Hexosaminidase A/HEXA Products
beta-Hexosaminidases are enzymes involved in the hydrolysis of terminal N-acetyl-D-hexosamine residues in GM2 gangliosides and globo-sphingolipids in lysosomes. The enzymes are composed of two alpha and/or beta subunits, which are coded by HEXA and HEXB genes, respectively. Different associations of the alpha and beta subunits gives rise to beta-hexosaminidase isoforms A, B and S (Hex A, B and S), which have the composition of alpha/beta, beta/beta and alpha/alpha, respectively. Our recombinant HEXA is presumably isoform Hex S, because only alpha subunit was expressed. Hex S is suggested to release non-reducing end N-acetylgalactosamine residues from dermatan sulfate, chondroitin sulfate and sulfated glycolipid SM2. Recombinant HEXA is also highly active on 4-methylumbelliferyl-N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminide. Mutations in HEXA and HEXB genes cause lysosomal lipid storage disorders. Specifically, mutations of HEXA cause Tay-Sachs disease, manifested by the harmful accumulation of ganglioside GM2 in tissues and nerve cells in the brain. Children with this disease usually die by age 4.
48 results for "Hexosaminidase A/HEXA" in Products
48 results for "Hexosaminidase A/HEXA" in Products
Hexosaminidase A/HEXA Products
beta-Hexosaminidases are enzymes involved in the hydrolysis of terminal N-acetyl-D-hexosamine residues in GM2 gangliosides and globo-sphingolipids in lysosomes. The enzymes are composed of two alpha and/or beta subunits, which are coded by HEXA and HEXB genes, respectively. Different associations of the alpha and beta subunits gives rise to beta-hexosaminidase isoforms A, B and S (Hex A, B and S), which have the composition of alpha/beta, beta/beta and alpha/alpha, respectively. Our recombinant HEXA is presumably isoform Hex S, because only alpha subunit was expressed. Hex S is suggested to release non-reducing end N-acetylgalactosamine residues from dermatan sulfate, chondroitin sulfate and sulfated glycolipid SM2. Recombinant HEXA is also highly active on 4-methylumbelliferyl-N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminide. Mutations in HEXA and HEXB genes cause lysosomal lipid storage disorders. Specifically, mutations of HEXA cause Tay-Sachs disease, manifested by the harmful accumulation of ganglioside GM2 in tissues and nerve cells in the brain. Children with this disease usually die by age 4.
| Source: | Sf 21 (baculovirus) |
| Accession #: | P06865 |
| Applications: | EnzAct |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG2b Monoclonal Clone #714729 |
| Applications: | WB, IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Sheep IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB, Simple Western |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG2B Monoclonal Clone #3F10 |
| Applications: | WB, ELISA, Flow, CyTOF-ready |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG2b Monoclonal Clone #714712 |
| Applications: | Neut |
| Applications: | ELISA |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 kappa Monoclonal Clone #3D1 |
| Applications: | WB, ELISA, ICC/IF |
| Reactivity: | Human, Rat |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | IHC, WB, ICC/IF |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG2a Lambda Monoclonal Clone #20F1 |
| Applications: | WB, ELISA, Flow |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | ICC/IF |
| Applications: | WB |
| Applications: | ELISA |
| Applications: | AC |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG2a Lambda Monoclonal Clone #20F1 |
| Applications: | WB, ELISA, Flow |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG2a Lambda Monoclonal Clone #20F1 |
| Applications: | WB, ELISA, Flow |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG2a Lambda Monoclonal Clone #20F1 |
| Applications: | WB, ELISA, Flow |
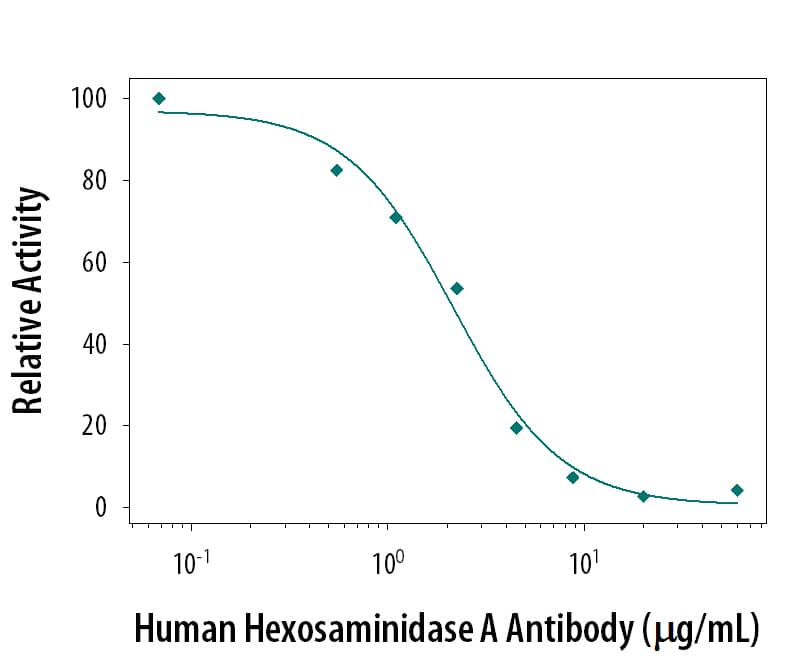
O-GlcNAcase and β-hexosaminidase inhibitor
| Chemical Name: | O-(2-Acetamido-2-deoxy-D-glucopyranosylidene)amino-Z-N-phenylcarbamate |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG2a Lambda Monoclonal Clone #20F1 |
| Applications: | WB, ELISA, Flow |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG2a Lambda Monoclonal Clone #20F1 |
| Applications: | WB, ELISA, Flow |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG2a Lambda Monoclonal Clone #20F1 |
| Applications: | WB, ELISA, Flow |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG2a Lambda Monoclonal Clone #20F1 |
| Applications: | WB, ELISA, Flow |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG2a Lambda Monoclonal Clone #20F1 |
| Applications: | WB, ELISA, Flow |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG2a Lambda Monoclonal Clone #20F1 |
| Applications: | WB, ELISA, Flow |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG2a Lambda Monoclonal Clone #20F1 |
| Applications: | WB, ELISA, Flow |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG2a Lambda Monoclonal Clone #20F1 |
| Applications: | WB, ELISA, Flow |
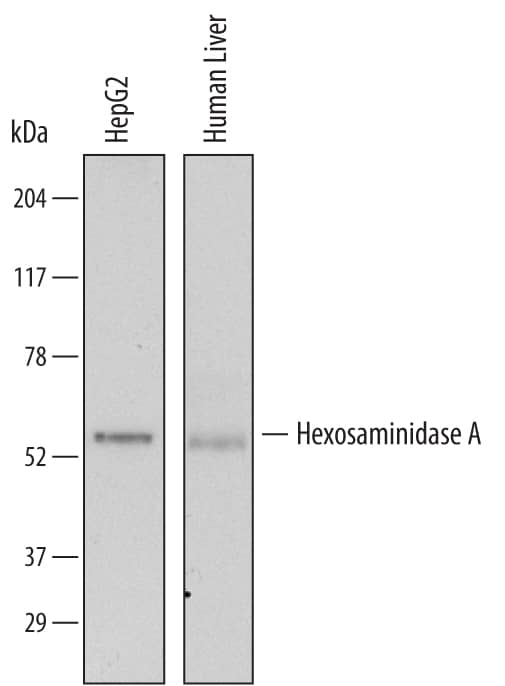



