4a overexpression in cervical and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinomas. Their novel multiplexing approach allowed what the researchers called “an easy interpretation”, “feasibility”, “complete automation”, and a potential for widespread “routine testing in several clinical laboratories”.
Cancer stroma and the role of micro-RNAs (miRs) in them has been an exciting and active area of research. Rajthala et al. provided dual visualization of miR and protein (pan-cytokeratin) by combining chromogen-based ISH and IHC to investigate stromal miR-204 expression as a prognostic marker in oral squamous cell carcinoma. This study provided a clinical utility of correlating miR-204 in cancer stroma with oral squamous cell carcinoma progression, partly by providing spatial distribution and regulation of miR-204.
In other instances, IHC can identify the cell type while ISH can describe the gene expression to characterize complex tissue structures. Regulation of gene expression is crucial in cell and developmental biology; combining IHC and ISH can shed light on this by allowing one to differentiate between protein instability and effect of transcription.
Co-detection of CD4 and FOXP3 in human breast cancer by Dual RNAScope ISH/IHC. CD4 mRNA (red) and FOXP3 protein (green) were detected in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue sections of human breast cancer. The Integrated Co-Detection Workflow was performed using Rabbit Anti-FOXP3 Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # NB600-245) and RNAScope Probe Hs-CD4 (Catalog # 605608). The tissue was stained on Leica Bond RX using RNAscope 2.5 LS Reagent Kit-RED (Catalog # 322150), BOND Polymer Refine Detection (DAB) and Hematoxylin (Catalog # 5222), BOND Polymer Refine Red Detection and Hematoxylin and RNAscope 2.5 LS Green Accessory Pack (Catalog #322550). Tissue was counterstained with 50% Hematoxylin (blue).
Dual ISH-IHC Workflow
Advanced Cell Diagnostics' (ACD, a Bio-Techne brand) Co-Detection assays allow inclusion of a wider range of antibodies to be combined with RNA ISH for simultaneous examination of cell-type specific gene expression and cellular sources of secreted proteins. First, permeabilization of cells or tissues is performed with detergents to remove membrane lipids in order to allow antibodies, probes and other big molecules to get inside.
Typical workflow of an optimized RNA ISH-IHC can be any of the following:
Scheme 1 (Integrated Co-Detection Assay)
Day 1
Step 1: Permeabilize cells/tissues
Step 2: Bind primary IHC antibody to protein (Overnight)
Day 2
Step 3: Hybridize ISH probe to RNA
Step 4: Amplify signal
Step 5: Add secondary IHC antibody
Step 6: Visualization
Scheme 2 (Sequential Dual ISH-IHC)
Day 1: Permeabilization and RNA ISH (Hybridizing ISH probe to RNA)
Day 2: RNA ISH detection and IHC primary antibody treatment
Day 3: IHC secondary antibody addition (detection and visualization)
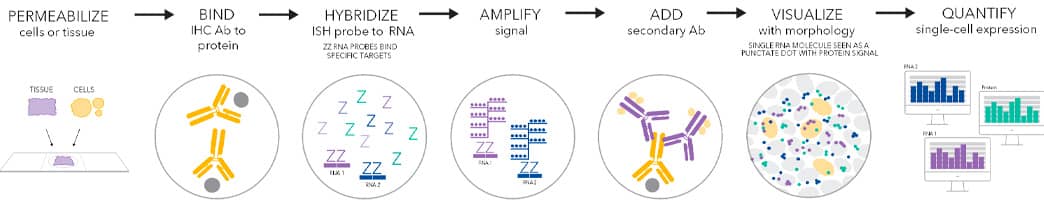
The Integrated Co-detection Workflow (ICW) schematic depicting the stepwise process for performing dual ISH-IHC. View Enlarged Image
The researchers highly recommend working out individual ISH and IHC protocols separately before combining them. Moreover, RNAscope pretreatments can affect protein stability. ISH protocol often leads to some protein degradation due to protease treatment. So, dual ISH-IHC requires antibody validation and typically works best for highly expressed proteins.
Overall, it is fair to conclude that dual ISH-IHC, especially RNAscope ISH-IHC, is a powerful technique that helps bridge the gap between RNA and protein analysis. This combined approach is used in many research areas today, such as cell and gene therapy, developmental biology, and immuno-oncology, and helps reveal key spatial and cell-cell interactions. Beyond the scientific benefits, utilizing the dual ISH-IHC workflow saves valuable time, money, and experimental resources.

Jamshed Arslan, Pharm D, PhD
Dr Arslan is an Assistant Professor at Salim Habib University (formerly, Barrett Hodgson University), Pakistan. His interest lies in neuropharmacology and preparing future pharmacists.
-
Annese, T. et al. (2020) RNAscope dual ISH-IHC technology to study angiogenesis in diffuse large B-cell lymphomas Histochem Cell Biol 153:185-192.
-
Grill, M. et al. (2019) Cellular localization and regulation of receptors and enzymes of the endocannabinoid system in intestinal and systemic inflammation Histochem Cell Biol 151:5-20.
-
Rajthala, S. et al. (2021) Combined In Situ Hybridization and Immunohistochemistry on Archival Tissues Reveals Stromal microRNA-204 as Prognostic Biomarker for Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cancers (Basel)
-
Zito Marino, F. et al. (2020) Multiplex HPV RNA in situ hybridization/p16 immunohistochemistry: a novel approach to detect papillomavirus in HPV-related cancers. A novel multiplex ISH/IHC assay to detect HPV Infect Agent Cancer