Ubiquitin Products
Ubiquitin is a 76 amino acid (aa) protein that is ubiquitously expressed in all eukaryotic organisms. Ubiquitin is highly conserved with 96% aa sequence identity shared between human and yeast Ubiquitin, and 100% aa sequence identity shared between human and mouse Ubiquitin. In mammals, four Ubiquitin genes encode for two Ubiquitin-ribosomal fus...
48 results for "Ubiquitin" in Products
48 results for "Ubiquitin" in Products
Ubiquitin Products
Ubiquitin is a 76 amino acid (aa) protein that is ubiquitously expressed in all eukaryotic organisms. Ubiquitin is highly conserved with 96% aa sequence identity shared between human and yeast Ubiquitin, and 100% aa sequence identity shared between human and mouse Ubiquitin. In mammals, four Ubiquitin genes encode for two Ubiquitin-ribosomal fus...
| Source: | E. coli |
| Accession #: | P0CG47.1 |
| Applications: | EnzAct |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG2b Monoclonal Clone #83406 |
| Applications: | WB, IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat, Monkey, Bovine, +8 More |
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 Monoclonal Clone #Ubi-1 |
| Applications: | IHC, WB, ICC/IF, Flow |
| Source: | E. coli |
| Accession #: | P0CG47.1 |
| Applications: | EnzAct |
| Source: | E. coli |
| Accession #: | P0CG47.1 |
| Applications: | EnzAct |
| Source: | Synthetic |
| Accession #: | P0CG47.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | IHC, WB, ICC/IF, Func |
| Source: | E. coli |
| Accession #: | P0CG47.1 |
| Applications: | EnzAct |
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody.
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Monoclonal Clone #1002A |
| Applications: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Bovine |
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 Monoclonal Clone #1B4-UB |
| Applications: | IHC, WB, ELISA, Flow, Simple Western |
| Source: | E. coli |
| Accession #: | P0CG47.1 |
| Applications: | EnzAct |
| Source: | E. coli |
| Accession #: | P0CG47.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine, Rabbit, +1 More |
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 Monoclonal Clone #P4G7-H11 |
| Applications: | IHC, WB, Flow |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 Lambda Monoclonal Clone #3E2-E6 |
| Applications: | IHC, WB, ELISA |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | ICC/IF |
| Applications: | WB |
| Applications: | AC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat, Monkey, Bovine, +7 More |
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 Monoclonal Clone #Ubi-1 |
| Applications: | IHC, WB, ICC/IF |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat, Monkey, Bovine, +7 More |
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 Monoclonal Clone #Ubi-1 |
| Applications: | IHC, WB, ICC/IF |
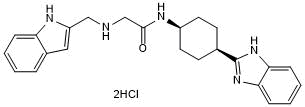
Selective GID4 antagonist
| Chemical Name: | N-((1s,4s)-4-(1H-Benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)cyclohexyl)-2-(((1H-indol-2-yl)methyl)amino)acetamide dihydrochloride |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
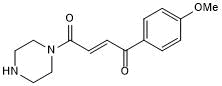
RNF126 chemical handle
| Chemical Name: | 1-(4-Methoxyphenyl)-4-(1-piperazinyl)-2-butene-1,4-dione hydrochloride |
| Purity: | ≥95% (HPLC) |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat, Monkey, Bovine, +7 More |
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 Monoclonal Clone #Ubi-1 |
| Applications: | IHC, WB, ICC/IF |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat, Monkey, Bovine, +7 More |
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 Monoclonal Clone #Ubi-1 |
| Applications: | IHC, WB, ICC/IF |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat, Monkey, Bovine, +7 More |
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 Monoclonal Clone #Ubi-1 |
| Applications: | IHC, WB, ICC/IF |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat, Monkey, Bovine, +7 More |
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 Monoclonal Clone #Ubi-1 |
| Applications: | IHC, WB, ICC/IF |




![Western Blot: Ubiquitin Antibody (Ubi-1) [NB300-130] Western Blot: Ubiquitin Antibody (Ubi-1) [NB300-130]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/Ubiquitin-Antibody-Ubi-1-Western-Blot-NB300-130-img0014.jpg)
![Western Blot: Ubiquitin Antibody [NB300-129] Western Blot: Ubiquitin Antibody [NB300-129]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/Ubiquitin-Antibody-Western-Blot-NB300-129-img0009.jpg)

![Western Blot: Ubiquitin Antibody (1B4-UB)BSA Free [NB600-776] Western Blot: Ubiquitin Antibody (1B4-UB)BSA Free [NB600-776]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/Ubiquitin-Antibody-1B4-UB-Western-Blot-NB600-776-img0002.jpg)
![Western Blot: Ubiquitin Antibody (P4G7-H11) [NBP1-19306] Western Blot: Ubiquitin Antibody (P4G7-H11) [NBP1-19306]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/Ubiquitin-Antibody-P4G7-H11-Western-Blot-NBP1-19306-img0002.jpg)
![Western Blot: Ubiquitin Antibody (3E2-E6) [H00006233-M01] Western Blot: Ubiquitin Antibody (3E2-E6) [H00006233-M01]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/Ubiquitin-Antibody-3E2-E6-Western-Blot-H00006233-M01-img0002.jpg)
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: Ubiquitin Antibody [NBP2-58398] Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: Ubiquitin Antibody [NBP2-58398]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/Ubiquitin-Antibody-Immunocytochemistry-Immunofluorescence-NBP2-58398-img0001.jpg)
![Western Blot: Ubiquitin Overexpression Lysate [NBL1-15568] Western Blot: Ubiquitin Overexpression Lysate [NBL1-15568]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/Ubiquitin-Overexpression-Lysate-Adult-Normal-Western-Blot-NBL1-15568-img0002.jpg)