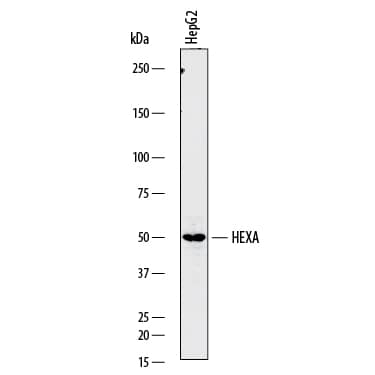

![Western Blot: Hexosaminidase A/HEXA Antibody (3F10)BSA Free [NBP2-37505] Western Blot: Hexosaminidase A/HEXA Antibody (3F10)BSA Free [NBP2-37505]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/Hexosaminidase-A-HEXA-Antibody-3F10-Western-Blot-NBP2-37505-img0003.jpg)
![ELISA: Human Hexosaminidase A/HEXA ELISA Kit (Colorimetric) [NBP3-31929] - Human Hexosaminidase A/HEXA ELISA Kit (Colorimetric)](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nbp3-31929_human-hexosaminidase-a-hexa-elisa-kit-colorimetric-206202415311350.png)
![Western Blot: Hexosaminidase A/HEXA Antibody (3D1) [H00003073-M06] Western Blot: Hexosaminidase A/HEXA Antibody (3D1) [H00003073-M06]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/Hexosaminidase-A-HEXA-Antibody-3D1-Western-Blot-H00003073-M06-img0004.jpg)
![Western Blot: Hexosaminidase A/HEXA Antibody [NBP1-74127] Western Blot: Hexosaminidase A/HEXA Antibody [NBP1-74127]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/Hexosaminidase-A-HEXA-Antibody-Western-Blot-NBP1-74127-img0006.jpg)
![Western Blot: Hexosaminidase A/HEXA Antibody (20F1)BSA Free [NBP2-42629] Western Blot: Hexosaminidase A/HEXA Antibody (20F1)BSA Free [NBP2-42629]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/Hexosaminidase-A-HEXA-Antibody-20F1-Western-Blot-NBP2-42629-img0002.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence: Hexosaminidase A/HEXA Antibody [NBP3-21239] - Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence: Hexosaminidase A/HEXA Antibody [NBP3-21239] -](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nbp3-21239_rabbit-hexosaminidase-a-hexa-pab-45202315481019.jpg)
![Western Blot: Hexosaminidase A/HEXA Overexpression Lysate [NBL1-11515] Western Blot: Hexosaminidase A/HEXA Overexpression Lysate [NBL1-11515]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/HEXA-Overexpression-Lysate-Adult-Normal-Western-Blot-NBL1-11515-img0002.jpg)
![ELISA: Human Hexosaminidase A/HEXA - Ready-To-Use ELISA Kit (Colorimetric) [NBP3-31930] - Human Hexosaminidase A/HEXA - Ready-To-Use ELISA Kit (Colorimetric)](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nbp3-31930_human-hexosaminidase-a-hexa-ready-to-use-elisa-kit-206202415351093.png)


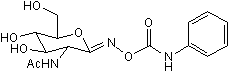
![Hexosaminidase A/HEXA Antibody (20F1) [mFluor Violet 610 SE] [NBP2-42629MFV610] - Hexosaminidase A/HEXA Antibody (20F1) [mFluor Violet 610 SE]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nbp2-42629mfv610_mouse-hexosaminidase-a-hexa-mab-20f1-mfv610-se-6720239131516.png)